Of course! When you ask about "Python 3.6 commands," it can mean a few different things. I'll cover the most common interpretations:
- How to run a Python script from your command line/terminal.
- Essential Python commands and functions you use within a Python script.
- Useful command-line tools that come with Python (like
pip).
Let's break them down.
Running Python Scripts from the Command Line (Terminal)
This is how you execute your Python code.
Step 1: Open Your Terminal
- Windows: Open Command Prompt, PowerShell, or the new Windows Terminal.
- macOS / Linux: Open the Terminal app.
Step 2: Check Your Python Version
First, verify that Python 3.6 is installed and accessible.
python --version
If this shows Python 3.6.x, you're good to go. On some systems (especially macOS and Linux), you might need to use python3:

python3 --version
Step 3: Navigate to Your Project Directory
Use the cd (change directory) command to go to the folder where your Python file is located.
# Example: Go to the Documents folder cd Documents cd my_python_project
Step 4: Run Your Python Script
Let's say you have a file named hello.py with the following content:
# hello.py
print("Hello from Python 3.6!")
name = input("What is your name? ")
print(f"Nice to meet you, {name}!")
To run it, use the python (or python3) command followed by the filename.
python hello.py
Output:

Hello from Python 3.6!
What is your name? Alice
Nice to meet you, Alice!Other Useful Execution Commands
-
Run with a specific version: If you have multiple Python versions, you can specify which one to use.
# On some systems, the executable is named python3.6 python3.6 hello.py
-
Execute code directly: You can run a single line of Python code without a file.
python -c "print('This runs directly from the command line')" -
Run in interactive mode: This opens the Python interpreter, letting you type commands and see results immediately.
python
You'll see a prompt like
>>>. Typeexit()or pressCtrl+Z(Windows) orCtrl+D(macOS/Linux) to quit.
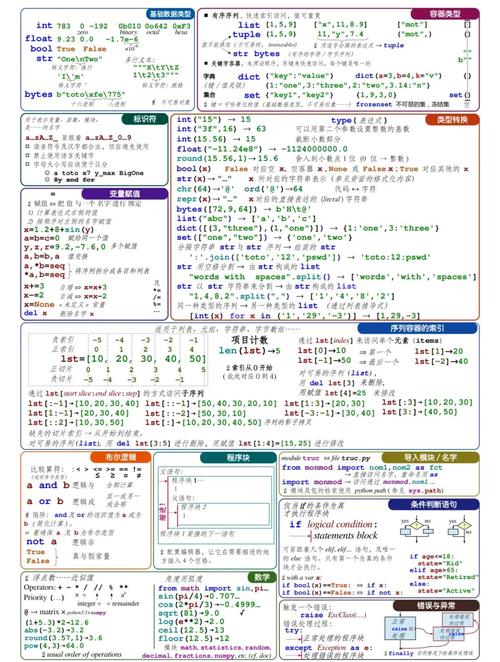
Essential Python Commands (Keywords and Built-in Functions)
These are the commands you use inside your Python scripts. Python 3.6 introduced several new features, most notably Formatted String Literals (f-strings).
Core Keywords (Control Flow)
These are the fundamental building blocks of your code.
| Command | Description | Example (Python 3.6+) |
|---|---|---|
if / elif / else |
Conditional logic. | if x > 0: print("Positive") |
for |
Loops over a sequence (like a list). | for item in my_list: |
while |
Loops as long as a condition is true. | while count > 0: |
def |
Defines a function. | def my_function(): |
class |
Defines a class (object-oriented programming). | class MyClass: |
import |
Imports a module (a library of code). | import math |
try / except |
Handles exceptions (errors) gracefully. | try: ... except ValueError: |
with |
Simplifies resource management (e.g., files). | with open('file.txt') as f: |
pass |
A null operation; does nothing. Used as a placeholder. | if condition: pass |
lambda |
Creates a small, anonymous function. | add = lambda x, y: x + y |
Key Built-in Functions
These are functions that are always available in Python.
| Function | Description | Example (Python 3.6+) |
|---|---|---|
print() |
Outputs text to the console. | print("Hello") |
input() |
Reads a line from the console. | name = input("Enter name: ") |
len() |
Returns the length of an object. | length = len("hello") |
range() |
Generates a sequence of numbers. | for i in range(5): |
type() |
Returns the type of an object. | print(type(42)) # <class 'int'> |
isinstance() |
Checks if an object is an instance of a class. | isinstance(x, int) |
open() |
Opens a file. | f = open('file.txt', 'r') |
str(), int(), float() |
Converts values to different data types. | num = int("10") |
list(), dict(), tuple() |
Creates new lists, dictionaries, or tuples. | my_list = list() |
Python 3.6's Major New Feature: f-Strings
This is the most important command-like feature introduced in Python 3.6. It's a much cleaner way to format strings.
Old way (Python 3.5 and below):
name = "Bob"
age = 30
print("Hello, my name is {} and I am {} years old.".format(name, age))
New f-string way (Python 3.6+):
name = "Bob"
age = 30
print(f"Hello, my name is {name} and I am {age} years old.")
The f before the string tells Python to evaluate the expressions inside the curly braces .
Command-Line Tools that Come with Python
When you install Python, you get several powerful command-line tools.
pip: The Package Installer
pip is used to install and manage third-party libraries from the Python Package Index (PyPI).
-
Install a package:
pip install requests
(Note: On some systems, you might need
pip3 install requests) -
Upgrade a package:
pip install --upgrade requests
-
Uninstall a package:
pip uninstall requests
-
List installed packages:
pip list
-
Show information about a package:
pip show requests
venv: The Virtual Environment Tool
This is a critical tool for managing projects. A virtual environment creates an isolated space for your project's dependencies, so they don't conflict with other projects.
-
Create a virtual environment: Navigate to your project folder and run:
# This creates a folder named 'venv' python -m venv venv
-
Activate the virtual environment:
- Windows:
venv\Scripts\activate
- macOS / Linux:
source venv/bin/activate
Your command prompt will change to show
(venv)at the beginning, indicating it's active.
- Windows:
-
Deactivate the virtual environment:
deactivate
Now, when you use pip install, it will only install packages inside this venv, keeping your project clean and portable.
Summary
| Category | Key Commands / Tools |
|---|---|
| Running Scripts | python your_script.py, python -c "...", python (interactive) |
| Core Keywords | if, for, while, def, class, import, try/except |
| Built-in Functions | print(), input(), len(), range(), open() |
| Python 3.6 Feature | f-strings: f"Hello, {name}!" |
| Essential Tools | pip (for installing libraries), venv (for project isolation) |