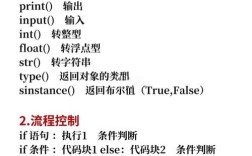
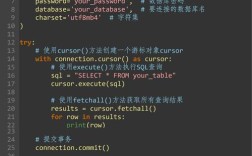
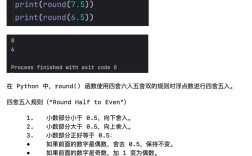
Of course. Working with Python 2.7 on CentOS 6 is a common task for maintaining legacy systems. CentOS 6 reached its End of Life (EOL) in November 2025, and Python 2.7 reached its End of Life in January 2025. This means no security updates or bug fixes are available for either.
Proceed with this understanding. This guide will walk you through the options for installing and using Python 2.7 on CentOS 6.
Summary of Methods
| Method | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| EPEL Repository | Easiest, managed by yum, handles dependencies. |
The Python version might be slightly older (e.g., 2.6.6 is the default, EPEL might have 2.7.x). | Most users who just need a working Python 2.7 quickly. |
| Manual Source Build | Full control, you get the latest Python 2.7.x version. | Complex, must compile all dependencies (like sqlite, openssl, readline) manually. |
Users who need a specific, newer Python 2.7 version and are comfortable with compiling from source. |
| SCL (Software Collections) | Isolated, doesn't conflict with system Python. Easy to switch versions. | Requires the centos-release-scl package. Python 2.7 is not in the default SCL repo for CentOS 6. |
Users who need to manage multiple Python versions on the same system. |
python27 Meta-package |
Very simple, one command. | Can pull in many dependencies you might not need. A blunt instrument. | The absolute simplest, "just get it done" approach. |
Method 1: Install from EPEL Repository (Recommended)
The Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL) repository is the safest and easiest way to get additional software on CentOS.
Step 1: Enable the EPEL Repository
First, you need to add the EPEL repository to your system. The command depends on your system's architecture.
# For x86_64 (64-bit) rpm -Uvh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm # For i386 (32-bit) rpm -Uvh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
Step 2: Install Python 2.7
Now you can use yum to install Python 2.7 and its tools.
sudo yum install python27 python27-devel python27-setuptools python27-pip
python27: The Python interpreter.python27-devel: Header files and libraries needed for compiling Python extensions (e.g., withsetuptools).python27-setuptools: Helps with packaging and distributing Python projects.python27-pip: The recommended tool for installing Python packages.
Step 3: Verify the Installation
The EPEL packages install Python 2.7 alongside the system Python 2.6.
# Check the default system Python (will be 2.6) python --version # Python 2.6.6 # Check your new Python 2.7 installation python2.7 --version # Python 2.7.18 <-- This is the final 2.7 version
Step 4: Using pip
The pip executable is specifically for Python 2.7.
# Install a package, e.g., requests pip2.7 install requests
Method 2: Manual Build from Source
Use this method if the version in EPEL is not sufficient for your needs.
Step 1: Install Dependencies
You must install all development libraries that Python needs to compile correctly.
sudo yum groupinstall "Development Tools" sudo yum install zlib-devel bzip2-devel openssl-devel ncurses-devel sqlite-devel readline-devel tk-devel gdbm-devel db4-devel libpcap-devel xz-devel
Step 2: Download the Python 2.7 Source Code
Go to the Python 2.7 download page to get the latest source tarball. As of this writing, 2.7.18 is the final version.
cd /tmp wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/2.7.18/Python-2.7.18.tgz tar -xvf Python-2.7.18.tgz cd Python-2.7.18
Step 3: Configure and Compile
It's best practice to install Python into a directory like /usr/local to avoid conflicts with the system's Python.
# Configure the build. --enable-optimizations is optional but recommended. ./configure --prefix=/usr/local --enable-optimizations # Compile the source code (this will take a few minutes) make -j 4 # Use -j with the number of CPU cores for faster compilation # Install the compiled files sudo make altinstall
Note: We use
make altinstallinstead ofmake install. This is crucial because it prevents overwriting the system'spythonandpipexecutables, avoiding potential conflicts.
Step 4: Verify the Installation
# Check the version /usr/local/bin/python2.7 --version # Python 2.7.18 # Check pip /usr/local/bin/pip2.7 --version # pip 9.0.3 from /usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/pip (python 2.7)
Method 3: Using Software Collections (SCL)
SCL allows you to install and use multiple versions of software on the same system without conflicts. While Python 2.7 isn't in the default centos-sclo-rh repo, a community collection often provides it.
Step 1: Enable SCL
sudo yum install centos-release-scl
Step 2: Install the Python Collection
Check if a python27 collection is available. If not, you may need to look for a community repo or stick to the other methods.
# Search for available python collections sudo yum search "python27.*"
If you find a collection named something like rh-python27, you would install it like this:
sudo yum install rh-python27
Step 3: Activate and Use the Collection
You use the scl command to enable the collection for your current shell session.
# Activate the Python 2.7 environment scl enable rh-python27 bash # Now the commands are available python --version # Python 2.7.x pip install --upgrade pip pip install some-package # To deactivate, just exit the shell or type: scl disable rh-python27
Important Considerations for Python 2.7 on CentOS 6
-
Security and EOL: This is the most important point. Your system is vulnerable. Treat it as such and isolate it from production networks if possible. Do not expose services running on it to the internet without a robust firewall.
-
setuptoolsandpip: Always update them to the latest 2.7-compatible versions.pip2.7 install --upgrade pip setuptools wheel
-
Virtual Environments: You must use virtual environments to avoid polluting your global Python installation with conflicting package versions.
# Install virtualenv pip2.7 install virtualenv # Create a new virtual environment virtualenv my_project_env # Activate it source my_project_env/bin/activate # Your shell prompt will change. Now you can install packages pip install django # Deactivate when done deactivate
-
Package Availability: Many modern Python packages no longer support Python 2.7. You may encounter errors during installation. You will need to find older, compatible versions of libraries. Use
pip2.7 install package==1.2.3to specify a version.