Of course! Working with fonts in openpyxl is a common and essential task for creating professional-looking Excel files. The key is to use the Font class from openpyxl.styles.

Here’s a complete guide, from the basics to more advanced examples.
The Basics: Importing and Creating a Font
First, you need to import the necessary classes from openpyxl.styles.
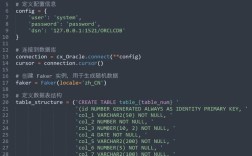
from openpyxl import Workbook from openpyxl.styles import Font, Alignment, PatternFill from openpyxl.utils import get_column_letter # Create a new workbook and select the active sheet wb = Workbook() ws = wb.active= "Font Styles"
The Font class is used to define all font-related properties. Here are the most common ones:
| Property | Description | Example Values |
|---|---|---|
name |
The name of the font. | 'Calibri', 'Arial', 'Times New Roman' |
size |
The font size in points. | 11, 14, 24 |
bold |
Makes the font bold. | True, False |
italic |
Makes the font italic. | True, False |
underline |
Adds an underline. | 'none', 'single', 'double' |
color |
Sets the font color. | An openpyxl.styles.colors.Color object or a hex string like 'FF0000' (for red). |
strike |
Adds a strikethrough line. | True, False |
Applying a Font to a Cell
Once you've created a Font object, you assign it to the font attribute of a cell's style.

# --- Example 1: Bold Font --- bold_font = Font(name='Arial', size=12, bold=True) ws['A1'] = 'This is Bold Text' ws['A1'].font = bold_font # --- Example 2: Italic and Underline --- italic_font = Font(name='Calibri', size=11, italic=True, underline='single') ws['A2'] = 'This is Italic and Underlined' ws['A2'].font = italic_font # --- Example 3: Different Color --- # You can use hex color codes red_font = Font(name='Times New Roman', size=14, color='FF0000') # Hex for red ws['A3'] = 'This is Red Text' ws['A3'].font = red_font # Or use the built-in colors module for named colors from openpyxl.styles.colors import GREEN green_font = Font(size=16, color=GREEN) ws['A4'] = 'This is Green Text' ws['A4'].font = green_font
Complete, Runnable Example
This example creates a new Excel file named styled_workbook.xlsx and demonstrates various font styles, along with other common styling options like alignment and fill.
import os
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.styles import Font, Alignment, PatternFill, Border, Side
from openpyxl.utils import get_column_letter
# Create a new workbook and select the active sheet
wb = Workbook()
ws = wb.active= "Styled Report"
# Define some reusable styles
header_font = Font(name='Calibri', size=11, bold=True, color='FFFFFF')
header_fill = PatternFill(start_color='366092', end_color='366092', fill_type='solid')
header_alignment = Alignment(horizontal='center', vertical='center')
data_font = Font(name='Calibri', size=10)
data_alignment = Alignment(horizontal='left', vertical='center')
# --- Style the Header Row ---
headers = ['Product', 'Sales Q1', 'Sales Q2', 'Total']
for col_num, header in enumerate(headers, 1):
cell = ws.cell(row=1, column=col_num)
cell.value = header
# Apply all header styles at once
cell.font = header_font
cell.fill = header_fill
cell.alignment = header_alignment
# --- Add and Style Some Data ---
data = [
['Laptop', 15000, 18000],
['Mouse', 2500, 3000],
['Keyboard', 3500, 4200],
['Monitor', 22000, 25000]
]
start_row = 2
for row_num, row_data in enumerate(data, start_row):
# Product name
product_cell = ws.cell(row=row_num, column=1, value=row_data[0])
product_cell.font = data_font
product_cell.alignment = data_alignment
# Sales Q1
q1_cell = ws.cell(row=row_num, column=2, value=row_data[1])
q1_cell.font = data_font
q1_cell.alignment = data_alignment
# Sales Q2
q2_cell = ws.cell(row=row_num, column=3, value=row_data[2])
q2_cell.font = data_font
q2_cell.alignment = data_alignment
# Total (Bold)
total = row_data[1] + row_data[2]
total_cell = ws.cell(row=row_num, column=4, value=total)
total_cell.font = Font(bold=True) # Reuse the base font and just make it bold
total_cell.alignment = data_alignment
# --- Add a Summary Cell with Strikethrough ---
summary_cell = ws.cell(row=7, column=1, value='Legacy Product Data')
summary_cell.font = Font(name='Arial', size=10, strike=True, color='808080')
summary_cell.alignment = Alignment(horizontal='center')
# --- Auto-adjust column widths ---
for col in ws.columns:
max_length = 0
column = col[0].column_letter # Get the column name
for cell in col:
try:
if len(str(cell.value)) > max_length:
max_length = len(str(cell.value))
except:
pass
adjusted_width = (max_length + 2) * 1.2
ws.column_dimensions[column].width = adjusted_width
# Save the workbook
output_filename = 'styled_workbook.xlsx'
wb.save(output_filename)
print(f"Successfully created '{output_filename}'")
When you run this code, it will generate a file named styled_workbook.xlsx that looks like this:
Key Concepts and Best Practices
A. Reusing Font Styles
Instead of creating a new Font object for every cell, it's much more efficient to define your styles once and reuse them.
# GOOD: Define styles oncefont = Font(name='Arial', size=16, bold=True, color='1F497D')
for cell in [ws['A1'], ws['B1'], ws['C1']]:
cell.font = title_font
# BAD: Define styles for every cell (inefficient)
ws['A1'].font = Font(name='Arial', size=16, bold=True, color='1F497D')
ws['B1'].font = Font(name='Arial', size=16, bold=True, color='1F497D')
ws['C1'].font = Font(name='Arial', size=16, bold=True, color='1F497D')
B. Combining Font with Other Styles
A font is just one part of a cell's style. You often want to combine it with Alignment, PatternFill, Border, etc. The best way is to create a NamedStyle.

from openpyxl.styles import NamedStyle
# Create a named style
highlight_style = NamedStyle(name="highlight")
highlight_style.font = Font(bold=True, size=12)
highlight_style.fill = PatternFill(start_color="FFFF00", end_color="FFFF00", fill_type="solid")
highlight_style.alignment = Alignment(horizontal="center")
# Apply the named style to multiple cells
for cell in [ws['A1'], ws['B1'], ws['C1']]:
cell.style = highlight_style
C. Performance Tip: Use write_only Mode
If you are generating a very large Excel file (e.g., 100,000+ rows), creating Cell objects one by one can be slow. In such cases, use the write_only=True mode.
In write_only mode, you cannot directly access or modify cells after they are written. You must apply styles to the cell at the moment of creation.
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.styles import Font
wb = Workbook(write_only=True)
ws = wb.create_sheet("Large Data")
# Define the font
my_font = Font(name='Courier New', size=10)
# You must apply the font during cell creation
# ws.cell() does not exist in write_only mode
# Instead, you append a tuple of (value, style)
for i in range(1000):
row_data = [f"Item {i}", i * 10, f"Status {'OK' if i % 2 == 0 else 'N/A'}"]
styled_row = []
for value in row_data:
# Create a cell with a value