Of course! This guide covers everything you need to know about using Python on Ubuntu 18.04, from the default versions to installing newer ones and managing your projects.
Summary for Quick Users
- Default Python 3:
python3 - Default Python 2:
python(legacy, do not use for new projects) - Recommended Installation: Use
deadsnakesPPA to install modern Python versions (3.8, 3.9, 3.10, etc.). - Package Management: Use
pipto install Python packages. - Virtual Environments: Always use
venvorvirtualenvto isolate project dependencies.
Checking Your Default Python Installation
Ubuntu 18.04 comes with Python pre-installed. It's important to know which versions are available by default.
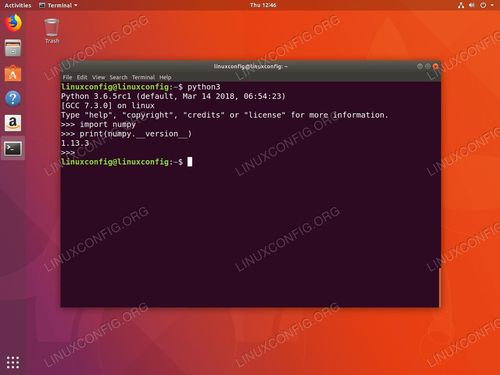
Check for Python 3
This is the modern, recommended version for all new development.
# Check the version of python3 python3 --version # Expected output: Python 3.6.9
Check for Python 2
Python 2 reached its end-of-life in January 2025. It is no longer supported and should not be used for new projects. It's often included for legacy system scripts.
# Check the version of python2 python2 --version # Expected output: Python 2.7.17
⚠️ Important Note: The
pythoncommand on Ubuntu 18.04 is often a symbolic link topython2orpython3. It is unreliable and can change. Always usepython3explicitly to ensure you are using the modern Python 3 interpreter.(图片来源网络,侵删)
Installing a Modern Python Version (e.g., Python 3.10)
The default python3 on Ubuntu 18.04 is version 3.6, which is quite old. For modern features, better performance, and security updates, you should install a newer version.
The best way to do this is by using a Personal Package Archive (PPA). The deadsnakes PPA is excellent for this.
Step 1: Add the Dead Snakes PPA
This PPA provides a wide range of Python versions.
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppa
You will be prompted to press Enter to continue.
Step 2: Update Your Package List
After adding the new repository, update your system's package list to include the new Python versions.
sudo apt update
Step 3: Install Your Desired Python Version
Let's install Python 3.10 as an example. You can replace 10 with any other version available in the PPA (e.g., 8, 9, 11).
sudo apt install python3.10
Step 4: Verify the Installation
Check that the new version was installed correctly.
python3.10 --version # Expected output: Python 3.10.12 (or similar)
You now have a modern Python interpreter ready to use!
Installing pip and venv
pip is the package installer for Python, and venv is the standard tool for creating virtual environments.
Install pip for Python 3.10
It's best to install pip specifically for the Python version you are using.
sudo apt install python3.10-venv python3.10-distutils curl -sS https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py | python3.10
python3.10-venv: Installs thevenvmodule.python3.10-distutils: Provides thedistutilspackage, whichget-pip.pyneeds.- The
curl | python3.10command runs the official pip installation script using your new Python interpreter.
Verify pip Installation
python3.10 -m pip --version
Using python -m pip is the recommended way to run pip.
Managing Python Projects with Virtual Environments
This is a critical best practice. A virtual environment creates an isolated space for your project's dependencies, preventing conflicts between different projects.
Step 1: Create a Project Directory
mkdir my-awesome-project cd my-awesome-project
Step 2: Create the Virtual Environment
We'll name our environment venv. It's a common convention.
# Use the python3.10 interpreter to create the venv python3.10 -m venv venv
This command creates a venv folder in your project directory containing a private copy of the Python interpreter and pip.
Step 3: Activate the Virtual Environment
Before you start working, you must activate the environment. Your shell prompt will change to show that it's active.
source venv/bin/activate
Your prompt will now look something like this: (venv) user@hostname:~/my-awesome-project$
Step 4: Work Inside the Environment
Now, any python or pip command you run will use the versions from the venv.
-
Install packages:
# Installs a package ONLY for this project pip install requests
-
Check installed packages:
pip list
-
Use the Python interpreter:
python --version # Output will be Python 3.10.x because the venv uses the interpreter it was created with
Step 5: Deactivate the Environment
When you are finished working, simply type deactivate to return to your normal shell.
deactivate
Your prompt will return to normal.
Making pip Use System Proxy (Optional)
If you are behind a corporate or university network, you might need to configure pip to use a proxy.
For HTTP/HTTPS Proxy
Set the HTTPS_PROXY and HTTP_PROXY environment variables.
# Example for a proxy on port 8080 export HTTPS_PROXY=http://user:password@proxy.yourcompany.com:8080 export HTTP_PROXY=http://user:password@proxy.yourcompany.com:8080
To make this permanent, add these lines to your ~/.bashrc or ~/.profile file.
For System-Wide Proxy
You can also configure pip to use the system's proxy settings by creating/editing the config file:
mkdir -p ~/.config/pip nano ~/.config/pip/pip.conf
Add the following content to the file:
[global] proxy = http://user:password@proxy.yourcompany.com:8080
Replace the URL with your actual proxy address.