Of course! In Python, converting an integer to its corresponding ASCII character is a common task. The primary function you'll use is chr().
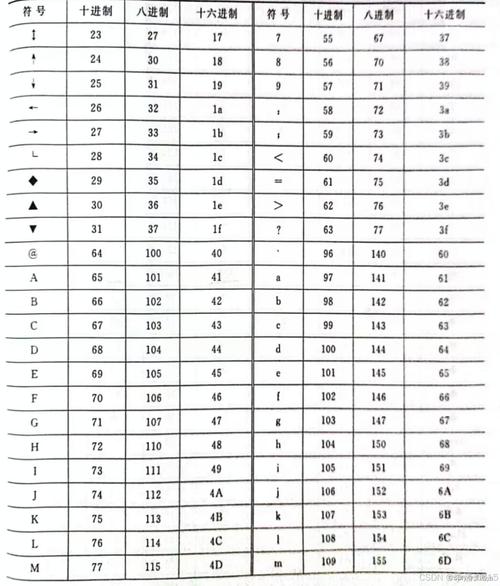
Here’s a complete guide, from the basics to more complex scenarios.
The Core Function: chr()
Python has a built-in function chr(i) that takes an integer i (representing a Unicode code point) and returns the corresponding character.
Important Note: In Python 3, strings are Unicode by default. The "ASCII" character set is a subset of Unicode (the first 128 characters, 0-127). So, chr() works perfectly for standard ASCII characters.
Basic Example
Let's convert the integer 65 to its ASCII character. The ASCII code for 'A' is 65.
# Convert integer 65 to its ASCII character char = chr(65) print(char) # Output: A # Convert integer 97 to its ASCII character char_lower = chr(97) print(char_lower) # Output: a
Practical Examples
Converting a Single Integer
This is the most straightforward case.
# Integer for 'H' print(chr(72)) # Output: H # Integer for '!' print(chr(33)) # Output: ! # Integer for '7' print(chr(55)) # Output: 7
Converting a List of Integers (e.g., a byte array)
A very common use case is converting a list of integers (like the output from ord() or a raw byte stream) into a string.
Let's say you have a list of integers representing the word "Python".
# A list of integers corresponding to 'P', 'y', 't', 'h', 'o', 'n' int_list = [80, 121, 116, 104, 111, 110] # Use a list comprehension to convert each integer to a character char_list = [chr(i) for i in int_list] # Join the characters to form a string result_string = "".join(char_list) print(result_string) # Output: Python
Converting a Range of Integers
You can use chr() in a loop or a list comprehension to generate a sequence of characters. For example, to get the alphabet:
# Generate uppercase letters (A-Z) # ASCII codes for 'A' is 65, for 'Z' is 90 uppercase_letters = [chr(i) for i in range(65, 91)] print(uppercase_letters) # Output: ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z'] # Generate lowercase letters (a-z) # ASCII codes for 'a' is 97, for 'z' is 122 lowercase_letters = [chr(i) for i in range(97, 123)] print(lowercase_letters) # Output: ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z'] # Generate all digits (0-9) # ASCII codes for '0' is 48, for '9' is 57 digits = [chr(i) for i in range(48, 58)] print(digits) # Output: ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9']
The Reverse Operation: chr() and ord()
It's helpful to know the reverse operation. If you have a character and want to get its integer (Unicode/ASCII) code, you use the ord() function.
# Get the integer code for 'A'
code = ord('A')
print(code)
# Output: 65
# Get the integer code for 'a'
code_lower = ord('a')
print(code_lower)
# Output: 97
# Get the integer code for '$'
code_symbol = ord('$')
print(code_symbol)
# Output: 36
Handling Errors
What happens if you try to convert an integer that is outside the valid range for a Unicode character?
- The valid range for
chr()is from0to0x10FFFF(inclusive). - Trying to use a negative integer or an integer outside this range will raise a
ValueError.
# This will work
print(chr(65)) # Output: A
# This will raise a ValueError
try:
print(chr(-1))
except ValueError as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
# Output: Error: chr() arg not in range(0x110000)
# This will also raise a ValueError
try:
print(chr(1114113)) # 0x110000 is one too high
except ValueError as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
# Output: Error: chr() arg not in range(0x110000)
Summary
| Task | Function | Example | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Integer to Character | chr() |
chr(65) |
'A' |
| Character to Integer | ord() |
ord('A') |
65 |
| Convert a list of integers | chr() |
chr(i) for i in [80, 121, 116] |
'Pyt' |
For converting an integer to an ASCII character in Python, chr() is the correct and standard function to use.