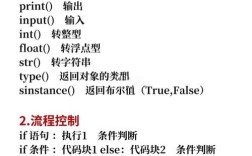
Of course! Working with datetime objects and their string representations is a fundamental task in Python. Here’s a comprehensive guide covering conversion, formatting, and parsing.
The Core Idea: Two Operations
- Formatting: Converting a
datetimeobject into a string. You control the format. - Parsing (or Strptime): Converting a string into a
datetimeobject. You must describe the format of the string.
Formatting a datetime Object to a String (strftime)
To format a datetime object as a string, you use the .strftime() method. The name stands for "string format time".
Syntax:
datetime_object.strftime(format_code)
The format_code is a string containing special directives (starting with ) that represent different parts of the date and time.
Common Format Codes
| Code | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
%Y |
Year with century | 2025 |
%y |
Year without century | 23 |
%m |
Month as a zero-padded number | 05 (for May) |
%B |
Full month name | May |
%b |
Abbreviated month name | May |
%d |
Day of the month | 09 |
%A |
Full weekday name | Tuesday |
%a |
Abbreviated weekday name | Tue |
%H |
Hour (24-hour clock) | 14 (for 2 PM) |
%I |
Hour (12-hour clock) | 02 (for 2 PM) |
%M |
Minute | 05 |
%S |
Second | 09 |
%p |
AM or PM | PM |
%f |
Microsecond | 000123 |
%Z |
Timezone name | UTC, EST |
%z |
UTC offset | +0000, -0500 |
| A literal character |
Example: strftime
import datetime
# 1. Create a datetime object
now = datetime.datetime.now()
print(f"Original datetime object: {now}")
# Example output: Original datetime object: 2025-10-27 10:30:55.123456
# 2. Format it into different string representations
# Standard ISO 8601 format
iso_format = now.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
print(f"ISO Format: {iso_format}")
# Example output: ISO Format: 2025-10-27 10:30:55
# More readable format
readable_format = now.strftime("%B %d, %Y at %I:%M %p")
print(f"Readable Format: {readable_format}")
# Example output: Readable Format: October 27, 2025 at 10:30 AM
# Another common format
file_name_format = now.strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
print(f"Filename Format: {file_name_format}")
# Example output: Filename Format: 20251027_103055
Parsing a String into a datetime Object (strptime)
To parse a string into a datetime object, you use the datetime.datetime.strptime() function. The name stands for "string parse time".
Syntax:
datetime.datetime.strptime(date_string, format_code)
date_string: The string you want to convert.format_code: The format that thedate_stringis in. This must match the string exactly.
Example: strptime
import datetime
# The string we want to parse
date_string = "2025-10-27 15:45:30"
# The format of that string
format_code = "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"
# Parse the string into a datetime object
parsed_datetime = datetime.datetime.strptime(date_string, format_code)
print(f"Original string: '{date_string}'")
print(f"Parsed datetime object: {parsed_datetime}")
print(f"Type of parsed object: {type(parsed_datetime)}")
Output:
Original string: '2025-10-27 15:45:30'
Parsed datetime object: 2025-10-27 15:45:30
Type of parsed object: <class 'datetime.datetime'>Parsing a More Complex String
# A more complex example with a timezone offset
tz_string = "2025-12-25 09:00:00-0500"
# The format code must match the string, including the timezone offset
tz_format_code = "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S%z"
# Note: Python 3.7+ handles %z correctly. In older versions, it might be tricky.
parsed_tz_datetime = datetime.datetime.strptime(tz_string, tz_format_code)
print(f"\nOriginal string: '{tz_string}'")
print(f"Parsed datetime object: {parsed_tz_datetime}")
print(f"Timezone info: {parsed_tz_datetime.tzinfo}")
Output:
Original string: '2025-12-25 09:00:00-0500'
Parsed datetime object: 2025-12-25 09:00:00-05:00
Timezone info: UTC-05:00The Modern Alternative: fromisoformat and isoformat
For the very common ISO 8601 format (e.g., YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS), Python 3.7+ provides simpler, more direct methods.
datetime.fromisoformat()
Parses a string in ISO format into a datetime object.
import datetime
iso_string = "2025-10-27T10:30:55.123456"
# Use the dedicated method
dt_object = datetime.datetime.fromisoformat(iso_string)
print(f"ISO String: {iso_string}")
print(f"Parsed object: {dt_object}")
Output:
ISO String: 2025-10-27T10:30:55.123456
Parsed object: 2025-10-27 10:30:55.123456datetime_object.isoformat()
Formats a datetime object into an ISO format string.
import datetime
dt_object = datetime.datetime.now()
# Use the dedicated method
iso_string = dt_object.isoformat()
print(f"Original datetime: {dt_object}")
print(f"ISO String: {iso_string}")
Output:
Original datetime: 2025-10-27 10:31:00.654321
ISO String: 2025-10-27T10:31:00.654321Handling Dates (without Time)
If you only care about the date part, it's best to use the datetime.date class. It has its own .strftime() and datetime.strptime() methods.
import datetime
# --- Formatting a date object ---
today = datetime.date.today()
print(f"Original date object: {today}")
# Format as a string
date_string = today.strftime("%A, %B %d, %Y")
print(f"Formatted date string: {date_string}")
# Example output: Friday, October 27, 2025
# --- Parsing a string into a date object ---
date_string_to_parse = "15-Aug-1990"
# The format code must match
format_code_for_date = "%d-%b-%Y"
parsed_date = datetime.datetime.strptime(date_string_to_parse, format_code_for_date).date()
print(f"\nParsed date string: '{date_string_to_parse}'")
print(f"Parsed date object: {parsed_date}")
print(f"Type: {type(parsed_date)}")
Output:
Original date object: 2025-10-27
Formatted date string: Friday, October 27, 2025
Parsed date string: '15-Aug-1990'
Parsed date object: 1990-08-15
Type: <class 'datetime.date'>Summary Table
| Goal | Method to Use | Example |
|---|---|---|
datetime -> String (Custom Format) |
datetime_object.strftime("%Y-%m-%d") |
now.strftime("%d/%m/%Y") |
String -> datetime (Custom Format) |
datetime.datetime.strptime("...", "%Y-%m-%d") |
datetime.datetime.strptime("27/10/2025", "%d/%m/%Y") |
datetime -> String (ISO Format) |
datetime_object.isoformat() |
now.isoformat() |
String -> datetime (ISO Format) |
datetime.datetime.fromisoformat("...") |
datetime.datetime.fromisoformat("2025-10-27") |
date -> String (Custom Format) |
date_object.strftime("%Y-%m-%d") |
today.strftime("%B %d, %Y") |
String -> date (Custom Format) |
datetime.datetime.strptime(...).date() |
datetime.datetime.strptime("15-Aug-1990", "%d-%b-%Y").date() |