Of course! Let's break down the relationship between Selenium, Python, and JavaScript (JS). This is a very common topic for web automation and testing.
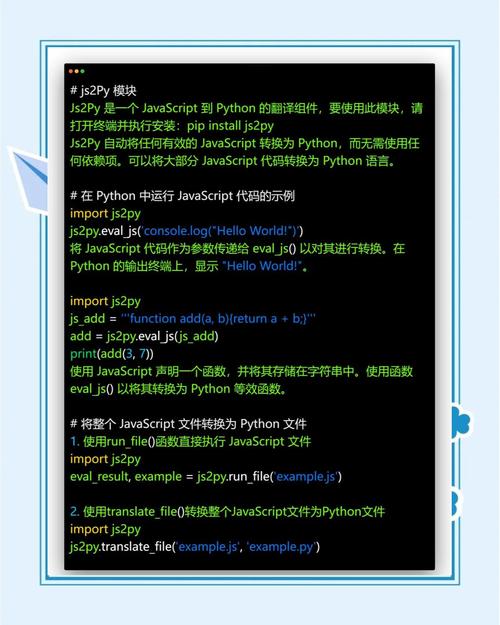
Here’s a comprehensive guide covering the key concepts, comparisons, and use cases.
The Big Picture: How They Work Together
Think of it like a team project with distinct roles:
- Selenium: The "Action Hero" or the "Browser Driver". Its only job is to take commands and make a web browser do things (click a button, type text, navigate to a URL). It doesn't know what to do, only how to do it.
- Python: The "Project Manager" or "Scripting Language". This is the language you use to write the instructions. You tell Selenium, "Hey, go to this website, find the search box, type 'Selenium Python', and press enter." Python is excellent for this because it's readable, has a simple syntax, and has a powerful library for Selenium.
- JavaScript (JS): The "Brain of the Website" or "The Content". This is the language that the website itself is written in. It controls the dynamic behavior, updates the page without reloading, validates forms, and creates interactive features. When you use Selenium, you are interacting with a page that has been built and is being controlled by JavaScript.
The Flow:
- Your Python script uses the Selenium library.
- Selenium opens a browser (like Chrome).
- The browser loads a webpage, which runs JavaScript in the background.
- Your Python script tells Selenium to find elements and perform actions.
- Selenium translates those actions into commands the browser understands, which then interact with the JS-powered webpage.
Python + Selenium: The Most Common Combination
This is the de-facto standard for web scraping, automation, and testing. Here’s why:
- Ease of Use: Python's syntax is clean and easy to learn, making it accessible for beginners and powerful for experts.
- Powerful Libraries: The
seleniumlibrary is mature, well-documented, and integrates seamlessly with other Python data science libraries (like Pandas for data analysis). - Rich Ecosystem: You can easily combine Selenium with libraries for handling waits (
WebDriverWait), reading files (os,csv), or making API calls (requests).
Quick Python + Selenium Example
This script opens Google, searches for "Selenium Python", and prints the page title.
# 1. Install the library first: pip install selenium
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service as ChromeService
from webdriver_manager.chrome import ChromeDriverManager
# 2. Set up the WebDriver (Selenium will manage the driver for you)
driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=ChromeService(ChromeDriverManager().install()))
try:
# 3. Navigate to a URL
driver.get("https://www.google.com")
# 4. Find an element and interact with it
# The search box has the name 'q'
search_box = driver.find_element(By.NAME, "q")
search_box.send_keys("Selenium Python")
search_box.send_keys(Keys.RETURN)
# 5. Wait for the results to load (optional but good practice)
driver.implicitly_wait(5) # Wait up to 5 seconds for elements to appear
# 6. Get some data from the page
print(f"Page Title is: {driver.title}")
finally:
# 7. Close the browser
driver.quit()
JavaScript + Selenium: The WebDriverJS Approach
You can also write your automation scripts directly in JavaScript. This is done using a library called Selenium WebDriverJS (or just selenium-webdriver).
When would you choose this?
- Your Project is in JavaScript: If your main application is a Node.js project, it's natural to keep your automation scripts in the same language.
- Browser-Specific Tools: This approach integrates well with other JavaScript-based testing frameworks like Cypress, Playwright, or TestCafe.
Quick JavaScript + Selenium (Node.js) Example
This does the exact same thing as the Python script above.

// 1. First, set up your Node.js project and install the library:
// npm init -y
// npm install selenium-webdriver
const { Builder, By, Key, until } = require('selenium-webdriver');
// 2. Set up the WebDriver (make sure you have ChromeDriver installed and in your PATH)
async function googleSearch() {
let driver = await new Builder().forBrowser('chrome').build();
try {
// 3. Navigate to a URL
await driver.get('https://www.google.com');
// 4. Find an element and interact with it
let searchBox = await driver.findElement(By.name('q'));
await searchBox.sendKeys('Selenium JavaScript');
await searchBox.sendKeys(Key.RETURN);
// 5. Wait for the results page to load
await driver.wait(until.titleIs('Selenium JavaScript - Google Search'), 1000);
// 6. Get some data from the page
console.log(`Page Title is: ${await driver.getTitle()}`);
} finally {
// 7. Close the browser
await driver.quit();
}
}
googleSearch();
Interacting with JavaScript on a Page (The Advanced Case)
Sometimes, the element you want to click is created or hidden by JavaScript. Python's Selenium can't just "wait" for it; you need to tell it how to wait.
This is where JavaScript Execution comes in. You can inject and run your own JavaScript code directly into the browser's context from your Python script.
Common Use Cases for execute_script()
- Scrolling Down: To bring an element into the viewport.
- Clicking an Element: When the standard
.click()method fails due to overlapping elements or dynamic rendering. - Getting Data: Extracting data that is stored in a JavaScript variable on the page.
- Updating a Value: Changing the value of an input field directly.
Python Example: Using execute_script()
Let's say a button only appears after you scroll down.
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service as ChromeService
from webdriver_manager.chrome import ChromeDriverManager
driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=ChromeService(ChromeDriverManager().install()))
driver.get("https://example.com/a-very-long-page")
# --- Standard Selenium might fail here ---
# hidden_button = driver.find_element(By.ID, "my-hidden-button")
# hidden_button.click() # Might raise an ElementNotInteractableException
# --- The JS Execution Solution ---
# 1. Scroll the page down by 500 pixels
driver.execute_script("window.scrollBy(0, 500);")
# 2. Now, find and click the element
# We can even click it using JS!
driver.execute_script("document.getElementById('my-hidden-button').click();")
# Or find it with Selenium and then use JS to click it
# button = driver.find_element(By.ID, "my-hidden-button")
# driver.execute_script("arguments[0].click();", button)
print("Successfully clicked the button using JavaScript!")
driver.quit()
Comparison Table: Python vs. JavaScript for Selenium
| Feature | Python + Selenium | JavaScript (WebDriverJS) + Selenium |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use Case | General-purpose automation, data scraping, backend testing. | Frontend testing, integration into existing JS/Node.js projects. |
| Learning Curve | Very gentle for beginners. Syntax is very readable. | Steeper if you don't know JavaScript/Node.js (npm, async/await). |
| Ecosystem | Massive. Integrates with Django, Flask, Pandas, NumPy, etc. | Massive. Integrates with React, Angular, Vue, and testing frameworks like Jest, Mocha. |
| Community & Docs | Extremely large and active community. Tons of tutorials. | Large and active community, especially within the frontend world. |
| Handling Waits | WebDriverWait is very explicit and powerful. |
driver.wait() is also powerful but relies more on Promises/async-await patterns. |
| Best For... | Quick scripts, data extraction, and general automation tasks. | Teams already using JavaScript for their entire tech stack. |
Summary and Final Recommendation
| Your Goal | Recommended Approach |
|---|---|
| I'm new to programming and want to automate a website. | Start with Python + Selenium. The learning curve is much gentler. |
| I'm a Python developer building a data scraper or automating a workflow. | Python + Selenium is the perfect fit. It's fast, powerful, and integrates well with other Python tools. |
| I'm a JavaScript/Node.js developer and need to test my web app. | Use JavaScript (WebDriverJS) + Selenium. It keeps your tech stack consistent. |
| I need to scroll the page or click an element that JavaScript is hiding. | Use Python's driver.execute_script() to inject and run your own JavaScript code. |
In short, Selenium is the engine, Python is a very popular and easy-to-use language to drive that engine, and JavaScript is the language of the road (the website) that the engine is driving on.


