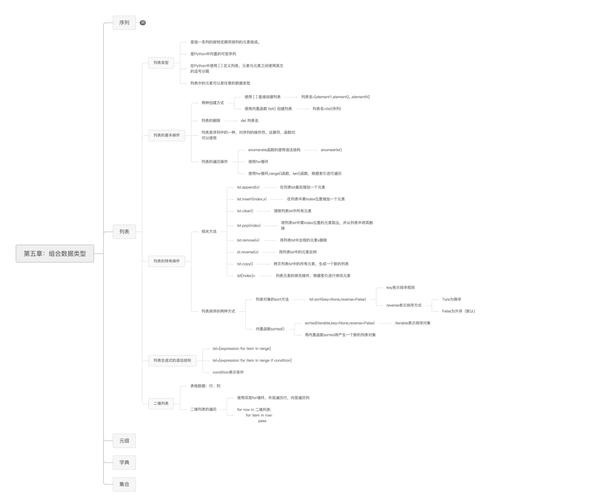
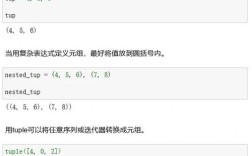
Of course! Node.js, Python, and Ruby are three of the most popular and powerful back-end programming languages. They all excel at building web applications and APIs, but they have different philosophies, strengths, and ecosystems.
Here’s a detailed comparison to help you understand the differences and choose the right one for your project.
At a Glance: The Core Idea
- Node.js: JavaScript on the Server. It uses the same JavaScript language that runs in your browser. Its main selling point is non-blocking, asynchronous I/O, making it incredibly fast for I/O-heavy applications.
- Python: The Batteries-Included Language. Known for its simple, readable syntax and vast ecosystem of libraries. It's a general-purpose language that's fantastic for web development, data science, machine learning, and scripting.
- Ruby: The Programmer's Best Friend. Famous for the Ruby on Rails framework, which emphasizes "Convention over Configuration" and "Don't Repeat Yourself" (DRY). It prioritizes developer happiness and rapid development.
Detailed Comparison Table
| Feature | Node.js | Python | Ruby |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paradigm | Event-driven, asynchronous. | Multi-paradigm (procedural, OOP, functional). | Primarily object-oriented. |
| Performance | Very High for I/O-bound tasks (network requests, file access). | Good, but generally slower than Node.js for raw web requests due to its Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) in CPython. | Good, but often considered slower than Node.js and Python for raw web tasks. |
| Ecosystem | npm (Node Package Manager) is the largest package registry in the world. Incredibly vast. | PyPI (Python Package Index) is massive, with high-quality libraries for everything. | RubyGems is mature and has a strong focus on web development. |
| Key Frameworks | Express.js (minimalist), NestJS (structured), Fastify (high-performance). | Django (batteries-included), Flask (microframework), FastAPI (modern, fast). | Ruby on Rails (full-stack), Sinatra (microframework). |
| Learning Curve | Low if you already know JavaScript. High if you're new to asynchronous programming (callbacks, promises, async/await). | Very low. Syntax is clean and readable, making it one of the best languages for beginners. | Low to moderate. Elegant and expressive, but some concepts like blocks can be tricky at first. |
| Primary Strength | Real-time Applications: Chat apps, live notifications, APIs, command-line tools, microservices. | Versatility: Web apps, data science, AI/ML, automation, scientific computing. | Rapid Development: Startups, MVPs (Minimum Viable Products), complex business logic applications. |
| Community | Massive and active, especially in the JavaScript/DevOps world. | Huge and diverse, spanning web development, science, and academia. | Passionate and supportive, heavily centered around the Rails framework. |
| Best For | - Real-time web apps - APIs - Microservices - Command-line tools |
- Data Science & Machine Learning - Web Development (Django/Flask) - Automation & Scripting - AI |
- Startups and MVPs - Complex business logic - Rapid prototyping |
In-Depth Breakdown
Node.js
Philosophy: "Use JavaScript everywhere." Node.js is not a language; it's a runtime environment that allows you to execute JavaScript code outside of a browser. Its core innovation is the Event Loop.
- How it Works: Instead of waiting for a task (like reading a file or making a database query) to finish, Node.js starts the task and then immediately moves on to the next one. When the task is complete, it gets notified and runs a "callback" function. This non-blocking model is extremely efficient for applications that handle many connections simultaneously.
- Strengths:
- Performance: Blazing fast for I/O-bound applications.
- Full-Stack JavaScript: Developers can use the same language for front-end and back-end, which can streamline development.
- Huge Ecosystem (npm): If you need a library, it almost certainly exists on npm.
- Weaknesses:
- Callback Hell: The old way of handling asynchronous code could become deeply nested and hard to read. (This is largely solved by
async/awaitsyntax now). - CPU-Intensive Tasks: Not ideal for heavy calculations, as it can block the event loop and slow down the entire application. (For this, you'd use worker threads or offload the task to another service).
- Callback Hell: The old way of handling asynchronous code could become deeply nested and hard to read. (This is largely solved by
- Popular Frameworks:
- Express.js: The de facto standard. Minimal, flexible, and unopinionated.
- NestJS: A more structured, opinionated framework built on TypeScript, inspired by Angular. Great for large, enterprise-level applications.
- Fastify: Extremely high-performance, focused on providing the fastest possible experience.
Python
Philosophy: "Readability counts." and "Simple is better than complex." Python was designed to be a highly readable language. Its syntax is clean and often resembles plain English.
- How it Works: Python is typically synchronous by default. When a function is called, the program waits for it to finish before moving on. This makes the code very easy to reason about. For high-concurrency needs, it uses threads or asynchronous libraries like
asyncio. - Strengths:
- Versatility: This is Python's superpower. It's the go-to language for web development, data analysis (Pandas, NumPy), machine learning (TensorFlow, PyTorch), and scripting.
- Readability: Easy to learn and write, leading to faster development and fewer bugs.
- Rich Ecosystem: PyPI has millions of high-quality packages.
- Weaknesses:
- Slower for Web: Due to the Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) in CPython, Python threads cannot run in parallel on multi-core processors for CPU-bound tasks. This makes it less performant than Node.js for handling many simultaneous web requests.
- High Memory Usage: Python is dynamically typed and can be more memory-intensive than statically typed languages.
- Popular Frameworks:
- Django: A "batteries-included" framework. It provides everything you need out of the box (admin panel, ORM, authentication) but can feel rigid.
- Flask: A micro-framework. It gives you the basics and lets you choose your own components (database, etc.). It's very flexible and great for smaller projects or APIs.
- FastAPI: A modern, high-performance framework that's incredibly easy to use and has automatic interactive API documentation.
Ruby
Philosophy: "Developer happiness." Ruby was created to make programming fun and productive. It's known for its elegant and expressive syntax.

- How it Works: Ruby is also synchronous by default. Its magic lies in its framework, Ruby on Rails, which provides a strong set of conventions that speed up development immensely.
- Strengths:
- Rapid Development: Rails' "Convention over Configuration" means you don't have to make a lot of decisions. The framework has an opinionated way of doing things, which leads to fast development once you learn its conventions.
- Elegant Syntax: Ruby feels natural and enjoyable to write for many developers.
- Strong Ecosystem: The community has built a vast number of high-quality "gems" (libraries) for Rails.
- Weaknesses:
- Performance: Generally considered the slowest of the three for raw web request handling. This is often a non-issue for most applications, but can be a bottleneck for very high-traffic systems.
- "Magic": The framework does a lot for you automatically, which can sometimes make it difficult to understand what's happening "under the hood" for beginners.
- Popular Frameworks:
- Ruby on Rails: The 800-pound gorilla. It revolutionized web development and is still the dominant force in the Ruby world.
- Sinatra: A micro-framework, similar to Flask, for building smaller web apps and APIs.
Which One Should You Choose?
-
Choose Node.js if:
- You are building a real-time application (chat, live feed).
- You need a high-performance API.
- Your team is already composed of front-end JavaScript developers.
- You are building microservices or command-line tools.
-
Choose Python if:
- Your project involves data science, machine learning, or AI.
- You need to build a web application and simplicity and readability are top priorities.
- You are doing a lot of automation or scripting.
- You need to build a fast API (especially with FastAPI).
-
Choose Ruby if:
- You are building a startup or an MVP and need to get to market as fast as possible.
- Developer happiness and productivity are your main concerns.
- You are building a complex web application with a lot of business logic.
- You want to use the Ruby on Rails framework.
Ultimately, all three are excellent choices. The "best" language depends entirely on your project's specific requirements, your team's expertise, and your development philosophy.