安装 cx_Oracle
你需要安装 cx_Oracle 库,可以通过 pip 进行安装:
pip install cx_Oracle
重要提示: cx_Oracle 是一个纯 Python 的驱动,但它依赖于 Oracle 客户端库(Instant Client),如果你的机器上没有安装 Oracle 客户端,cx_Oracle 将无法正常工作。
如何安装 Oracle 客户端?
-
下载 Instant Client:
- 访问 Oracle 官网 Instant Client 下载页面:Oracle Instant Client Downloads
- 根据你的操作系统(Windows, Linux, macOS)和架构选择合适的版本,对于大多数用户,选择 "Basic" 或 "Light" 版本即可。
-
配置环境变量:
- Windows:
- 将下载并解压后的
instantclient_XX_XX文件夹路径添加到系统的PATH环境变量中,如果你的解压路径是C:\oracle\instantclient_19_10,就将这个路径添加到PATH。 - 重启你的命令行或 IDE,使环境变量生效。
- 将下载并解压后的
- Linux / macOS:
- 将解压后的文件夹放置在一个合适的位置,
/usr/local/oracle。 - 将该路径添加到
LD_LIBRARY_PATH(Linux) 或DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH(macOS) 环境变量中。 - 在 Linux 的
~/.bashrc或~/.zshrc文件中添加:export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/oracle/instantclient_19_10:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
- 运行
source ~/.bashrc或source ~/.zshrc使其生效。
- 将解压后的文件夹放置在一个合适的位置,
- Windows:
安装完成后,你可以在 Python 中尝试导入 cx_Oracle,如果没有报错,说明安装成功。
import cx_Oracle
print("cx_Oracle 版本:", cx_Oracle.version)
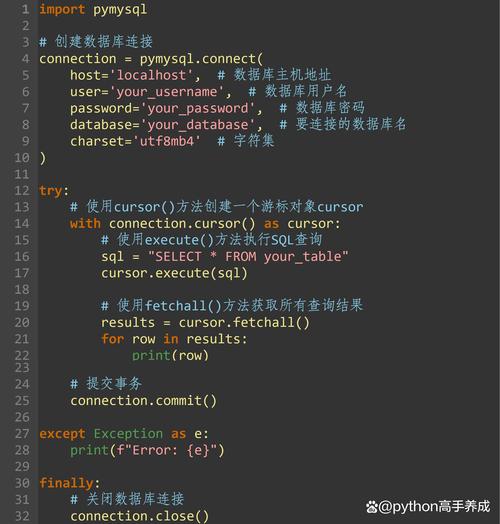
连接到 Oracle 数据库
连接数据库需要提供用户名、密码、数据库服务名(或 SID)以及主机地址和端口。
连接字符串格式:
username/password@hostname:port/service_name
或者使用 SID(较旧的方式):
username/password@hostname:port/sid
示例代码:
import cx_Oracle
# --- 配置信息 ---
# 建议使用环境变量或配置文件来存储敏感信息,而不是硬编码在代码中
db_user = "your_username"
db_password = "your_password"
db_dsn = "hostname:1521/your_service_name" # "mydb.example.com:1521/ORCLCDB"
try:
# 1. 创建连接
connection = cx_Oracle.connect(user=db_user, password=db_password, dsn=db_dsn)
# 2. 创建游标
# 游标用于执行 SQL 语句并获取结果
cursor = connection.cursor()
print("成功连接到 Oracle 数据库!")
# ... 在这里执行你的 SQL 操作 ...
except cx_Oracle.DatabaseError as e:
error, = e.args
print(f"数据库错误: {error.code} - {error.message}")
finally:
# 3. 关闭游标和连接
if 'cursor' in locals():
cursor.close()
if 'connection' in locals():
connection.close()
print("数据库连接已关闭。")
执行 SQL 语句
cx_Oracle 支持两种主要的 SQL 执行方式:execute() 用于单条语句,executemany() 用于批量操作。
1 查询数据 (SELECT)
使用 cursor.execute() 执行查询,然后用 cursor.fetchall(), cursor.fetchone(), 或 cursor.fetchmany() 获取结果。
import cx_Oracle
# ... (连接代码同上) ...
try:
connection = cx_Oracle.connect(user=db_user, password=db_password, dsn=db_dsn)
cursor = connection.cursor()
# 执行查询
sql_query = "SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name FROM employees WHERE rownum <= 5"
cursor.execute(sql_query)
# 获取所有结果
print("\n--- 使用 fetchall() ---")
rows = cursor.fetchall()
for row in rows:
print(f"ID: {row[0]}, Name: {row[1]} {row[2]}")
# 获取单行结果
print("\n--- 使用 fetchone() ---")
cursor.execute(sql_query) # 需要重新执行,因为游标已经移动到末尾
first_row = cursor.fetchone()
if first_row:
print(f"第一行: ID: {first_row[0]}, Name: {first_row[1]} {first_row[2]}")
# 获取多行结果
print("\n--- 使用 fetchmany(2) ---")
cursor.execute(sql_query) # 再次重新执行
next_two_rows = cursor.fetchmany(2)
for row in next_two_rows:
print(f"ID: {row[0]}, Name: {row[1]} {row[2]}")
# 获取列名
print("\n--- 列名 ---")
columns = [col[0] for col in cursor.description]
print("列名:", columns)
except cx_Oracle.DatabaseError as e:
# ... (错误处理代码同上) ...
finally:
# ... (关闭游标和连接代码同上) ...
2 插入、更新、删除数据 (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE)
这些操作会修改数据库,因此必须调用 connection.commit() 来提交事务,否则更改不会永久保存。
import cx_Oracle
# ... (连接代码同上) ...
try:
connection = cx_Oracle.connect(user=db_user, password=db_password, dsn=db_dsn)
cursor = connection.cursor()
# --- 插入数据 ---
print("\n--- 插入数据 ---")
insert_sql = "INSERT INTO departments (department_id, department_name) VALUES (dept_seq.NEXTVAL, 'Python Development')"
cursor.execute(insert_sql)
connection.commit() # 提交事务
print("插入成功!")
# --- 更新数据 ---
print("\n--- 更新数据 ---")
update_sql = "UPDATE departments SET department_name = 'Data Science' WHERE department_name = 'Python Development'"
cursor.execute(update_sql)
connection.commit() # 提交事务
print(f"更新了 {cursor.rowcount} 行数据。")
# --- 删除数据 ---
print("\n--- 删除数据 ---")
delete_sql = "DELETE FROM departments WHERE department_name = 'Data Science'"
cursor.execute(delete_sql)
connection.commit() # 提交事务
print(f"删除了 {cursor.rowcount} 行数据。")
except cx_Oracle.DatabaseError as e:
# 发生错误时回滚
if 'connection' in locals():
connection.rollback()
print(f"数据库错误: {e}")
finally:
# ... (关闭游标和连接代码同上) ...
使用参数化查询(防止 SQL 注入)
永远不要使用 Python 的字符串拼接来构建 SQL 语句! 这会导致严重的 SQL 注入漏洞。cx_Oracle 提供了安全的参数化查询方式。
命名参数 (param_name)
import cx_Oracle
# ... (连接代码同上) ...
try:
connection = cx_Oracle.connect(user=db_user, password=db_password, dsn=db_dsn)
cursor = connection.cursor()
employee_id_to_find = 101
sql = "SELECT first_name, last_name, salary FROM employees WHERE employee_id = :id"
# 使用字典传递命名参数
cursor.execute(sql, {'id': employee_id_to_find})
result = cursor.fetchone()
if result:
print(f"员工姓名: {result[0]} {result[1]}, 薪资: {result[2]}")
else:
print("未找到该员工。")
except cx_Oracle.DatabaseError as e:
# ... (错误处理代码同上) ...
finally:
# ... (关闭游标和连接代码同上) ...
位置参数 (%s)
import cx_Oracle
# ... (连接代码同上) ...
try:
connection = cx_Oracle.connect(user=db_user, password=db_password, dsn=db_dsn)
cursor = connection.cursor()
min_salary = 5000
sql = "SELECT first_name, last_name FROM employees WHERE salary > :min_sal"
# 也可以直接作为关键字参数传递
cursor.execute(sql, min_sal=min_salary)
results = cursor.fetchall()
print(f"薪资大于 {min_salary} 的员工:")
for row in results:
print(f"- {row[0]} {row[1]}")
except cx_Oracle.DatabaseError as e:
# ... (错误处理代码同上) ...
finally:
# ... (关闭游标和连接代码同上) ...
批量操作 (executemany)
当需要插入或更新大量数据时,使用 executemany() 比循环调用 execute() 效率要高得多。
import cx_Oracle
# ... (连接代码同上) ...
try:
connection = cx_Oracle.connect(user=db_user, password=db_password, dsn=db_dsn)
cursor = connection.cursor()
# 准备批量数据
new_employees = [
(200, 'John', 'Doe', 'IT'),
(201, 'Jane', 'Smith', 'HR'),
(202, 'Peter', 'Jones', 'Finance')
]
# SQL 语句中使用占位符
insert_sql = "INSERT INTO employees (employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id) VALUES (:1, :2, :3, (SELECT department_id FROM departments WHERE department_name = :4))"
# 执行批量插入
cursor.executemany(insert_sql, new_employees)
connection.commit() # 提交所有更改
print(f"成功批量插入了 {cursor.rowcount} 行数据。")
except cx_Oracle.DatabaseError as e:
if 'connection' in locals():
connection.rollback()
print(f"数据库错误: {e}")
finally:
# ... (关闭游标和连接代码同上) ...
使用 with 语句(推荐)
为了确保资源(游标和连接)总是被正确关闭,可以使用 with 语句,它会自动处理 close() 操作。
import cx_Oracle
db_user = "your_username"
db_password = "your_password"
db_dsn = "hostname:1521/your_service_name"
# 连接对象也可以使用 with 语句
with cx_Oracle.connect(user=db_user, password=db_password, dsn=db_dsn) as connection:
# 游标也可以使用 with 语句
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql = "SELECT first_name, last_name FROM employees WHERE employee_id = :id"
cursor.execute(sql, id=101)
result = cursor.fetchone()
if result:
print(f"员工姓名: {result[0]} {result[1]}")
# 不需要手动调用 cursor.close()
# 不需要手动调用 connection.close()
print("连接和游标已自动关闭。")
高级特性:返回结果为字典
默认情况下,cx_Oracle 返回的是 cx_Oracle.LOB 或 tuple 对象,如果你希望结果直接是字典形式,可以创建一个字典游标。
import cx_Oracle
# 创建一个字典游标工厂函数
def make_dict_cursor(connection):
return connection.cursor()
# ... (连接代码同上) ...
try:
with cx_Oracle.connect(user=db_user, password=db_password, dsn=db_dsn) as conn:
# 使用字典游标
with conn.cursor() as cursor:
# 将游标转换为字典游标
cursor = make_dict_cursor(conn)
cursor.execute("SELECT employee_id, first_name, salary FROM employees WHERE rownum <= 3")
for row in cursor:
# 现在可以通过列名访问数据
print(f"ID: {row['EMPLOYEE_ID']}, Name: {row['FIRST_NAME']}, Salary: {row['SALARY']}")
except cx_Oracle.DatabaseError as e:
# ... (错误处理代码同上) ...
| 操作 | 关键方法/步骤 | 注意事项 |
|---|---|---|
| 安装 | pip install cx_Oracle |
必须安装 Oracle Instant Client 并配置 PATH。 |
| 连接 | cx_Oracle.connect() |
处理异常,并在 finally 块中关闭连接。 |
| 查询 | cursor.execute() + fetchall()/fetchone() |
获取结果后,游标会移动,注意获取方式。 |
| 增删改 | cursor.execute() |
必须调用 connection.commit() 提交事务,出错时调用 connection.rollback()。 |
| 安全查询 | cursor.execute(sql, {'param': value}) |
永远不要用字符串拼接 SQL,防止 SQL 注入。 |
| 批量操作 | cursor.executemany() |
性能远高于循环 execute(),适合大数据量。 |
| 资源管理 | 使用 with 语句 |
强烈推荐,能自动管理游标和连接的关闭。 |
遵循以上指南,你就可以在 Python 中安全、高效地操作 Oracle 数据库了。