下面我将从几个核心层面,详细讲解 JavaScript 和 Python 如何交互,并提供代码示例。
核心交互模式
JavaScript 和 Python 运行在不同的环境中(浏览器/Node.js vs Python 解释器),因此它们不能直接调用对方的函数或共享内存,交互的本质是 进程间通信。
主要有以下几种模式:
- HTTP API 交互(最常用、最灵活)
- 命令行调用(简单直接)
- 在浏览器中运行 Python(Pyodide)
- 在 Node.js 中运行 Python(Node.js 的
child_process) - 共享文件系统
HTTP API 交互(RESTful API)
这是最通用、最健壮的交互方式,一个语言作为 服务器,提供 API;另一个语言作为 客户端,调用 API。
场景:Python 后端提供机器学习服务,JavaScript 前端调用并展示结果。
Python 服务器端 (使用 Flask 框架)
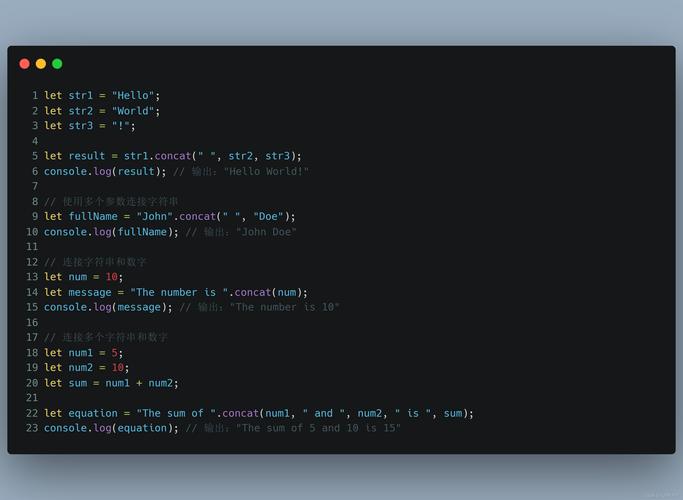
Flask 是一个轻量级的 Python Web 框架,非常适合快速构建 API。
# app.py
from flask import Flask, jsonify, request
import random
app = Flask(__name__)
# 模拟一个机器学习模型,输入数字,返回其平方
@app.route('/api/square', methods=['POST'])
def square_number():
data = request.get_json()
if not data or 'number' not in data:
return jsonify({'error': 'Missing "number" in request body'}), 400
number = data['number']
result = number * number
print(f"Python: Received number {number}, returning {result}")
return jsonify({'input': number, 'result': result})
# 模拟一个推荐系统
@app.route('/api/recommend', methods=['GET'])
def get_recommendation():
recommendations = ["Python", "JavaScript", "Machine Learning", "Web Development"]
rec = random.choice(recommendations)
print(f"Python: Recommended {rec}")
return jsonify({'recommendation': rec})
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 运行在 0.0.0.0:5000,允许外部访问
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5000, debug=True)
JavaScript 客户端 (在浏览器或 Node.js 中)
使用 fetch API 来调用 Python 服务器。
// client.js (可以在浏览器控制台或 Node.js 中运行)
// API 基础 URL
const API_URL = 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/api';
// 调用 /api/square 接口
async function callSquareApi() {
const numberToSquare = 9;
const response = await fetch(`${API_URL}/square`, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({ number: numberToSquare }),
});
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error('Network response was not ok');
}
const data = await response.json();
console.log('JavaScript Received:', data);
// 输出: JavaScript Received: {input: 9, result: 81}
}
// 调用 /api/recommend 接口
async function callRecommendApi() {
const response = await fetch(`${API_URL}/recommend`);
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error('Network response was not ok');
}
const data = await response.json();
console.log('JavaScript Received:', data);
// 输出: JavaScript Received: {recommendation: "Web Development"}
}
// 执行调用
callSquareApi();
callRecommendApi();
如何运行:
- 首先安装 Flask:
pip install Flask - 运行 Python 服务器:
python app.py - 在另一个终端运行 JavaScript 客户端:
node client.js(或在浏览器开发者工具的 Console 中粘贴client.js的代码)
命令行调用
如果任务是一次性的、简单的,可以直接让 JavaScript 调用 Python 脚本,并通过命令行参数和标准输入/输出进行通信。
Python 脚本 (接收参数并返回结果)
# cli_script.py
import sys
# 从命令行参数获取输入
if len(sys.argv) > 1:
name = sys.argv[1]
# 将结果打印到标准输出
print(f"Hello, {name}! From Python.")
else:
print("Error: No name provided.")
JavaScript 代码 (Node.js)
使用 child_process 模块。
// cli_client.js
const { exec } = require('child_process');
const userName = 'Alice';
// 使用模板字符串构建命令
const command = `python cli_script.py "${userName}"`;
exec(command, (error, stdout, stderr) => {
if (error) {
console.error(`exec error: ${error}`);
return;
}
if (stderr) {
console.error(`stderr: ${stderr}`);
return;
}
// stdout 包含 Python 脚本打印的输出
console.log(`JavaScript received from Python: ${stdout.trim()}`);
// 输出: JavaScript received from Python: Hello, Alice! From Python.
});
如何运行:
- 确保已安装 Python。
- 运行 JavaScript 客户端:
node cli_client.js
在浏览器中运行 Python (Pyodide)
这是一个非常酷的技术,它允许你直接在 浏览器 中运行 Python 代码,Pyodide 是一个 WebAssembly 的 Python 发行版。
准备 HTML 文件
<!-- index.html -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">Python in Browser with Pyodide</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/pyodide/v0.24.1/full/pyodide.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Python in the Browser</h1>
<button id="loadButton">Load Pyodide</button>
<button id="runPythonButton" disabled>Run Python Code</button>
<pre id="output"></pre>
<script>
const output = document.getElementById('output');
const loadButton = document.getElementById('loadButton');
const runButton = document.getElementById('runPythonButton');
let pyodide;
loadButton.addEventListener('click', async () => {
output.textContent = "Loading Pyodide...";
pyodide = await loadPyodide();
output.textContent = "Pyodide loaded successfully!";
runButton.disabled = false;
});
runButton.addEventListener('click', async () => {
try {
// JavaScript 调用 Python 函数
const jsResult = await pyodide.runPythonAsync(`
import math
def greet(name):
return f"Hello, {name}! The square root of 100 is {math.sqrt(100)}."
greet("World from Python")
`);
output.textContent = `Result from Python: ${jsResult}`;
} catch (err) {
output.textContent = `Error: ${err.message}`;
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
如何运行:
- 将上述代码保存为
index.html。 - 用浏览器打开这个文件。
- 点击 "Load Pyodide" 按钮,等待加载完成。
- 点击 "Run Python Code" 按钮,即可看到 Python 代码的执行结果。
在 Node.js 中运行 Python (Child Process)
这与模式二类似,但更侧重于持续交互,而不仅仅是单次命令执行。
Python 脚本 (持续交互式脚本)
# interactive_script.py
import sys
for line in sys.stdin:
# 从标准输入读取一行
data = line.strip()
if not data:
break
print(f"Python received: {data}")
# 处理数据并返回
processed = data.upper()
print(f"Python sending back: {processed}")
JavaScript 代码 (Node.js)
// node_client.js
const { spawn } = require('child_process');
// 启动 Python 进程
const python = spawn('python', ['interactive_script.py']);
// 向 Python 进程发送数据
python.stdin.write('hello from js\n');
python.stdin.write('another message\n');
python.stdin.end(); // 结束输入流
// 监听 Python 进程的输出
python.stdout.on('data', (data) => {
console.log(`Received from Python: ${data.toString()}`);
});
// 监听错误
python.stderr.on('data', (data) => {
console.error(`Python stderr: ${data.toString()}`);
});
// 监听进程结束
python.on('close', (code) => {
console.log(`Python process exited with code ${code}`);
});
如何运行:
- 运行 JavaScript 客户端:
node node_client.js - 你会看到它立即打印出 Python 脚本处理后的结果。
共享文件系统
这是一种简单粗暴但有效的方式,两个程序通过读写同一个文件来通信,适用于异步任务,比如一个程序生成数据,另一个程序稍后处理。
Python 生成数据
# python_writer.py
import json
data = {
'user_id': 123,
'action': 'login',
'timestamp': '2025-10-27T10:00:00Z'
}
with open('data.json', 'w') as f:
json.dump(data, f)
print("Python has written data to data.json")
JavaScript 读取数据
// js_reader.js
const fs = require('fs');
// 等待文件被创建(在实际应用中可能需要更健壮的轮询或事件监听机制)
setTimeout(() => {
try {
const data = fs.readFileSync('data.json', 'utf8');
const jsonData = JSON.parse(data);
console.log('JavaScript read data:', jsonData);
// 输出: JavaScript read data: { user_id: 123, action: 'login', ... }
} catch (err) {
console.error("Error reading file:", err);
}
}, 1000); // 延迟1秒,确保文件已创建
如何运行:
- 先运行 Python:
python python_writer.py - 再运行 JavaScript:
node js_reader.js
总结与选择
| 交互模式 | 优点 | 缺点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| HTTP API | 最通用、最健壮、可扩展、解耦 | 需要一个 Web 服务器,相对复杂 | Web 应用(前端 JS 调用后端 Python API)、微服务架构 |
| 命令行调用 | 简单直接,无需额外框架 | 性能开销大,不适合高频交互,耦合度高 | 一次性脚本任务、简单的工具调用 |
| Pyodide | 在浏览器中直接运行 Python,无需后端 | 性能受限,加载时间长,生态不完全 | Web 教育平台、数据可视化工具、需要前端复杂数据计算的场景 |
| Node.js Child Process | 可以实现持续的双向流式通信 | 管理多个进程复杂,错误处理繁琐 | Node.js 应用中需要调用 Python 库,且需要频繁交互的场景 |
| 共享文件 | 实现简单,无需网络 | 速度慢,有文件I/O瓶颈,容易产生竞态条件 | 异批处理任务、日志分析、ETL 流水线 |
如何选择?
- 开发 Web 应用? -> 首选 HTTP API,这是行业标准,也是最灵活、最可维护的方案。
- 需要在浏览器里直接跑 Python 代码做计算? -> 选择 Pyodide,它能让你的 Web 应用拥有强大的后端计算能力。
- 只是想快速写个脚本,让 JS 调用一下现成的 Python 工具? -> 命令行调用 足够简单。
- 在 Node.js 项目中,需要复用某个 Python 库,并且交互频繁? -> Node.js Child Process 可以实现。
- 处理数据,且两个程序是异步运行的? -> 共享文件 是一种简单可行的方案。
希望这个详细的指南能帮助你理解并实现 JavaScript 和 Python 的交互!