Of course! "Python 小豆酱" (Python Xiaodoujiang) is a fantastic and very popular Python learning resource, especially for beginners in the Chinese-speaking community.

Let's break down what it is, why it's so great, and how you can use it.
What is "Python 小豆酱" (Python Xiaodoujiang)?
"小豆酱" literally translates to "Little Bean Sauce." In this context, it's a cute, memorable nickname for a Python learning project. The most famous one is "廖雪峰的 Python 小豆酱" (Liao Xuefeng's Python Xiaodoujiang).
It's essentially a beginner-friendly, project-based Python tutorial created by Liao Xuefeng (廖雪峰), a well-known and highly respected technical author and educator in China. Instead of just dry syntax explanations, it guides you through building small, complete, and practical applications from scratch.
Key Features of Python 小豆酱
- Project-Oriented (项目驱动): You learn by doing. Each tutorial focuses on building a specific, tangible application.
- Practical and Relevant (实用性强): The projects are not just toy examples. They often involve real-world concepts like web development, data processing, and automation.
- Step-by-Step Guidance (手把手教学): The tutorials are extremely detailed, with clear explanations for every line of code. It's like having a patient mentor sitting next to you.
- Beginner-Friendly (适合新手): It assumes you have little to no prior programming experience. It explains fundamental concepts like variables, loops, and functions in the context of the project you're building.
- High-Quality Explanations (讲解清晰): Liao Xuefeng is famous for his ability to explain complex technical concepts in simple, easy-to-understand Chinese.
What Kind of Projects Will You Build?
The "小豆酱" tutorials typically cover a range of interesting projects. Here are some common examples you might find:

Web Development Projects
This is the most popular category. You'll learn to build web applications using Python web frameworks.
-
Build a Simple Blog (构建一个简单的博客):
- Tech Stack: Python, Flask (a lightweight web framework), SQLite (a database).
- What you'll learn: How to set up a web server, create web pages (templates), handle user input (forms), store and retrieve data from a database, and user authentication (login/logout).
-
Build a Web Crawler / Scraper (构建网络爬虫):
- Tech Stack: Python,
requestslibrary (for fetching web pages),BeautifulSouporlxmllibrary (for parsing HTML). - What you'll learn: How to send HTTP requests to a website, download its content, extract specific information (like article titles, links, or product prices), and save it to a file or database.
- Tech Stack: Python,
Data Analysis & Automation Projects
These projects focus on using Python to handle data and automate repetitive tasks.

-
Data Analysis with Pandas (使用 Pandas 进行数据分析):
- Tech Stack: Python, Pandas library, Matplotlib/Seaborn library.
- What you'll learn: How to read data from CSV files, clean and manipulate data (filtering, grouping, calculating), and create visualizations (charts and graphs) to find insights.
-
Automate Office Tasks (自动化办公):
- Tech Stack: Python,
openpyxllibrary (for Excel files),python-docxlibrary (for Word documents). - What you'll learn: How to write scripts that can automatically read data from an Excel sheet, generate a report in a Word document, or rename hundreds of files in a folder, saving you hours of manual work.
- Tech Stack: Python,
Fun & GUI Projects
These projects are great for understanding the basics and building something visual.
-
Build a Simple Game (构建一个简单的游戏):
- Tech Stack: Python,
Pygamelibrary. - What you'll learn: Game development fundamentals like game loops, handling user input (keyboard/mouse), drawing graphics on a screen, and collision detection.
- Tech Stack: Python,
-
Create a Desktop Application (创建一个桌面应用):
- Tech Stack: Python,
Tkinter(which comes built-in with Python). - What you'll learn: How to create windows, buttons, text boxes, and other graphical user interface (GUI) elements to build a simple desktop tool.
- Tech Stack: Python,
How to Get Started with Python 小豆酱?
It's very easy to start.
- Find the Tutorial: Search for "廖雪峰 Python 小豆酱" or "Liao Xuefeng Python tutorial" online. The official website is
https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/. You can find the Python tutorials under the "Python" section. - Set Up Your Environment:
- Install Python: If you haven't already, download and install Python from the official website (
python.org). Make sure to check the box that says "Add Python to PATH" during installation. - Choose a Code Editor: A good code editor will make your life much easier. Visual Studio Code (VS Code) is an excellent free choice. You can also install the official Python extension for VS Code to get features like syntax highlighting and auto-completion.
- Install Python: If you haven't already, download and install Python from the official website (
- Follow the Tutorial Step-by-Step: Read each section carefully. Don't just copy and paste the code! Type it out yourself. This helps build muscle memory.
- Understand the "Why": Pay close attention to the explanations. Don't move on to the next step until you understand why a certain piece of code is needed.
- Experiment and Modify: Once you've successfully built the project as described in the tutorial, try changing it. Add a new feature, change a color, or modify the logic. This is the most important step for truly learning.
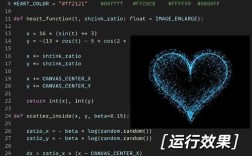
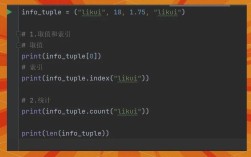
Example: A Tiny Taste of a "小豆酱" Style Project
Let's imagine a very simple "小豆酱" project: a command-line number guessing game.
Goal: The computer picks a random number, and the user has to guess it.
The "小豆酱" approach would explain it like this:
- Step 1: Import the tool. "To generate random numbers, Python has a special tool called
random. Let's import it first."import random
- Step 2: Let the computer choose a number. "Now, we'll use the
randomtool to pick a secret number between 1 and 100."secret_number = random.randint(1, 100)
- Step 3: Set up the main loop. "We want to keep asking the user for a guess until they get it right. We can use a
while True:loop for this."while True: # The code to ask for a guess and check it will go here - Step 4: Get input from the user. "Inside the loop, we'll ask the user to enter their guess. We use
input()for this. Sinceinput()gives us text, we need to convert it to a number usingint()."guess = int(input("请输入你猜的数字 (1-100): ")) - Step 5: Check the guess and give feedback. "Now we compare the user's guess with the secret number. We use
if/elif/elseto give different messages."if guess > secret_number: print("太大了!") elif guess < secret_number: print("太小了!") else: print(f"恭喜你!猜对了!答案是 {secret_number}。") break # Use break to exit the loop when they guess correctly
This step-by-step, contextual explanation is the core of the "小豆酱" philosophy.
Summary
Python 小豆酱 is not a single program, but a highly effective learning methodology and a set of tutorials. It's the perfect starting point for any Chinese-speaking beginner who wants to learn Python by building real, fun projects. If you follow it diligently, you'll gain a solid foundation in Python programming and the confidence to tackle more complex challenges.