在 Python 中,可以使用正则表达式(re 模块)来解析和提取 HTML 内容,但需要注意正则表达式在解析 HTML 时的局限性(如嵌套标签、复杂结构等),以下是详细说明和示例:

基本正则表达式提取 HTML 内容
提取所有 HTML 标签
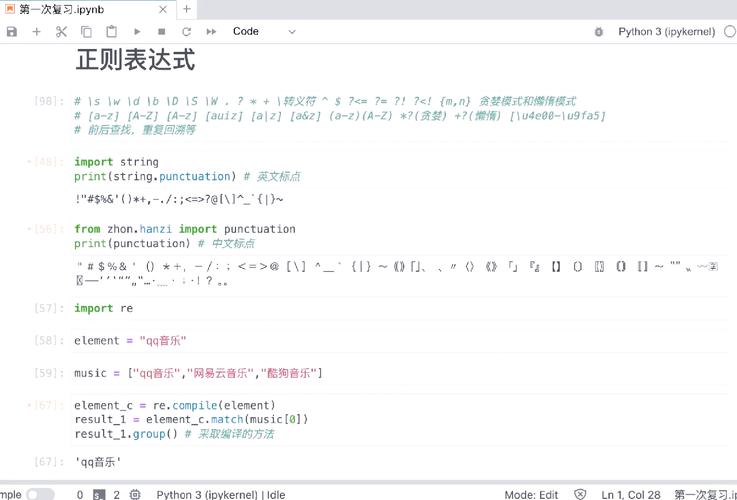
import re html = "<div>Hello <span>World</span></div>" pattern = r"<[^>]+>" # 匹配所有标签(如 <div>, <span>) tags = re.findall(pattern, html) print(tags) # 输出: ['<div>', '<span>', '</span>', '</div>']
提取标签内的文本
pattern = r">([^<]+)<" # 匹配标签之间的文本 text = re.findall(pattern, html) print(text) # 输出: ['Hello ', 'World']
提取特定标签的属性或内容
提取所有 <a> 标签的 href 属性
html = '<a href="https://example.com">Link</a><a href="page.html">Another</a>' pattern = r'href="([^"]+)"' # 匹配双引号内的 href 值 hrefs = re.findall(pattern, html) print(hrefs) # 输出: ['https://example.com', 'page.html']
提取 <div> 标签的 id 属性
html = '<div id="main">Content</div>' pattern = r'id="([^"]+)"' ids = re.findall(pattern, html) print(ids) # 输出: ['main']
正则表达式的局限性
正则表达式不适合解析复杂或嵌套的 HTML,
- 无法正确处理嵌套标签(如
<div><span>...</span></div>)。 - 对格式不规范的 HTML(如未闭合标签)可能失效。
- 维护成本高,规则易出错。
示例问题:
html = "<div><span>Nested</span></div>" # 正则可能错误匹配或遗漏嵌套内容
推荐替代方案:使用 BeautifulSoup
对于 HTML 解析,建议使用专门的库(如 BeautifulSoup),它更健壮且功能强大:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = "<div id='main'><span>Hello</span></div>"
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
# 提取 div 的 id
div_id = soup.div['id'] # 输出: 'main'
# 提取所有 span 的文本
spans = soup.find_all('span')
for span in spans:
print(span.text) # 输出: 'Hello'
正则与 BeautifulSoup 结合使用
如果仅需提取简单模式(如提取所有链接),可以结合两者:

from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import re
html = """
<html>
<body>
<a href="https://example.com">Example</a>
<a href="http://test.org">Test</a>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
links = soup.find_all('a', href=re.compile(r'^https?://')) # 仅匹配 HTTP/HTTPS 链接
for link in links:
print(link['href']) # 输出: https://example.com, http://test.org
| 方法 | 适用场景 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
正则表达式 (re) |
简单模式匹配(如提取属性、纯文本) | 不适合复杂/嵌套 HTML |
BeautifulSoup |
完整解析 HTML(推荐) | 需要安装第三方库 |
| 混合使用 | 结合两者的优势 | 需根据需求权衡 |
建议:优先使用 BeautifulSoup,仅在极简单场景下用正则表达式。