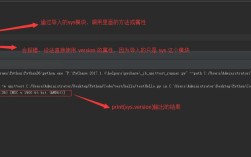
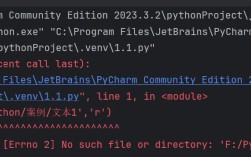
Of course! Let's dive deep into tkinter.messagebox, which is a standard module in Python's tkinter library for creating simple, pre-built dialog boxes.

What is tkinter.messagebox?
tkinter.messagebox provides a set of functions that create modal dialog boxes to display messages to the user and get a simple response. These are perfect for showing warnings, errors, information, or asking simple "Yes/No" questions.
A modal dialog box is one that blocks interaction with the main application window until it is closed. The user must respond to the message box before they can continue using the application.
How to Use It
First, you need to import the module. It's common practice to import it directly into your namespace for easier access.
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import messagebox
The Core Functions
tkinter.messagebox has several functions, each corresponding to a different type of dialog box. The most common ones are:
showinfo(): For displaying informational messages.showwarning(): For displaying warning messages.showerror(): For displaying error messages.askquestion(): For asking a question with "yes" and "no" answers.askokcancel(): For asking "OK" or "Cancel".askyesno(): For asking "Yes" or "No".askyesnocancel(): For asking "Yes", "No", or "Cancel".
Detailed Examples
Let's create a main window with buttons to trigger each type of message box.
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox
# --- Create the main window ---
root = tk.Tk()"Messagebox Examples")
root.geometry("300x200")
# --- Function to show different message boxes ---
def show_info():
"""Displays an information message box."""
messagebox.showinfo("Information", "This is an informational message.")
def show_warning():
"""Displays a warning message box."""
messagebox.showwarning("Warning", "This is a warning message!")
def show_error():
"""Displays an error message box."""
messagebox.showerror("Error", "An error has occurred!")
def ask_question():
"""Asks a question and returns 'yes' or 'no'."""
response = messagebox.askquestion("Question", "Do you like Python?")
if response == 'yes':
print("User likes Python!")
else:
print("User does not like Python.")
def ask_ok_cancel():
"""Asks 'OK' or 'Cancel' and returns a boolean."""
response = messagebox.askokcancel("Confirmation", "Do you want to proceed?")
if response:
print("User clicked OK. Proceeding...")
else:
print("User clicked Cancel. Aborting.")
def ask_yes_no():
"""Asks 'Yes' or 'No' and returns a boolean."""
response = messagebox.askyesno("Choice", "Do you want to save changes?")
if response:
print("Saving changes...")
else:
print("Discarding changes.")
def ask_yes_no_cancel():
"""Asks 'Yes', 'No', or 'Cancel' and returns a string."""
response = messagebox.askyesnocancel("Save", "Save before closing?")
if response == True: # Yes
print("Saving and closing...")
elif response == False: # No
print("Closing without saving...")
else: # Cancel
print("Operation cancelled.")
# --- Create buttons in the main window ---
btn_info = tk.Button(root, text="Show Info", command=show_info)
btn_info.pack(pady=5, padx=20, fill=tk.X)
btn_warning = tk.Button(root, text="Show Warning", command=show_warning)
btn_warning.pack(pady=5, padx=20, fill=tk.X)
btn_error = tk.Button(root, text="Show Error", command=show_error)
btn_error.pack(pady=5, padx=20, fill=tk.X)
btn_question = tk.Button(root, text="Ask Question", command=ask_question)
btn_question.pack(pady=5, padx=20, fill=tk.X)
btn_ok_cancel = tk.Button(root, text="Ask OK/Cancel", command=ask_ok_cancel)
btn_ok_cancel.pack(pady=5, padx=20, fill=tk.X)
btn_yes_no = tk.Button(root, text="Ask Yes/No", command=ask_yes_no)
btn_yes_no.pack(pady=5, padx=20, fill=tk.X)
btn_yes_no_cancel = tk.Button(root, text="Ask Yes/No/Cancel", command=ask_yes_no_cancel)
btn_yes_no_cancel.pack(pady=5, padx=20, fill=tk.X)
# --- Start the Tkinter event loop ---
root.mainloop()
Return Values and How to Use Them
The power of these dialog boxes comes from their return values, which you can use to control your program's logic.
| Function | Return Value(s) | Type | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|
showinfo |
None |
N/A | Just display information. |
showwarning |
None |
N/A | Just display a warning. |
showerror |
None |
N/A | Just display an error. |
askquestion |
'yes' or 'no' |
str |
Simple string-based branching. |
askokcancel |
True or False |
bool |
Confirming an action. |
askyesno |
True or False |
bool |
Making a binary choice. |
askyesnocancel |
True, False, or None |
bool or None |
Making a choice with a third option to abort. |
Key Point: askyesno and askokcancel return True for the positive/affirmative choice and False for the negative one. askyesnocancel adds None to represent the "Cancel" button.
Advanced Options
You can customize the message boxes further using optional keyword arguments.
Customizing the Title and Icon
title: Sets the text in the title bar of the dialog box.icon: Sets the icon displayed in the box. Common icons are:messagebox.INFO(ormessagebox.OK, the default)messagebox.WARNINGmessagebox.ERRORmessagebox.QUESTION
# Example with a custom title and icon
response = messagebox.askyesno("Important Decision",
message="Are you sure you want to delete this file?",
icon=messagebox.WARNING # Shows a warning icon
)
Customizing Buttons
-
type: Foraskyesnoand similar functions, you can change the default buttons.messagebox.OK(forshowinfo, etc.)messagebox.OKCANCELmessagebox.YESNOmessagebox.YESNOCANCELmessagebox.RETRYCANCELmessagebox.ABORTRETRYIGNORE
-
default: Sets which button is highlighted (focused) by default. This is great for accessibility and guiding the user.messagebox.OKmessagebox.CANCELmessagebox.YESmessagebox.NOmessagebox.RETRYmessagebox.IGNORE
Example: A "Save As" dialog where "Cancel" is the default choice, preventing accidental overwrites.
def save_as_dialog():
response = messagebox.askyesnocancel(
"Save As",
"File already exists. Overwrite?",
icon=messagebox.WARNING,
type=messagebox.YESNOCANCEL,
default=messagebox.CANCEL # Highlights "Cancel" by default
)
if response is None: # Cancel was pressed
print("Save operation cancelled.")
elif response: # Yes was pressed
print("Overwriting file...")
else: # No was pressed
print("Saving with a new name...")
# You would call this function from a menu or button
Summary Table
| Function | Purpose | Return Value | Common Icon |
|---|---|---|---|
showinfo() |
Display general information. | None |
INFO |
showwarning() |
Display a potential problem. | None |
WARNING |
showerror() |
Display a serious error. | None |
ERROR |
askquestion() |
Ask a question. | 'yes' or 'no' |
QUESTION |
askokcancel() |
Confirm an action. | True or False |
QUESTION |
askyesno() |
Ask a yes/no question. | True or False |
QUESTION |
askyesnocancel() |
Ask a yes/no/cancel question. | True, False, or None |
QUESTION |