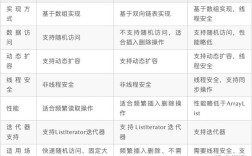
Of course! Encoding and decoding are fundamental operations in Java, used for converting data between different formats. The terms are often used interchangeably, but there's a subtle difference:
- Encoding: The process of converting data from one format to another. For example, converting a
Stringinto a sequence of bytes using a specific character set (like UTF-8). - Decoding: The process of reversing the encoding, converting the encoded data back to its original format. For example, converting a sequence of bytes back into a
String.
The most common scenario in Java is converting between String objects (which hold characters) and byte[] arrays (which are the raw, binary data). The key to this process is specifying the correct Character Set.
The Core Concept: String to byte[] and Back
The two primary classes you'll use are java.lang.String and java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets.
Key Methods:
String.getBytes(Charset charset): Encodes aStringinto a sequence of bytes.new String(byte[] bytes, Charset charset): Decodes a sequence of bytes into aString.
Why is the Character Set Critical?
If you encode a string with one character set and try to decode it with another, you will get mojibake (garbled text).
Example: The Importance of Character Sets
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class CharsetExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String originalString = "Hello, 世界!"; // Contains non-ASCII characters
// --- CORRECT ENCODING/DECODING ---
System.out.println("--- Correct (UTF-8) ---");
// 1. Encode the String to bytes using UTF-8
byte[] utf8Bytes = originalString.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("Original String: " + originalString);
System.out.println("Encoded Bytes (UTF-8): " + java.util.Arrays.toString(utf8Bytes));
// 2. Decode the bytes back to a String using UTF-8
String decodedString = new String(utf8Bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("Decoded String: " + decodedString);
System.out.println("Are they equal? " + originalString.equals(decodedString)); // true
System.out.println("\n--- INCORRECT DECODING (ISO-8859-1) ---");
// 1. Let's say we encoded with UTF-8 (same as above)
byte[] someUtf8Bytes = originalString.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// 2. WRONG: Try to decode using a different character set (ISO-8859-1)
String wrongDecodedString = new String(someUtf8Bytes, StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1);
System.out.println("Original String: " + originalString);
System.out.println("Decoded String (wrong): " + wrongDecodedString); // Garbled!
System.out.println("Are they equal? " + originalString.equals(wrongDecodedString)); // false
}
}
URL Encoding/Decoding
When you include special characters (like spaces, &, , ) in a URL, they must be encoded to be transmitted correctly. Java provides java.net.URLEncoder and java.net.URLDecoder.
Important Note: These classes work with the application/x-www-form-urlencoded MIME type, which is used for form data. For encoding a full URL path, a library like Apache Commons Codec is often better.
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.net.URLDecoder;
import java.net.URLEncoder;
public class UrlEncodingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String originalUrl = "https://example.com/search?q=java tutorial&page=1";
try {
// ENCODING
// Encode spaces and special characters
String encodedUrl = URLEncoder.encode(originalUrl, StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name());
System.out.println("Original URL: " + originalUrl);
System.out.println("Encoded URL: " + encodedUrl);
// Output: Original URL: https://example.com/search?q=java%20tutorial&page=1
// Encoded URL: https%3A%2F%2Fexample.com%2Fsearch%3Fq%3Djava+tutorial%26page%3D1
// DECODING
// Decode it back to the original string
String decodedUrl = URLDecoder.decode(encodedUrl, StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name());
System.out.println("\nDecoded URL: " + decodedUrl);
System.out.println("Are they equal? " + originalUrl.equals(decodedUrl)); // true
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
// This exception is thrown if the specified charset is not supported.
// UTF-8 is always supported, so this is unlikely to happen in practice.
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Base64 Encoding/Decoding
Base64 is an encoding scheme that represents binary data in an ASCII string format by translating it into a radix-64 representation. It's commonly used for embedding images in HTML, sending data in JSON/XML, or ensuring data integrity over text-based protocols.
Java 8 introduced a built-in, easy-to-use Base64 API in the java.util package.
import java.util.Base64;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class Base64Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String originalString = "This is a secret message!";
// Get the Base64 encoder and decoder
Base64.Encoder encoder = Base64.getEncoder();
Base64.Decoder decoder = Base64.getDecoder();
// ENCODING
// 1. Convert the string to bytes
byte[] bytesToEncode = originalString.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// 2. Encode the bytes
String encodedString = encoder.encodeToString(bytesToEncode);
System.out.println("Original String: " + originalString);
System.out.println("Base64 Encoded: " + encodedString);
// Output: VGhpcyBpcyBhIHNlY3JldCBtZXNzYWdlIQ==
// DECODING
// 1. Decode the Base64 string back to bytes
byte[] decodedBytes = decoder.decode(encodedString);
// 2. Convert the bytes back to a string
String decodedString = new String(decodedBytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("\nDecoded String: " + decodedString);
System.out.println("Are they equal? " + originalString.equals(decodedString)); // true
// You can also encode directly to a byte array
byte[] encodedBytes = encoder.encode(bytesToEncode);
System.out.println("\nEncoded to byte array length: " + encodedBytes.length);
}
}
Hexadecimal Encoding/Decoding
Converting bytes to a hexadecimal string is another common requirement for representing binary data in a readable format.
There is no built-in hex encoder/decoder in the standard Java library, but you can easily write one or use a library like Apache Commons Codec.
Method 1: Manual Implementation (Using StringBuilder)
public class HexExampleManual {
private static final char[] HEX_ARRAY = "0123456789ABCDEF".toCharArray();
public static String bytesToHex(byte[] bytes) {
char[] hexChars = new char[bytes.length * 2];
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
int v = bytes[i] & 0xFF; // Ensure unsigned byte value
hexChars[i * 2] = HEX_ARRAY[v >>> 4]; // High nibble
hexChars[i * 2 + 1] = HEX_ARRAY[v & 0x0F]; // Low nibble
}
return new String(hexChars);
}
public static byte[] hexToBytes(String s) {
int len = s.length();
byte[] data = new byte[len / 2];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i += 2) {
data[i / 2] = (byte) ((Character.digit(s.charAt(i), 16) << 4)
+ Character.digit(s.charAt(i+1), 16));
}
return data;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String originalString = "Hello, Java!";
byte[] bytes = originalString.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
String hexString = bytesToHex(bytes);
System.out.println("Original String: " + originalString);
System.out.println("Hex Encoded: " + hexString);
// Output: 48656C6C6F2C204A61766121
byte[] decodedBytes = hexToBytes(hexString);
String decodedString = new String(decodedBytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("\nDecoded String: " + decodedString);
System.out.println("Are they equal? " + originalString.equals(decodedString)); // true
}
}
Method 2: Using Apache Commons Codec (Recommended)
If you're already using Apache Commons Lang or Codec, this is much simpler.
Add this to your pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-codec</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-codec</artifactId>
<version>1.15</version>
</dependency>
import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Hex;
public class HexExampleCodec {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String originalString = "Hello, Java!";
byte[] bytes = originalString.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// ENCODING
String hexString = Hex.encodeHexString(bytes);
System.out.println("Original String: " + originalString);
System.out.println("Hex Encoded: " + hexString);
// DECODING
byte[] decodedBytes = Hex.decodeHex(hexString);
String decodedString = new String(decodedBytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("\nDecoded String: " + decodedString);
}
}
Summary: Which One to Use?
| Use Case | Recommended Method | Key Classes/Tools |
|---|---|---|
| General String <-> Bytes | String.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8) |
java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets |
| URLs (Form Data) | URLEncoder / URLDecoder |
java.net.URLEncoder, java.net.URLDecoder |
| Embedding Binary Data (JSON, Email, etc.) | Base64.getEncoder() / Base64.getDecoder() |
java.util.Base64 (Java 8+) |
| Representing Bytes in Readable Format | Apache Commons Codec Hex.encodeHexString() |
org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Hex |
| Password Hashing / Cryptography | java.security.MessageDigest (e.g., SHA-256) |
java.security.MessageDigest |