Of course! Here is a comprehensive guide on how to use MD5withRSA in Java, covering the concepts, code examples, security warnings, and best practices.
What is MD5withRSA?
MD5withRSA is a digital signature algorithm. It's not a single algorithm but a combination of two:
-
MD5 (Message-Digest Algorithm 5): A cryptographic hash function. It takes an input (of any size) and produces a fixed-size, 128-bit (16-byte) "hash" or "digest." The key properties are:
- One-way: You cannot reverse the hash to get the original message.
- Deterministic: The same input will always produce the same hash.
- Avalanche effect: A tiny change in the input (e.g., flipping one bit) will produce a completely different, unpredictable hash.
-
RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman): A public-key cryptosystem. It uses a pair of keys:
- Private Key: Kept secret by the sender. Used to sign data.
- Public Key: Shared with anyone. Used to verify the signature.
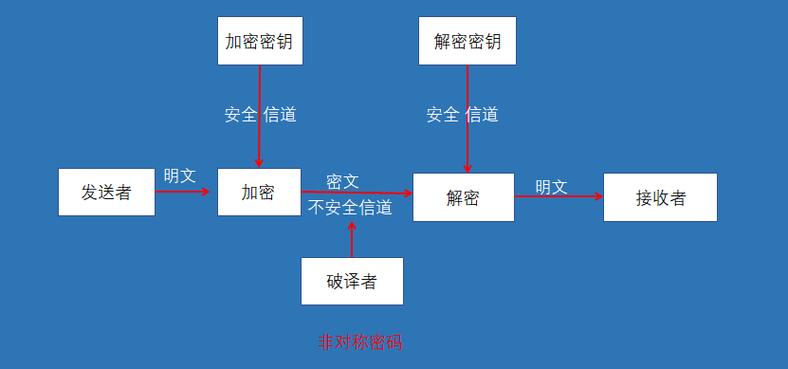
How MD5withRSA works together:

-
Signing:
- The sender calculates the MD5 hash of the original message.
- The sender then encrypts this hash with their private RSA key.
- The result is the digital signature. This signature is sent along with the original message.
-
Verification:
- The receiver receives the message and the signature.
- The receiver calculates the MD5 hash of the received message.
- The receiver decrypts the signature using the sender's public RSA key. This should reveal the original hash.
- The receiver compares the hash they calculated (from step 2) with the hash they decrypted (from step 3).
- If they match, the message is authentic (it came from the sender) and untampered (it wasn't changed in transit).
- If they don't match, the message has been altered or is not from the claimed sender.
⚠️ Critical Security Warning: Do Not Use MD5withRSA for New Systems
This is the most important part of this guide. MD5 is cryptographically broken and should not be used for security-sensitive applications.
- Collision Vulnerabilities: It's possible to create two different input messages that produce the exact same MD5 hash. Attackers can exploit this to create fraudulent data that appears legitimate.
- Pre-image Attacks: While not yet practical for breaking security in the way collisions are, research has shown that MD5's resistance to pre-image attacks is significantly weakened.
Why is it still mentioned?
You will encounter MD5withRSA in older systems, legacy protocols (like some TLS/SSL cipher suites), and specific non-security contexts (e.g., checksumming files for integrity against accidental corruption, not malicious tampering).
Recommendation: For any new application requiring digital signatures, use a modern, secure algorithm like:
- SHA-256withRSA (or SHA-384, SHA-512)
- Ed25519
- ECDSA with SHA-256
Java Code Example: MD5withRSA
Here is a complete, runnable Java example that demonstrates how to sign data and then verify the signature.
This example uses the KeyPairGenerator to create a temporary RSA key pair for demonstration purposes. In a real application, you would load your existing private key (e.g., from a PKCS#12 keystore or PEM file) and the corresponding public key.
MD5withRSADemo.java
import java.security.*;
import java.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec;
import java.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MD5withRSADemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. Generate an RSA Key Pair
KeyPair keyPair = generateRSAKeyPair();
PrivateKey privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate();
PublicKey publicKey = keyPair.getPublic();
System.out.println("RSA Key Pair Generated.");
System.out.println("Public Key: " + publicKey);
System.out.println("Private Key: " + privateKey);
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
// 2. The original message to be signed
String originalMessage = "This is a secret message that needs to be signed.";
System.out.println("Original Message: " + originalMessage);
// 3. Sign the message
byte[] signature = signMD5withRSA(originalMessage.getBytes(), privateKey);
System.out.println("\nSignature (Hex): " + bytesToHex(signature));
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
// 4. Verify the signature with the original message
boolean isVerified = verifyMD5withRSA(originalMessage.getBytes(), signature, publicKey);
System.out.println("Verification Result (Original Message): " + isVerified);
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
// 5. Tamper with the message and try to verify again
String tamperedMessage = "This is a secret message that needs to be signed!!"; // Note the '!!'
System.out.println("Tampered Message: " + tamperedMessage);
boolean isTamperedVerified = verifyMD5withRSA(tamperedMessage.getBytes(), signature, publicKey);
System.out.println("Verification Result (Tampered Message): " + isTamperedVerified);
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
}
/**
* Generates an RSA Key Pair.
*/
public static KeyPair generateRSAKeyPair() throws Exception {
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA");
keyPairGenerator.initialize(2048); // 2048 is a secure key size
return keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair();
}
/**
* Signs the data using the MD5withRSA algorithm.
* @param data The data to sign.
* @param privateKey The private key to use for signing.
* @return The signature bytes.
*/
public static byte[] signMD5withRSA(byte[] data, PrivateKey privateKey) throws Exception {
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance("MD5withRSA");
signature.initSign(privateKey);
signature.update(data);
return signature.sign();
}
/**
* Verifies the signature for the given data using the MD5withRSA algorithm.
* @param data The original data.
* @param signature The signature to verify.
* @param publicKey The public key to use for verification.
* @return true if the signature is valid, false otherwise.
*/
public static boolean verifyMD5withRSA(byte[] data, byte[] signature, PublicKey publicKey) throws Exception {
Signature sig = Signature.getInstance("MD5withRSA");
sig.initVerify(publicKey);
sig.update(data);
return sig.verify(signature);
}
/**
* Helper method to convert a byte array to a hexadecimal string.
*/
private static String bytesToHex(byte[] bytes) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : bytes) {
sb.append(String.format("%02x", b));
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
How to Run the Code:
- Save the code as
MD5withRSADemo.java. - Compile it:
javac MD5withRSADemo.java - Run it:
java MD5withRSADemo
Expected Output:
RSA Key Pair Generated.
Public Key: RSA Public Key, 2048 bits
modulus: 2484...
exponent: 65537
Private Key: RSA Private Key, 2048 bits
modulus: 2484...
private exponent: ...
----------------------------------------
Original Message: This is a secret message that needs to be signed.
Signature (Hex): 5d1a... (a long hex string)
----------------------------------------
Verification Result (Original Message): true
----------------------------------------
Tampered Message: This is a secret message that needs to be signed!!
Verification Result (Tampered Message): false
----------------------------------------As you can see, the verification succeeds for the original message but fails for the tampered one, demonstrating the core functionality.
Best Practices and Alternatives
Best Practices for Signing in General:
-
Use a Secure Hash Algorithm: Replace
MD5withSHA-256,SHA-384, orSHA-512.- To sign with
SHA-256and RSA, the algorithm name isSHA256withRSA. - Example:
Signature.getInstance("SHA256withRSA");
- To sign with
-
Use a Strong Key Size: For RSA, a key size of 2048 bits is the minimum recommended today. For long-term security, 3072 or 4096 bits is better.
-
Store Keys Securely: Never hardcode private keys in your source code. Use a secure keystore, such as a Java KeyStore (JKS) or the more modern PKCS#12 format, and protect it with a strong password.
-
Use Standard Libraries: Always use the
java.securitypackage. Do not try to implement cryptographic algorithms yourself.
How to Use a Modern Alternative (SHA256withRSA)
The code is almost identical. You only need to change the algorithm name.
// In the sign method:
// Signature signature = Signature.getInstance("MD5withRSA");
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance("SHA256withRSA"); // <-- CHANGE HERE
// In the verify method:
// Signature sig = Signature.getInstance("MD5withRSA");
Signature sig = Signature.getInstance("SHA256withRSA"); // <-- CHANGE HERE
This small change gives you a secure, industry-standard digital signature scheme suitable for new applications.