Of course! This is an excellent question that gets to the heart of choosing the right tools for the job. Let's break down Eclipse, Java, and Python, how they relate to each other, and when you would use each one.
The Short Answer (TL;DR)
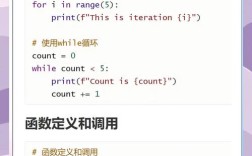
- Java and Python are programming languages. They are the sets of rules and syntax for writing software.
- Eclipse is an Integrated Development Environment (IDE). It's a powerful application (a program for writing programs) that provides tools to make coding, debugging, and managing projects much easier.
You can use the Eclipse IDE to write code in both Java and Python, as well as many other languages.
Java: The Programming Language
Java is a class-based, object-oriented programming language designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible. It's known for its "write once, run anywhere" (WORA) philosophy.
-
Key Characteristics:
- Strongly Typed: You must declare the type of a variable (e.g.,
int,String) and it cannot be changed. - Platform Independent: Java code is compiled into an intermediate format called "bytecode," which can run on any device with a Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
- Object-Oriented: Everything in Java is an object (or part of an object), which helps in organizing complex applications.
- Verbose: The code often requires more lines to accomplish the same task compared to Python.
- Memory Management: Uses automatic garbage collection to clean up unused memory.
- Strongly Typed: You must declare the type of a variable (e.g.,
-
Common Use Cases:
 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删)- Enterprise Applications: Large-scale, backend systems for banks, insurance companies, etc. (e.g., Spring Framework).
- Android App Development: The primary language for building Android apps (though Kotlin is now the official recommended language).
- Big Data: Frameworks like Hadoop, Spark, and Kafka are heavily based on Java.
- Web Applications: Server-side backend logic.
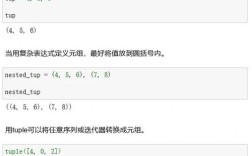
Python: The Programming Language
Python is a high-level, interpreted, general-purpose programming language. It's famous for its simple, readable syntax.
-
Key Characteristics:
- Interpreted: Code is executed line by line by an interpreter, which makes it slower than compiled languages like Java but great for scripting and rapid development.
- Dynamically Typed: You don't declare variable types. The type is inferred at runtime. This makes code faster to write but can lead to runtime errors that would be caught at compile-time in Java.
- Readable and Concise: The syntax is clean and looks like pseudocode, making it one of the easiest languages for beginners.
- Vast Ecosystem: "batteries included" philosophy and a massive collection of third-party packages available via the Python Package Index (PyPI).
-
Common Use Cases:
- Data Science & Machine Learning: The undisputed leader in this field (NumPy, Pandas, TensorFlow, PyTorch).
- Web Development: Frameworks like Django and Flask are very popular.
- Automation & Scripting: Used to automate repetitive tasks on your computer.
- Artificial Intelligence: A top choice for building AI and ML models.
- Education: It's often the first language taught in introductory computer science courses.
Eclipse: The Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
An IDE is a software application that provides comprehensive facilities to computer programmers for software development. Eclipse is one of the most popular and powerful open-source IDEs.
- What an IDE provides:
- Code Editor: A text editor with syntax highlighting, auto-completion, and code formatting.
- Compiler/Interpreter: It connects to the language's compiler (like
javacfor Java) or interpreter (likepython.exe). - Debugger: A tool to find and fix bugs by letting you step through your code line by line, inspect variables, and set breakpoints.
- Build Tools: Helps manage project dependencies and automate the build process (e.g., Maven for Java).
- Version Control: Integration with systems like Git.
- Extensibility: This is Eclipse's superpower. Its core can be extended with "plugins" to support different languages and tools.
How They Work Together
This is where it all comes together. Eclipse itself is just a platform. To make it useful for a specific language, you install a "plugin" or "development tool."
Eclipse for Java Development
This is the most classic and powerful use of Eclipse.
- How it works: You download the standard "Eclipse IDE for Java Developers" package. This bundle already includes the necessary plugins, most notably the Java Development Tools (JDT).
- What you get:
- A highly intelligent Java editor with real-time error checking.
- Seamless integration with the Java compiler.
- A powerful graphical debugger.
- Integration with Maven and Gradle for project and dependency management.
- Refactoring tools to automatically restructure your code safely.
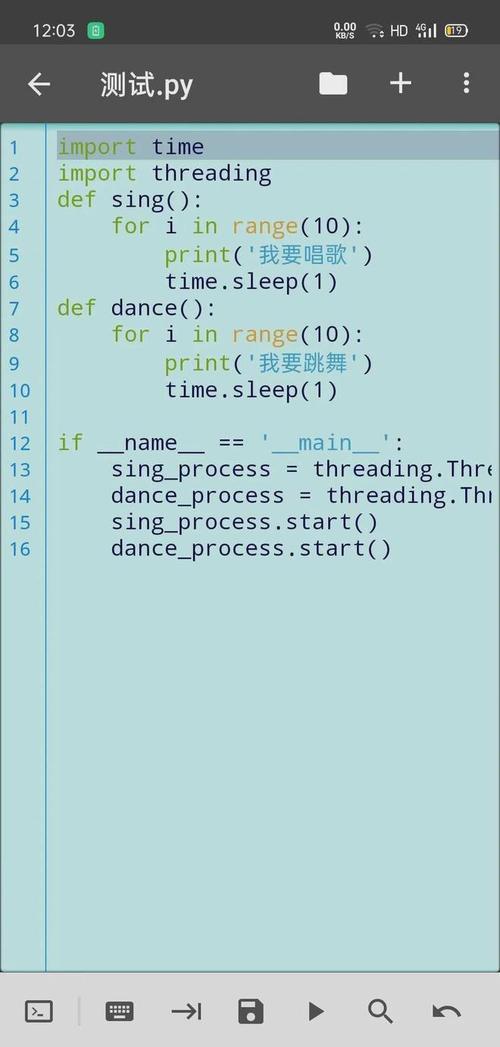
Eclipse for Python Development
You can absolutely use Eclipse for Python development, but it requires an extra step.
- How it works: You download the standard "Eclipse IDE for Java Developers" (or any Eclipse package) and then install the PyDev plugin.
- What you get (with PyDev):
- A Python code editor with syntax highlighting, code completion, and outlining.
- An integrated debugger for Python scripts.
- Support for unit testing (e.g., with
unittestorpytest). - Basic integration with virtual environments (like
venv).
- A Note: While PyDev is very capable, many Python developers prefer other IDEs that are more tailored to the Python ecosystem, such as Visual Studio Code (VS Code) or PyCharm, which offer more "out-of-the-box" features for Python, data science, and web development.
Comparison Table: Java vs. Python
| Feature | Java | Python |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Compiled (to bytecode) | Interpreted |
| Syntax | Verbose, more formal | Concise, readable, like English |
| Performance | Generally faster due to JIT compilation | Slower, but often fast enough for most tasks |
| Typing | Strong, Static | Dynamic, Duck |
| Use Cases | Enterprise, Android, Big Data | Data Science, AI, Web, Scripting |
| Learning Curve | Steeper for absolute beginners | Very gentle, great for beginners |
Summary: Which One Should I Use?
-
Use Java if: You are building large, scalable, high-performance backend systems, developing Android apps, or working in the big data space. You value strong typing and performance over code brevity.
-
Use Python if: You are getting started with programming, working in data science or machine learning, building a web application quickly, or automating tasks. You value rapid development and readability.
-
Use Eclipse if: You want a powerful, all-in-one, free, and open-source tool for your development work. It's an excellent choice for Java development. For Python, it works well, but you might also want to consider VS Code or PyCharm which are more lightweight and Python-centric.