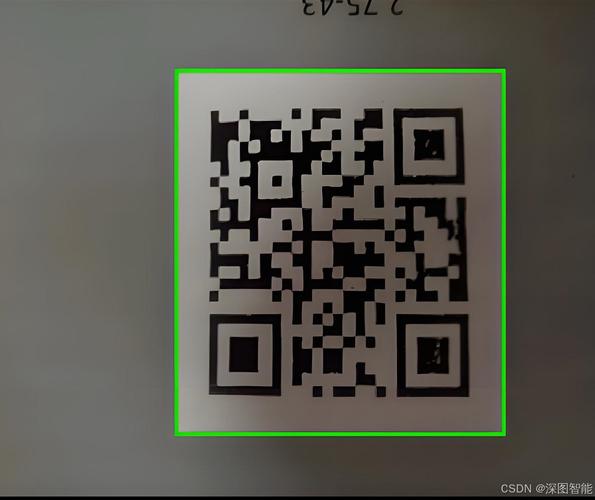
Of course! Using Python and OpenCV to read QR codes is a common and powerful task. While OpenCV has built-in QR code detection capabilities, the most robust and widely used method is to use the pyzbar library, which is a wrapper for the excellent ZBar library.
Here's a complete guide covering three scenarios:
- Reading QR codes from an image file.
- Reading QR codes from your webcam in real-time.
- Detecting QR codes in a live video stream and drawing a bounding box around them.
Prerequisites: Installation
First, you need to install the necessary libraries. opencv-python is for image/video processing, and pyzbar is for the QR code decoding.
pip install opencv-python pip install pyzbar
Important Note for Linux Users: pyzbar relies on the zbar library. You need to install its system dependencies first.
- For Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install libzbar0
- For Fedora/CentOS:
sudo dnf install zbar
Method 1: Reading QR Codes from an Image File
This is the simplest case. We'll load an image, find all QR codes in it, and print their data.
Code
import cv2
from pyzbar.pyzbar import decode
# 1. Load the image
image_path = 'qrcode.png' # Replace with your image path
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
if image is None:
print(f"Error: Could not read image from {image_path}")
exit()
# 2. Decode the QR codes
# The decode function returns a list of Decoded objects
decoded_objects = decode(image)
# 3. Process the decoded data
print(f"Found {len(decoded_objects)} QR code(s).")
for obj in decoded_objects:
# Get the data and type
qr_data = obj.data.decode('utf-8')
qr_type = obj.type
print(f"Type: {qr_type}")
print(f"Data: {qr_data}")
# Get the bounding box coordinates
# obj.rect is a Rect object with (x, y, w, h)
(x, y, w, h) = obj.rect
# Draw a rectangle around the QR code
cv2.rectangle(image, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 3)
# Put the text above the rectangle
text_y = y - 10 if y - 10 > 10 else y + h + 20
cv2.putText(image, qr_data, (x, text_y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 255, 0), 2)
# 4. Display the result
cv2.imshow('QR Code Detection', image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Explanation
cv2.imread(): Loads the image from the specified file path.decode(image): This is the core function frompyzbar. It scans the image and returns a list of all detected barcodes/QR codes.- Looping through
decoded_objects: Each object in the list represents one detected code.obj.data: The raw data of the code (bytes). We decode it to a UTF-8 string.obj.type: The type of barcode (e.g., 'QRCODE', 'CODE128', 'EAN13').obj.rect: The coordinates of the bounding box around the code.
- Drawing: We use OpenCV's drawing functions (
rectangle,putText) to visually mark the detected QR code and display its data on the image. cv2.imshow(): Displays the final image with the annotations.
Method 2: Reading QR Codes from a Webcam (Real-Time)
This method continuously captures frames from your webcam, decodes any QR codes found in each frame, and prints the data to the console.
Code
import cv2
from pyzbar.pyzbar import decode
# Initialize the webcam
# 0 is usually the default webcam
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
if not cap.isOpened():
print("Error: Could not open webcam.")
exit()
print("Starting QR code scanner. Press 'q' to quit.")
while True:
# Read a frame from the webcam
success, frame = cap.read()
if not success:
print("Error: Failed to capture frame.")
break
# Decode QR codes in the current frame
decoded_objects = decode(frame)
for obj in decoded_objects:
qr_data = obj.data.decode('utf-8')
print(f"QR Code Data: {qr_data}")
# Optional: Draw bounding box and text on the frame
(x, y, w, h) = obj.rect
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.putText(frame, qr_data, (x, y - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 255, 0), 2)
# Display the frame
cv2.imshow('Live QR Code Scanner', frame)
# Exit the loop if 'q' is pressed
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
# Release resources
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Explanation
cv2.VideoCapture(0): Initializes the video capture object using the default webcam.while Trueloop: This creates a real-time video stream.cap.read(): Captures one frame from the webcam.successis a boolean indicating if the frame was captured correctly.- Decoding and Drawing: The logic is identical to the image method, but it's applied to every frame of the video stream.
cv2.waitKey(1): This is crucial for real-time applications. It waits for 1 millisecond for a key press. This prevents the window from freezing and allows the loop to continue.ord('q'): Checks if the 'q' key was pressed to break the loop and stop the scanner.cap.release()andcv2.destroyAllWindows(): Properly closes the video stream and all OpenCV windows.
Method 3: Advanced - Live Stream with Bounding Box and Data
This is an enhanced version of Method 2. It draws a bounding box around the QR code and also displays the decoded data on the screen, making it more user-friendly.
Code
import cv2
from pyzbar.pyzbar import decode
# Initialize the webcam
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# Check if the webcam is opened correctly
if not cap.isOpened():
print("Error: Could not open webcam.")
exit()
print("Starting QR code scanner. Press 'q' to quit.")
while True:
success, frame = cap.read()
if not success:
break
# Convert the frame to grayscale for potentially faster decoding
# (though pyzbar handles color well, this can be an optimization)
# gray_frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# decoded_objects = decode(gray_frame)
decoded_objects = decode(frame)
for obj in decoded_objects:
# Get data and coordinates
qr_data = obj.data.decode('utf-8')
(x, y, w, h) = obj.rect
# Draw a green rectangle around the QR code
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 3)
# Prepare the text to be displayed
text = f"Data: {qr_data}"
# Get the width and height of the text to position the background
(text_width, text_height), baseline = cv2.getTextSize(text, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
# Draw a filled rectangle behind the text for better readability
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y - text_height - baseline), (x + text_width, y), (0, 255, 0), -1)
# Put the text on the frame
cv2.putText(frame, text, (x, y - baseline), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), 1)
# Display the resulting frame
cv2.imshow('QR Code Scanner with Data', frame)
# Break the loop on 'q' key press
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
# Release everything
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Explanation
The main difference here is how the text is rendered.
cv2.getTextSize(): This function calculates