- Excel 解析: Apache POI - 这是 Java 处理 Office 文件(如 .xlsx, .xls)的事实标准。
- 数据库操作: JDBC - Java 官方提供的数据库连接标准。
- 数据库: MySQL - 作为示例数据库,但此方法同样适用于 Oracle, SQL Server, PostgreSQL 等。
- 构建工具: Maven - 用于管理项目依赖。
目录
- 环境准备
- 数据库与表准备
- Maven 项目配置 (pom.xml)
- Java 代码实现
- 1 创建数据库连接工具类
- 2 创建实体类 (Model)
- 3 创建 Excel 数据读取与导入服务类
- 4 创建主程序入口
- 代码解析与关键点
- 进阶优化
- 1 使用
PreparedStatement防止 SQL 注入 - 2 事务管理
- 3 性能优化 (批量插入)
- 4 错误处理与日志
- 1 使用
环境准备
确保你的开发环境已经安装:
- JDK 8 或更高版本
- Maven
- MySQL 数据库 并已创建好数据库。
数据库与表准备
假设我们要导入一份员工信息表,首先在 MySQL 中创建数据库和对应的表。
-- 创建数据库 CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `demo_db` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci; -- 使用数据库 USE `demo_db`; -- 创建员工表 CREATE TABLE `employee` ( `id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键ID', `name` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL COMMENT '姓名', `age` INT NOT NULL COMMENT '年龄', `email` VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '邮箱', `department` VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '部门', `create_time` DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='员工信息表';
Excel 文件准备 (employees.xlsx)
创建一个 Excel 文件,内容如下,并确保第一行是列名,与数据库表的列名对应。
| name | age | department | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 张三 | 28 | zhangsan@example.com | 技术部 |
| 李四 | 32 | lisi@example.com | 市场部 |
| 王五 | 25 | wangwu@example.com | 人事部 |
| 赵六 | 45 | zhaoliu@example.com | 财务部 |
| 钱七 | 29 | qianqi@example.com | 技术部 |
注意: Excel 文件最好保存为 .xlsx 格式(即 Office 2007 及以后版本),因为 .xls 格式处理起来更复杂且存在行数限制,如果使用 .xls,代码中需要使用 HSSFWorkbook 而不是 XSSFWorkbook。
Maven 项目配置 (pom.xml)
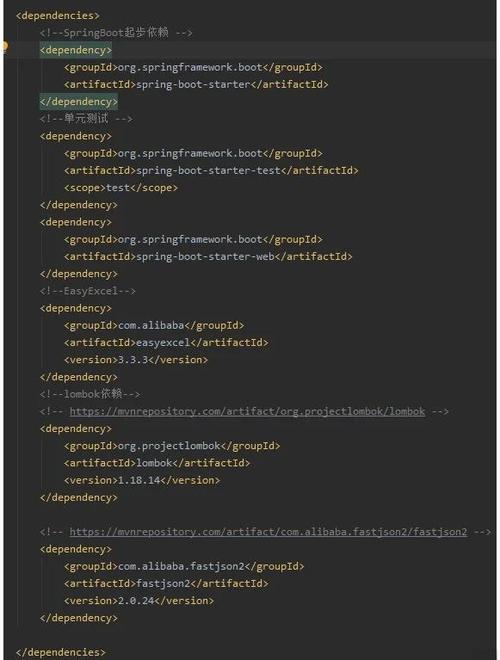
在你的 Maven 项目的 pom.xml 文件中添加以下依赖:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>excel-import-demo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Apache POI for Excel (.xlsx) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>5.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL Connector/J -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.28</version>
</dependency>
<!-- SLF4J and Logback for logging (optional but recommended) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.11</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Java 代码实现
1 创建数据库连接工具类 (DBUtil.java)
这个类负责获取和关闭数据库连接。
package com.example.util;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class DBUtil {
// 数据库连接信息 (请根据你的实际情况修改)
private static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo_db?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=UTF-8";
private static final String USER = "root"; // 你的数据库用户名
private static final String PASSWORD = "your_password"; // 你的数据库密码
static {
try {
// 加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to load MySQL driver!");
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USER, PASSWORD);
}
public static void closeConnection(Connection conn) {
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2 创建实体类 (Employee.java)
用于映射 Excel 中的一行数据。
package com.example.model;
public class Employee {
private String name;
private int age;
private String email;
private String department;
// Getters and Setters
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
public int getAge() { return age; }
public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; }
public String getEmail() { return email; }
public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email; }
public String getDepartment() { return department; }
public void setDepartment(String department) { this.department = department; }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", department='" + department + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
3 创建 Excel 数据读取与导入服务类 (ExcelImportService.java)
这是核心逻辑所在。
package com.example.service;
import com.example.model.Employee;
import com.example.util.DBUtil;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ExcelImportService {
public void importDataFromExcel(String excelFilePath) {
List<Employee> employeeList = parseExcel(excelFilePath);
if (employeeList == null || employeeList.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Excel file is empty or could not be parsed.");
return;
}
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
// 关闭自动提交,开启事务
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
// 使用PreparedStatement进行批量插入,性能更高且安全
String sql = "INSERT INTO employee (name, age, email, department) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)";
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (Employee employee : employeeList) {
pstmt.setString(1, employee.getName());
pstmt.setInt(2, employee.getAge());
pstmt.setString(3, employee.getEmail());
pstmt.setString(4, employee.getDepartment());
pstmt.addBatch(); // 将此语句添加到批处理命令中
}
int[] results = pstmt.executeBatch(); // 执行批处理
conn.commit(); // 提交事务
System.out.println("成功导入 " + results.length + " 条数据到数据库。");
} catch (IOException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.rollback(); // 发生异常时回滚事务
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("数据导入失败,已回滚。");
} finally {
if (conn != null) {
try {
// 恢复自动提交
conn.setAutoCommit(true);
DBUtil.closeConnection(conn);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
private List<Employee> parseExcel(String excelFilePath) throws IOException {
List<Employee> employeeList = new ArrayList<>();
File excelFile = new File(excelFilePath);
if (!excelFile.exists()) {
System.out.println("Excel file not found: " + excelFilePath);
return null;
}
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(excelFile);
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fis)) { // .xlsx 格式使用 XSSFWorkbook
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0); // 获取第一个工作表
// 跳过表头,从第二行开始读取
for (int i = 1; i <= sheet.getLastRowNum(); i++) {
Row row = sheet.getRow(i);
if (row == null) {
continue; // 跳过空行
}
Cell nameCell = row.getCell(0);
Cell ageCell = row.getCell(1);
Cell emailCell = row.getCell(2);
Cell departmentCell = row.getCell(3);
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setName(getCellValueAsString(nameCell));
employee.setAge((int) getCellValueAsNumber(ageCell));
employee.setEmail(getCellValueAsString(emailCell));
employee.setDepartment(getCellValueAsString(departmentCell));
employeeList.add(employee);
}
}
return employeeList;
}
private String getCellValueAsString(Cell cell) {
if (cell == null) {
return "";
}
switch (cell.getCellType()) {
case STRING:
return cell.getStringCellValue();
case NUMERIC:
// 处理数字类型,如年龄
if (DateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)) {
return cell.getDateCellValue().toString();
} else {
return String.valueOf((int) cell.getNumericCellValue());
}
case BOOLEAN:
return String.valueOf(cell.getBooleanCellValue());
case FORMULA:
return cell.getCellFormula();
default:
return "";
}
}
private double getCellValueAsNumber(Cell cell) {
if (cell == null) {
return 0;
}
return cell.getNumericCellValue();
}
}
4 创建主程序入口 (Main.java)
package com.example;
import com.example.service.ExcelImportService;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 请确保你的 employees.xlsx 文件路径正确
String excelPath = "path/to/your/employees.xlsx"; // 修改为你的文件路径
ExcelImportService importService = new ExcelImportService();
importService.importDataFromExcel(excelPath);
}
}
代码解析与关键点
XSSFWorkbook: 用于处理.xlsx格式,如果是.xls,需要使用HSSFWorkbook。Sheet和Row:Workbook代表整个 Excel 文件,Sheet代表其中的一个工作表,Row代表一行。Cell: 代表一个单元格。cell.getCellType()判断单元格的数据类型(字符串、数字、布尔值等),然后使用对应的getXXXCellValue()方法获取值。- 跳过表头:
for (int i = 1; ...)直接从第二行开始遍历。 PreparedStatement: 这是防止 SQL 注入的最佳实践,我们使用 作为占位符,然后通过setXXX()方法设置参数。addBatch()和executeBatch(): 这是批量插入的核心。addBatch()将 SQL 语句加入批处理队列,executeBatch()一次性执行所有队列中的语句,大大减少了与数据库的交互次数,性能提升显著。
进阶优化
1 使用 PreparedStatement 防止 SQL 注入
(已在核心代码中实现)PreparedStatement 会对输入参数进行转义,从根本上杜绝了 SQL 注入的风险。
2 事务管理
(已在核心代码中实现)
conn.setAutoCommit(false);: 关闭 JDBC 的自动提交模式。conn.commit();: 在所有数据成功插入后,手动提交事务。conn.rollback();: 如果过程中发生任何异常,回滚事务,确保数据一致性。
3 性能优化 (批量插入)
(已在核心代码中实现)使用 addBatch() 和 executeBatch() 是最有效的性能优化手段,对于十万甚至百万级别的数据导入,这是必须的。
4 错误处理与日志
- 日志: 使用 SLF4J + Logback (已在 pom.xml 中添加依赖) 来替代
System.out.println,可以更好地管理日志级别(DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR)和输出位置(控制台、文件)。 - 错误处理: 当前代码在解析 Excel 时如果某一行格式错误,会跳过该行,你可以根据需求,将这些错误行记录下来,生成一个错误报告文件。
通过以上步骤,你已经成功搭建了一个完整的 Java Excel 导入数据库的系统,这个方案具有良好的健壮性和可扩展性。
核心流程回顾:
- 读取 Excel: 使用 Apache POI 逐行读取数据,并封装到 Java 对象(List)中。
- 连接数据库: 使用 JDBC 获取数据库连接。
- 开启事务: 确保数据导入的原子性。
- 批量写入: 使用
PreparedStatement的批处理功能高效地将数据插入数据库。 - 提交/回滚: 成功则提交,失败则回滚,保证数据一致性。
- 关闭资源: 释放数据库连接等资源。
你可以基于这个框架,轻松扩展以支持更复杂的场景,例如数据验证、读取多个 Sheet、处理更复杂的 Excel 格式等。