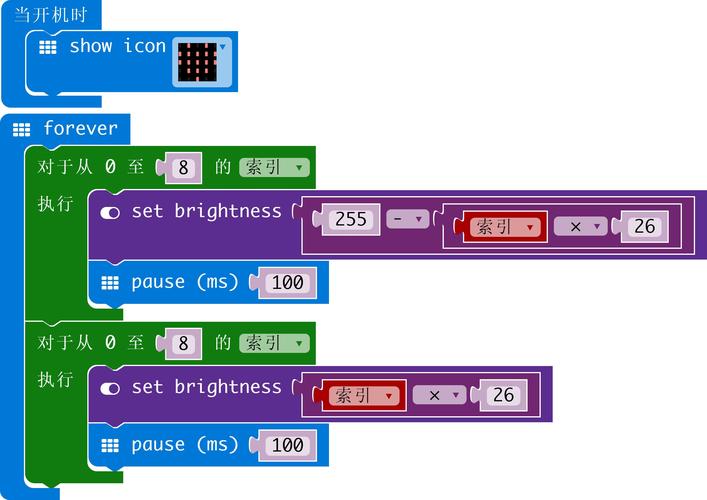
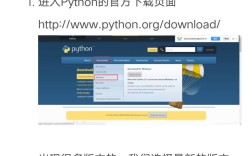
Of course! The term "Python microexchange" can mean a few different things, from a literal stock exchange simulation to a small, targeted API service. I'll cover the most common interpretations with practical examples.
Here are the main interpretations:
- A Simulated Stock Exchange (for learning): A program that mimics a stock market where you can create users, list assets, place buy/sell orders, and see a live order book. This is excellent for learning about data structures, algorithms, and basic financial concepts.
- A Microservice for an Exchange API: A small, focused backend service (e.g., using Flask or FastAPI) that provides a specific API endpoint for an exchange, like getting the latest price or placing an order.
- A Script for Interacting with a Real Exchange: A Python script that uses an official API (like Binance, Coinbase, or Kraken) to automate trading or fetch data.
Let's explore each one with code.
Simulated Stock Exchange (The "Micro" Exchange)
This is a fantastic project for understanding core concepts. We'll build a command-line application that can:
- Create users with a balance.
- Create tradable assets (stocks).
- Place limit orders (buy/sell at a specific price).
- Match orders and execute trades.
- Display the real-time order book.
Core Concepts:
- Order Book: A list of buy orders (bids) and sell orders (asks), sorted by price.
- Limit Order: An order to buy or sell an asset at a specific price or better.
- Trade Execution: When a buy order's price is greater than or equal to a sell order's price, a trade occurs.
Code Structure:
We'll use Python classes to organize our logic.
# micro_exchange.py
import collections
class Asset:
"""Represents a tradable asset, like a stock."""
def __init__(self, symbol, name):
self.symbol = symbol
self.name = name
class User:
"""Represents a user with a cash balance and holdings."""
def __init__(self, user_id, name):
self.user_id = user_id
self.name = name
self.cash_balance = 10000.00 # Starting with $10,000
self.holdings = collections.defaultdict(float) # {symbol: quantity}
def __str__(self):
return f"User({self.user_id}, {self.name}, Cash: ${self.cash_balance:.2f})"
class Order:
"""Represents a buy or sell order."""
def __init__(self, user_id, asset_symbol, quantity, price, order_type):
self.user_id = user_id
self.asset_symbol = asset_symbol
self.quantity = quantity
self.price = price
self.order_type = order_type.upper() # 'BUY' or 'SELL'
self.filled = 0
self.remaining = quantity
def __str__(self):
status = "FILLED" if self.remaining == 0 else f"PARTIALLY FILLED ({self.remaining}/{self.quantity})"
return f"Order: {self.user_id} {self.order_type} {self.quantity} {self.asset_symbol} @ ${self.price:.2f} [{status}]"
class MicroExchange:
"""The main exchange engine."""
def __init__(self):
self.users = {}
self.assets = {}
self.order_book = collections.defaultdict(list) # {symbol: [Order]}
self.trade_history = []
def add_user(self, user_id, name):
if user_id in self.users:
print(f"Error: User {user_id} already exists.")
else:
self.users[user_id] = User(user_id, name)
print(f"User {name} ({user_id}) created successfully.")
def add_asset(self, symbol, name):
if symbol in self.assets:
print(f"Error: Asset {symbol} already exists.")
else:
self.assets[symbol] = Asset(symbol, name)
print(f"Asset {name} ({symbol}) added successfully.")
def place_order(self, user_id, asset_symbol, quantity, price, order_type):
if user_id not in self.users:
print(f"Error: User {user_id} not found.")
return
if asset_symbol not in self.assets:
print(f"Error: Asset {asset_symbol} not found.")
return
order = Order(user_id, asset_symbol, quantity, price, order_type)
print(f"\n--- Placing Order ---\n{order}")
# Add order to the book
self.order_book[asset_symbol].append(order)
# Sort the order book
# Buy orders are sorted by price descending (highest bid first)
# Sell orders are sorted by price ascending (lowest ask first)
if order_type == 'BUY':
self.order_book[asset_symbol].sort(key=lambda o: o.price, reverse=True)
else: # SELL
self.order_book[asset_symbol].sort(key=lambda o: o.price)
# Try to match the new order
self._match_orders(asset_symbol)
def _match_orders(self, asset_symbol):
"""The core matching engine."""
if asset_symbol not in self.order_book:
return
buys = self.order_book[asset_symbol]
sells = self.order_book[asset_symbol]
# We need separate lists for buys and sells to iterate through them
# A more robust implementation would use deques or separate lists.
# For simplicity, we'll use a pointer-based approach.
buy_index = 0
sell_index = 0
while buy_index < len(buys) and sell_index < len(sells):
buy_order = buys[buy_index]
sell_order = sells[sell_index]
# A trade happens if the highest buy price >= lowest sell price
if buy_order.price >= sell_order.price and buy_order.remaining > 0 and sell_order.remaining > 0:
# Determine the trade quantity
trade_quantity = min(buy_order.remaining, sell_order.remaining)
# Execute the trade
self._execute_trade(buy_order, sell_order, trade_quantity, asset_symbol)
# Move pointers if an order is fully filled
if buy_order.remaining == 0:
buy_index += 1
if sell_order.remaining == 0:
sell_index += 1
else:
# No more matches possible for this pair of orders
break
def _execute_trade(self, buy_order, sell_order, quantity, asset_symbol):
"""Fills an order and updates user balances."""
trade_price = (buy_order.price + sell_order.price) / 2 # Mid-price execution
total_value = quantity * trade_price
# Get user objects
buyer = self.users[buy_order.user_id]
seller = self.users[sell_order.user_id]
# Update balances
buyer.cash_balance -= total_value
seller.cash_balance += total_value
buyer.holdings[asset_symbol] += quantity
seller.holdings[asset_symbol] -= quantity
# Update order status
buy_order.filled += quantity
buy_order.remaining -= quantity
sell_order.filled += quantity
sell_order.remaining -= quantity
# Record the trade
trade_record = {
'asset': asset_symbol,
'buyer': buy_order.user_id,
'seller': sell_order.user_id,
'quantity': quantity,
'price': trade_price
}
self.trade_history.append(trade_record)
print(f"\n>>> TRADE EXECUTED! <<<")
print(f" {quantity} {asset_symbol} @ ${trade_price:.2f}")
print(f" Buyer: {buyer.name}, Seller: {seller.name}\n")
def show_order_book(self, asset_symbol):
"""Displays the current order book for an asset."""
if asset_symbol not in self.assets:
print(f"Error: Asset {asset_symbol} not found.")
return
print(f"\n--- Order Book for {asset_symbol} ({self.assets[asset_symbol].name}) ---")
# Get and separate buy/sell orders
all_orders = self.order_book[asset_symbol]
buys = [o for o in all_orders if o.order_type == 'BUY' and o.remaining > 0]
sells = [o for o in all_orders if o.order_type == 'SELL' and o.remaining > 0]
print("BIDS (Buy Orders):")
if not buys:
print(" No buy orders.")
else:
for order in buys:
print(f" {order}")
print("\nASKS (Sell Orders):")
if not sells:
print(" No sell orders.")
else:
for order in sells:
print(f" {order}")
print("-" * 20)
def show_user_status(self, user_id):
"""Shows a user's cash balance and asset holdings."""
if user_id not in self.users:
print(f"Error: User {user_id} not found.")
return
user = self.users[user_id]
print(f"\n--- User Status for {user.name} ({user_id}) ---")
print(f"Cash Balance: ${user.cash_balance:.