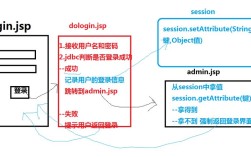
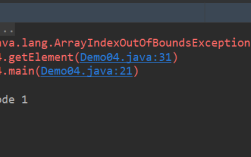
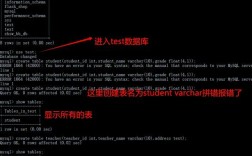
第2章:Java基础
复习题
1 写出以下表达式的结果:
a. 3 + 4 * 4 + 5 * (4 + 6)
b. 3 * (9 + (10 * 8) / 2)

答案与解析: a. 遵循运算符优先级:括号 > 乘法 > 加法
4 * 4 = 164 + 6 = 105 * 10 = 503 + 16 + 50 = 69- 结果:69
b. 遵循运算符优先级:括号 > 乘法/除法(从左到右)> 加法
10 * 8 = 8080 / 2 = 409 + 40 = 493 * 49 = 147- 结果:147
2 判断以下标识符是否合法:
a. 12age
b. #123
c. class
d. $4
e. s
答案与解析:
Java标识符规则:字母、数字、下划线(_)或美元符号($)组成,不能以数字开头,不能是关键字。
a. 12age:不合法,不能以数字开头。
b. #123:不合法,包含了非法字符 。
c. class:不合法。class 是 Java 的关键字。
d. $4:合法,以 开头,后面跟数字。
e. s:合法,单个字母是合法的标识符。

3 编写一个程序,提示用户输入一个半径,然后计算并显示圆的周长和面积。
答案与解析:
- 需要导入
Scanner类来获取用户输入。 - 使用
Math.PI获取精确的圆周率值。 - 周长公式:
2 * radius * Math.PI - 面积公式:
radius * radius * Math.PI
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ComputeCircle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 创建一个Scanner对象
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// 2. 提示用户输入半径
System.out.print("Enter the radius of a circle: ");
double radius = input.nextDouble();
// 3. 计算周长和面积
double perimeter = 2 * radius * Math.PI;
double area = radius * radius * Math.PI;
// 4. 显示结果,保留两位小数
System.out.println("The perimeter of the circle is " + perimeter);
System.out.println("The area of the circle is " + area);
// 5. 关闭Scanner
input.close();
}
}
第3章:选择语句
复习题
1 写出 if-else 语句的语法结构。
答案与解析:
if-else 语句用于在两个条件分支中选择一个执行。

if (condition) {
// 当条件 (condition) 为 true 时执行的代码块
} else {
// 当条件 (condition) 为 false 时执行的代码块
}
2 判断以下代码的输出:
int x = 1;
int y = 2;
if (x > 0) {
if (y > 0) {
System.out.println("x and y are positive");
} else {
System.out.println("x is positive and y is not positive");
}
} else {
System.out.println("x is not positive");
}
答案与解析:
x的值是1,x > 0的条件为true,所以进入第一个if语句块。- 在第一个
if块内,y的值是2,y > 0的条件为true,所以进入内部的if语句块。 - 执行
System.out.println("x and y are positive"); - 输出:
x and y are positive
3 编写一个程序,提示用户输入一个整数,然后判断该数是奇数还是偶数。
答案与解析:
- 一个整数是偶数当且仅当它能被2整除,即
number % 2 == 0。 - 使用
if-else结构进行判断。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CheckEvenOdd {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter an integer: ");
int number = input.nextInt();
// 使用取模运算符判断
if (number % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println(number + " is an even number.");
} else {
System.out.println(number + " is an odd number.");
}
input.close();
}
}
第4章:数学函数、字符与字符串
复习题
1 编写一个语句,生成一个 0 到 10 之间的随机整数(包括0和10)。
答案与解析:
Math.random()方法生成一个[0.0, 1.0)区间的 double 值。- 要生成
[0, 10]的整数,公式为:(int)(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min - 这里
min=0,max=10。 (int)(Math.random() * 11)会生成[0, 10]的整数。
int randomNumber = (int)(Math.random() * 11);
System.out.println("Random number between 0 and 10: " + randomNumber);
2 编写一个程序,提示用户输入一个字符串和一个字符,然后计算该字符在字符串中出现的次数。
答案与解析:
- 使用
Scanner获取字符串和字符。 - 字符的输入用
next().charAt(0)来获取第一个字符。 - 使用一个循环遍历字符串的每一个字符,用
charAt()方法比较,并计数。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CountChar {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a string: ");
String str = input.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter a character: ");
char ch = input.next().charAt(0);
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
if (str.charAt(i) == ch) {
count++;
}
}
System.out.println("The character '" + ch + "' appears " + count + " times in the string.");
input.close();
}
}
3 解释 String 和 char 的区别。
答案与解析:
char(字符):- 是一个基本数据类型。
- 表示单个字符,用单引号括起来,
'A','1', '$'。 - 在内存中占2个字节(使用UTF-16编码)。
String(字符串):- 是一个对象,属于
java.lang.String类。 - 表示一个字符序列,用双引号括起来,
"Hello","A", "123"。 - 在内存中占用可变的空间,内容不可变(一旦创建,对象内容不能改变)。
- 是一个对象,属于
第5章:循环
复习题
1 while 循环和 do-while 循环有什么区别?
答案与解析:
while循环 (先判断,后执行):- 语法:
while (condition) { ... } - 在执行循环体之前,先检查条件
condition。 - 如果条件一开始就为
false,则循环体一次都不会执行。
- 语法:
do-while循环 (先执行,后判断):- 语法:
do { ... } while (condition); - 至少执行一次循环体,然后在每次执行之后检查条件
condition。 - 即使条件一开始就为
false,循环体也会被执行一次。
- 语法:
2 编写一个 for 循环,打印从 100 递减