目录
- 环境准备
- 安装 Elasticsearch
- 安装 Python 客户端
- 创建索引并添加示例数据
- 基础查询
- 连接到 Elasticsearch
- 全文搜索
- 精确匹配
- 分页
- 进阶查询
bool查询 - 组合多个查询条件- 范围查询
- 排序
- 过滤
- 聚合查询
- 分组聚合
- 指标聚合
- 最佳实践与注意事项
环境准备
a. 安装 Elasticsearch
如果你还没有 Elasticsearch,最简单的方式是使用 Docker,确保你的 Docker 服务正在运行,然后执行:
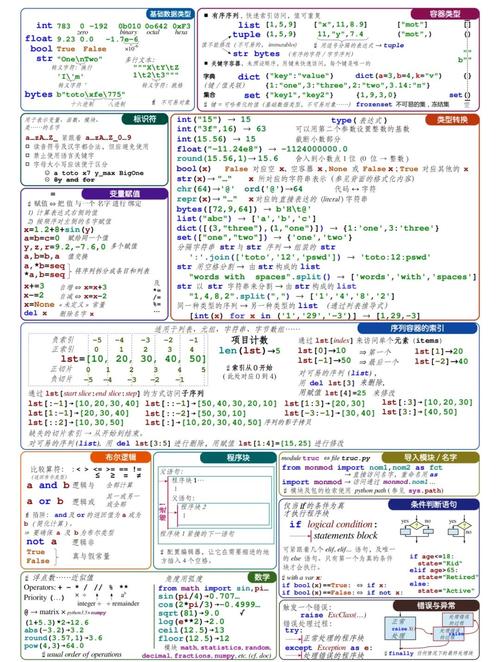
docker run -d --name elasticsearch -p 9200:9200 -e "discovery.type=single-node" elasticsearch:8.8.1
-d: 后台运行--name elasticsearch: 容器名称-p 9200:9200: 将容器的 9200 端口映射到宿主机,这是 REST API 的默认端口。-e "discovery.type=single-node": 以单节点模式启动,方便开发和测试。
启动后,你可以通过访问 http://localhost:9200 来确认服务是否正常,首次启动时,它会生成一个默认的用户名和密码,输出中会包含 elastic 和密码。
b. 安装 Python 客户端
我们推荐使用官方的 elasticsearch-py 客户端。
pip install elasticsearch
c. 创建索引并添加示例数据
为了后续的查询演示,我们先创建一个名为 products 的索引,并插入一些数据。
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
# 连接到 Elasticsearch (默认本地)
es = Elasticsearch("http://localhost:9200")
# 如果需要认证 (根据你的ES版本)
# es = Elasticsearch(
# "http://localhost:9200",
# basic_auth=("elastic", "your_password_here"),
# # 如果使用较新的ES版本,可能需要禁用SSL验证(仅限开发环境)
# verify_certs=False
# )
# 定义索引的映射(Mapping),类似于数据库的表结构)
index_mapping = {
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"product_name": {"type": "text"},
"category": {"type": "keyword"},
"price": {"type": "float"},
"stock": {"type": "integer"},
"in_stock": {"type": "boolean"}
}
}
}
# 创建索引
if es.indices.exists(index="products"):
es.indices.delete(index="products") # 如果已存在则删除
es.indices.create(index="products", body=index_mapping)
# 示例数据
products = [
{"product_name": "MacBook Pro 16\"", "category": "laptop", "price": 2499.0, "stock": 50, "in_stock": True},
{"product_name": "iPhone 15 Pro", "category": "smartphone", "price": 999.0, "stock": 200, "in_stock": True},
{"product_name": "Dell XPS 13", "category": "laptop", "price": 1299.0, "stock": 30, "in_stock": True},
{"product_name": "Samsung Galaxy S24", "category": "smartphone", "price": 899.0, "stock": 0, "in_stock": False},
{"product_name": "Sony WH-1000XM5", "category": "headphones", "price": 399.0, "stock": 75, "in_stock": True},
{"product_name": "iPad Air", "category": "tablet", "price": 599.0, "stock": 60, "in_stock": True},
{"product_name": "Logitech MX Master 3S", "category": "mouse", "price": 99.0, "stock": 120, "in_stock": True},
]
# 使用 bulk API 批量插入数据
from elasticsearch.helpers import bulk
def generate_actions():
for i, p in enumerate(products):
yield {
"_index": "products",
"_id": i + 1, # 为每个文档指定一个ID
"_source": p
}
success, failed = bulk(es, generate_actions())
print(f"Successfully indexed {success} documents.")
print(f"Failed to index {failed} documents.")
基础查询
a. 连接到 Elasticsearch
这部分我们在环境准备中已经完成,核心是创建 Elasticsearch 对象。
es = Elasticsearch("http://localhost:9200")
b. 全文搜索
使用 match 查询,它会对 text 类型的字段进行分词后搜索。
# 搜索产品名称中包含 "macbook" 或 "pro" 的文档
query = {
"query": {
"match": {
"product_name": "macbook pro"
}
}
}
response = es.search(index="products", body=query)
print(f"Found {response['hits']['total']['value']} products.")
for hit in response['hits']['hits']:
print(f" - ID: {hit['_id']}, Product: {hit['_source']['product_name']}, Price: ${hit['_source']['price']}")
c. 精确匹配
使用 term 查询,它会对 keyword 类型的字段进行精确匹配。
# 搜索类别为 "laptop" 的所有产品
query = {
"query": {
"term": {
"category": "laptop"
}
}
}
response = es.search(index="products", body=query)
print(f"Found {response['hits']['total']['value']} laptops.")
for hit in response['hits']['hits']:
print(f" - ID: {hit['_id']}, Product: {hit['_source']['product_name']}")
d. 分页
使用 from 和 size 参数控制分页。
from: 从第几条结果开始(从0开始)。size: 每页返回多少条结果。
# 查询第2页,每页2条记录
query = {
"query": {
"match_all": {} # 匹配所有文档
},
"from": 2, # 从第2条开始 (索引为2)
"size": 2 # 返回2条
}
response = es.search(index="products", body=query)
print("Page 2 (2 items per page):")
for hit in response['hits']['hits']:
print(f" - ID: {hit['_id']}, Product: {hit['_source']['product_name']}")
进阶查询
a. bool 查询 - 组合多个查询条件
bool 查询是 Elasticsearch 中最强大、最常用的查询,它通过组合子句来实现复杂的逻辑。

must: 必须匹配 (AND)should: 应该匹配 (OR),可以设置minimum_should_matchfilter: 必须匹配,但不计算相关性分数,性能更高must_not: 必须不匹配 (NOT)
示例:查找类别为 "laptop" 且价格在 1500 到 2500 之间,并且有库存的产品。
query = {
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "term": { "category": "laptop" } }
],
"filter": [ # 使用 filter 提高性能
{ "range": { "price": { "gte": 1500, "lte": 2500 } } },
{ "term": { "in_stock": True } }
]
}
}
}
response = es.search(index="products", body=query)
print("Laptops between $1500 and $2500 that are in stock:")
for hit in response['hits']['hits']:
print(f" - ID: {hit['_id']}, Product: {hit['_source']['product_name']}, Price: ${hit['_source']['price']}")
b. 范围查询
range 查询用于数值、日期、字符串等范围。
gt: 大于 (greater than)gte: 大于等于 (greater than or equal)lt: 小于 (less than)lte: 小于等于 (less than or equal)
# 查找价格低于 1000 美元的产品
query = {
"query": {