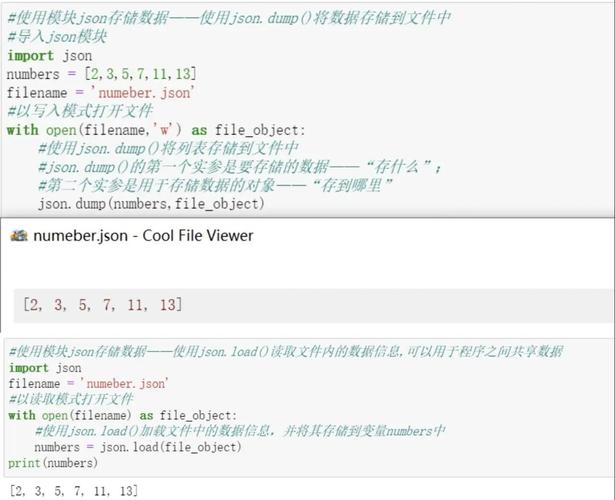
Python wordcloud 库详细文档
wordcloud 是一个非常流行且易于使用的 Python 库,它可以将文本数据中词语的频率信息可视化为一个“词云”图像,在词云图中,词语的大小、颜色和字体等视觉属性通常与它们在文本中出现的频率成正比,使得高频词一目了然。
安装
在使用之前,你需要先安装 wordcloud 库,推荐使用 pip 进行安装:
pip install wordcloud
为了支持中文分词,你还需要安装 jieba 库:
pip install jieba
wordcloud 依赖于一些图像处理库,如 Pillow 和 numpy,它们通常会在安装 wordcloud 时自动作为依赖项被安装,如果遇到问题,可以手动安装:
pip install Pillow numpy matplotlib
基本用法
1 从文本字符串生成词云
这是最基本的使用方式,你需要一个文本字符串,然后将其传递给 WordCloud 对象的 generate() 方法。
示例代码:
from wordcloud import WordCloud
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 1. 准备文本数据
text = """
Python is an interpreted, high-level and general-purpose programming language.
Python's design philosophy emphasizes code readability with its notable use of significant indentation.
As a general-purpose language, Python is used in many domains, from web development to data science and machine learning.
"""
# 2. 创建 WordCloud 对象
# 可以在这里设置一些基本参数,如宽度、高度、背景色等
wordcloud = WordCloud(width=800, height=400, background_color='white').generate(text)
# 3. 使用 matplotlib 显示词云图
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5)) # 创建一个图形窗口
plt.imshow(wordcloud, interpolation='bilinear') # 使用 bilinear 插值使图像更平滑
plt.axis("off") # 关闭坐标轴"Basic Word Cloud from Text")
plt.show()
代码解释:
text: 包含所有文本内容的字符串。WordCloud(...): 创建一个词云对象。width和height: 设置输出图像的尺寸。background_color: 设置背景颜色。
- **
.generate(text): 核心方法,接收文本字符串并计算词频,生成词云图像数据。 matplotlib.pyplot: 用于显示图像。plt.imshow(): 显示词云图像。interpolation='bilinear'可以让图像边缘更平滑。plt.axis("off"): 隐藏图像的坐标轴。
2 从词频字典生成词云
如果你已经计算好了词频(使用 collections.Counter),可以直接传入一个字典来生成词云,这比从长文本生成更高效。
示例代码:
from wordcloud import WordCloud
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 1. 准备词频字典
word_freq = {
'python': 50,
'language': 40,
'code': 35,
'data': 30,
'machine learning': 25,
'web': 20,
'science': 15,
'readability': 10
}
# 2. 创建 WordCloud 对象并生成词云
wordcloud = WordCloud(width=800, height=400, background_color='white').generate_from_frequencies(word_freq)
# 3. 显示图像
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
plt.imshow(wordcloud, interpolation='bilinear')
plt.axis("off")"Word Cloud from Frequencies")
plt.show()
代码解释:
generate_from_frequencies(word_freq): 这个方法直接接收一个字典,其中键是词语,值是对应的频率。
核心参数详解
WordCloud 类的构造函数有很多参数,通过调整它们可以定制词云的外观。
| 参数 | 类型 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
width |
int |
800 |
输出图像的宽度(像素)。 |
height |
int |
400 |
输出图像的高度(像素)。 |
background_color |
str |
'black' |
背景颜色,可以是颜色名称(如 'white')或十六进制码(如 '#FFFFFF')。 |
max_words |
int |
200 |
词云中显示的最大词语数量。 |
min_font_size |
int |
4 |
最小字体大小。 |
max_font_size |
int |
None |
最大字体大小,如果为 None,则根据图像高度自动确定。 |
scale |
float |
1 |
缩放比例,大于1的值会生成更高分辨率的图像,但生成速度更慢。 |
colormap |
str |
'viridis' |
词语的颜色方案,可以使用 Matplotlib 的所有 colormap 名称,如 'viridis', 'plasma', 'magma', 'cividis', 'coolwarm' 等。 |
relative_scaling |
float |
5 |
词大小与词频相关的敏感度。0 表示仅按排名,1 表示完全按频率。5 是一个不错的折中。 |
collocations |
bool |
True |
是否包括两个词的组合(bigrams),将 "machine learning" 视为一个整体。 |
colormap |
str |
'viridis' |
指定词语的颜色映射。'Set2', 'Pastel1'。 |
mask |
numpy.ndarray |
None |
一个掩码图像,词云将只在这个形状内生成。 |
contour_width |
int |
0 |
词云轮廓的宽度。 |
contour_color |
str |
'steelblue' |
词云轮廓的颜色。 |
示例:使用不同参数
from wordcloud import WordCloud
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
text = "Python python python data science machine learning python python code code code"
# 1. 默认词云
wc1 = WordCloud().generate(text)
# 2. 自定义参数的词云
wc2 = WordCloud(
width=600,
height=300,
background_color='white',
max_words=50,
colormap='plasma', # 使用不同的颜色方案
contour_width=3, # 添加轮廓
contour_color='firebrick'
).generate(text)
# 显示两个词云进行对比
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 7))
axes[0].imshow(wc1, interpolation='bilinear')
axes[0].axis("off")
axes[0].set_title("Default WordCloud")
axes[1].imshow(wc2, interpolation='bilinear')
axes[1].axis("off")
axes[1].set_title("Customized WordCloud")
plt.show()
高级用法
1 使用自定义形状(Mask)
通过提供一个掩码图像,你可以将词云塑造成任何你想要的形状,掩码图像通常是一个带有白色背景和黑色(或深色)形状的 PNG 图片。
步骤:
- 准备一张掩码图片(
mask_image.png)。 - 使用
Pillow或OpenCV将其读入为numpy数组。 - 将数组传递给
WordCloud的mask参数。
示例代码:
from wordcloud import WordCloud
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import os
# 确保你有一张名为 'mask.png' 的图片在同一目录下
# 这里我们用一个圆形作为示例,你可以替换成任何形状的图片
if not os.path.exists('mask.png'):
# 如果没有图片,我们创建一个简单的圆形掩码
x, y = np.ogrid[:300, :300]
mask = (x - 150) ** 2 + (y - 150) ** 2 > 130 ** 2
mask = 255 * mask.astype(int)
Image.fromarray(mask).save('mask.png')
# 1. 加载掩码
mask_img = np.array(Image.open("mask.png"))
# 2. 准备文本
text = "circle shape mask wordcloud python data visualization"
# 3. 创建 WordCloud 对象,传入 mask
wc = WordCloud(background_color="white", mask=mask_img, contour_width=1, contour_color='blue').generate(text)
# 4. 显示图像
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow(wc, interpolation='bilinear')
plt.axis("off")"WordCloud with Custom Mask")
plt.show()
2 处理中文文本
wordcloud 库本身不直接支持中文,因为它需要能正确处理中文字符的字体,处理中文文本的步骤如下:
- 使用
jieba进行分词:将连续的中文文本切分成单个词语。 - 指定中文字体路径:提供一个
.ttf或.otf格式的中文字体文件路径,wordcloud需要用它来渲染汉字。
示例代码:
import jieba
from wordcloud import WordCloud
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from collections import Counter
# 1. 准备中文文本
chinese_text = """
Python是一种广泛使用的高级编程语言,由吉多·范罗苏姆创造。
第一版发布于1991年,Python的设计哲学强调代码的可读性,
其语法清晰明了,使得程序员能够用更少的代码表达想法。
Python支持多种编程范式,包括面向对象、命令式、函数式和过程式编程。
它拥有强大的标准库和丰富的第三方库,在数据科学、人工智能、
Web开发、自动化脚本等领域都有广泛应用。
"""
# 2. 使用 jieba 进行分词
# jieba.cut() 返回一个生成器,需要用 join() 合并成一个字符串
words = jieba.cut(chinese_text)
word_str = " ".join(words)
# 3. 指定中文字体路径
# 你需要下载一个中文字体文件,'SimHei.ttf' (黑体)
# Windows 系统字体通常在 C:\Windows\Fonts 目录下
# macOS 系统字体通常在 /System/Library/Fonts 或 /Library/Fonts 目录下
# Linux 系统字体通常在 /usr/share/fonts 目录下
# 请将 'path/to/your/SimHei.ttf' 替换为你系统上实际存在的字体路径
font_path = "path/to/your/SimHei.ttf" # <--- 修改这里!
# 4. 生成词云
wc = WordCloud(
font_path=font_path, # 关键:指定中文字体
width=1000,
height=600,
background_color='white',
max_words=100
).generate(word_str)
# 5. 显示图像
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.imshow(wc, interpolation='bilinear')
plt.axis("off")"中文词云示例")
plt.show()
保存词云图像
生成词云后,你可以使用 to_file() 方法将其保存为图片文件。
示例代码:
# ... (前面的代码,生成了一个 wc 对象)
# 保存词云为 PNG 文件
wc.to_file("my_wordcloud.png")
print("词云已保存为 my_wordcloud.png")
完整工作流示例
下面是一个更完整的示例,展示了如何从网络文章的 URL 开始,抓取文本、分词、生成并保存词云。
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import jieba
from wordcloud import WordCloud
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from collections import Counter
# --- 1. 数据获取 (假设有一篇关于Python的文章) ---
# 这里用一个示例URL,实际使用时请替换为有效的URL
url = "https://www.python.org/doc/essays/" # Python官网的随笔页面,内容较多
try:
response = requests.get(url)
response.raise_for_status() # 如果请求失败则抛出异常
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
# 提取所有段落文本
paragraphs = soup.find_all('p')
full_text = ' '.join([p.get_text() for p in paragraphs])
if not full_text:
print("未能从页面提取到有效文本,请检查URL或页面结构。")
full_text = "Python 编程 语言 数据 科学 机器 学习 开发" # 备用文本
except Exception as e:
print(f"获取数据时出错: {e}")
full_text = "Python 编程 语言 数据 科学 机器 学习 开发" # 备用文本
# --- 2. 中文分词 ---
words = jieba.cut(full_text)
word_str = " ".join(words)
# --- 3. 过滤停用词 (可选但推荐) ---
# 你可以创建一个停用词列表文件 stopwords.txt
# 常见的停用词如:的,了,和,是,在,我,有...
try:
with open('stopwords.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
stopwords = set([line.strip() for line in f])
# 过滤掉停用词
words_filtered = [word for word in words if word not in stopwords and len(word) > 1]
word_str_filtered = " ".join(words_filtered)
except FileNotFoundError:
print("未找到停用词文件 stopwords.txt,将不过滤。")
word_str_filtered = word_str
# --- 4. 生成词云 ---
# 你需要下载一个中文字体文件,'SimHei.ttf'
# 请将 'path/to/your/SimHei.ttf' 替换为你系统上实际存在的字体路径
font_path = "path/to/your/SimHei.ttf" # <--- 修改这里!
wc = WordCloud(
font_path=font_path,
background_color="white",
width=1200,
height=800,
max_words=150,
contour_width=2,
contour_color='steelblue'
).generate(word_str_filtered)
# --- 5. 显示和保存 ---
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
plt.imshow(wc, interpolation='bilinear')
plt.axis("off")"Python 相关文章词云", fontsize=20)
# 保存图像
wc.to_file("python_article_wordcloud.png")
plt.show()
print("词云已生成并保存为 python_article_wordcloud.png")
wordcloud 库是一个功能强大且灵活的工具,能够快速将文本数据转化为直观的视觉图表,通过掌握其基本用法、核心参数以及高级功能(如自定义形状和中文处理),你可以轻松地在数据分析报告、博客文章或数据科学项目中使用它来突出文本中的关键信息。