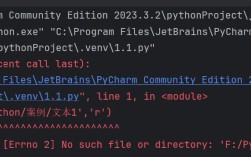
Of course! The term "linesentence" in Python isn't a built-in data structure or a standard library function. It's a descriptive name that almost certainly refers to a list of strings, where each string represents a sentence or a line of text.

This is a very common and fundamental pattern in Python, especially when dealing with text files, data processing, or natural language processing (NLP).
Let's break down what a "linesentence" is, how to create one, and how to work with it effectively.
What is a "linesentence"?
A "linesentence" is simply a Python list where each element is a string that is either:
- A single line from a file.
- A complete sentence.
- A paragraph.
Example:
# A list of sentences
linesentence = [
"Python is a versatile programming language.",
"It is known for its readability and simplicity.",
"You can use it for web development, data analysis, and more."
]
# A list of lines from a file (or as if they were)
lines_from_file = [
"Name: Alice",
"Age: 30",
"City: New York",
"---",
"Name: Bob",
"Age: 24",
"City: London"
]
How to Create a "linesentence"
There are several common ways to create this structure.
Method 1: Directly from a List Literal
This is the most straightforward way, as shown in the example above.
sentences = [
"The quick brown fox",
"jumps over the lazy dog.",
"This is a classic pangram."
]
Method 2: From a Text File (Most Common Use Case)
This is the most frequent reason for encountering a "linesentence". You read a file line by line and store each line in a list.
# Assume 'my_document.txt' contains:
# Hello world.
# This is the second line.
# And a third.
linesentence = []
# Using a 'for' loop (explicit and clear)
with open('my_document.txt', 'r') as file:
for line in file:
# The 'line' variable includes the newline character '\n'
# We use .strip() to remove it
cleaned_line = line.strip()
if cleaned_line: # Add only non-empty lines
linesentence.append(cleaned_line)
print(linesentence)
# Output: ['Hello world.', 'This is the second line.', 'And a third.']
A more "Pythonic" and concise way to do the same thing is with a list comprehension:

with open('my_document.txt', 'r') as file:
# This one line does the same as the for loop above
linesentence = [line.strip() for line in file if line.strip()]
print(linesentence)
# Output: ['Hello world.', 'This is the second line.', 'And a third.']
Method 3: From a Single Multi-line String
If you have a block of text in a variable, you can split it into a list of lines using the .splitlines() method.
full_text = """This is the first line. This is the second line. This is the third line.""" linesentence = full_text.splitlines() print(linesentence) # Output: ['This is the first line.', 'This is the second line.', 'This is the third line.']
How to Work with a "linesentence"
Once you have your list, you can perform all standard list operations, plus some text-specific ones.
Basic List Operations
linesentence = ["First sentence.", "Second sentence.", "Third sentence."]
# Get the length
print(f"Number of lines: {len(linesentence)}")
# Access an item by index
print(f"First line: {linesentence[0]}")
# Slice the list
print(f"First two lines: {linesentence[:2]}")
# Loop through the lines
print("\n--- All Lines ---")
for line in linesentence:
print(line)
Common Text Manipulations
Filtering Lines: Let's say you only want lines that contain the word "Python".
data = [
"I love Python programming.",
"Java is another language.",
"Python is great for data science."
]
python_lines = [line for line in data if "Python" in line]
print(python_lines)
# Output: ["I love Python programming.", "Python is great for data science."]
Searching for a Line:
Use the in operator to check for existence.
if "Java is another language." in data:
print("Found the Java line!")
Modifying Lines: For example, let's make every line uppercase.
uppercase_lines = [line.upper() for line in data] print(uppercase_lines) # Output: ['I LOVE PYTHON PROGRAMMING.', 'JAVA IS ANOTHER LANGUAGE.', 'PYTHON IS GREAT FOR DATA SCIENCE.']
Joining Lines Back into a String:
The str.join() method is perfect for this.
# Join with a newline character single_string = "\n".join(linesentence) print(single_string) # Join with a space single_string_space = " ".join(linesentence) print(single_string_space)
Advanced Usage: The linecache Module
If you are working with very large files and only need to access specific lines randomly, reading the entire file into a list can be memory-intensive. Python's standard library has a linecache module designed for this.
It "caches" (stores) lines from files so you can retrieve them by line number without re-reading the file every time.
import linecache
# Assume 'my_document.txt' is in the same directory
# and has 1000 lines.
# Get line number 5 (1-based index)
line_5 = linecache.getline('my_document.txt', 5)
print(f"Line 5: {line_5.strip()}")
# Get line number 999
line_999 = linecache.getline('my_document.txt', 999)
print(f"Line 999: {line_999.strip()}")
Summary
| Concept | Description | Python Code Example |
|---|---|---|
| What it is | A list of strings, where each string is a line or sentence. | my_list = ["line 1", "line 2"] |
| Creation | From a file, using a for loop or list comprehension. |
lines = [line.strip() for f in open('file.txt')] |
| Basic Ops | len(), indexing, slicing, looping. |
print(lines[0])for line in lines: |
| Filtering | Using list comprehensions with an if condition. |
[line for line in lines if 'error' in line] |
| Joining | Using "\n".join(list) to create a single string. |
text = "\n".join(lines) |
| Advanced | Using linecache for memory-efficient random access. |
import linecacheline = linecache.getline('file.txt', 10) |
In short, when you think "linesentence" in Python, think list[str] (a list of strings) and use the powerful tools Python provides for file I/O and list manipulation.