Of course! Using Python to monitor a Redis instance is a common and powerful task. It allows you to build custom dashboards, trigger alerts, analyze usage patterns, or debug performance issues.
There are two primary approaches to monitoring Redis with Python:
- Polling: Your Python script periodically runs Redis commands (like
INFO,SLOWLOG,LATENCY DOCTOR) and processes the output. This is simple but has a slight delay. - Real-time Monitoring (Push): Your Python script subscribes to Redis's built-in publish/subscribe channels (like
__keyspace@<db>__:*and__keyevent@<db>__:*). This provides instant, event-driven notifications as things happen in Redis.
Let's explore both, starting with the most common and powerful method: Real-time Monitoring with Pub/Sub.
Method 1: Real-time Monitoring with Redis Pub/Sub
This is the most efficient way to monitor key events in real-time. Redis can publish messages on specific channels when certain events occur, and your Python client can subscribe to these channels.
Key Pub/Sub Channels for Monitoring
__keyspace@<db>__:<key_pattern>: Subscribe to notifications about keys in a specific database. For example,__keyspace@0__:*will get notifications for all keys in database 0. The messages are the command that was executed (e.g.,SET,DEL,EXPIRE).__keyevent@<db>__:<event_type>: Subscribe to notifications about events in a specific database. For example,__keyevent@0__:will get notifications for all events in database 0. The messages are the keys involved in the event (e.g., a key that was evicted, expired, or caused an error).
Example: Monitoring Key Set/Expire/Delete Events
Let's write a Python script that connects to Redis and prints a message every time a key is set, deleted, or expires in database 0.

Prerequisites:
First, you need to enable key notifications in your redis.conf file. Find the notify-keyspace-events directive and set it to the appropriate value.
KEA:K(Keyspace events),E(Keyevent events),g(Generic commands), (String commands),l(List commands),s(Set commands),h(Hash commands),z(Sorted set commands),x(Expired events),e(Evicted events).- For our example,
KEAis a good, comprehensive choice.
# In redis.conf notify-keyspace-events KEA
After changing the config, restart your Redis server.
Python Code (monitor_redis.py):
import redis
import time
def monitor_redis_events(host='localhost', port=6379, db=0):
"""
Connects to Redis and monitors key events (set, del, expire) in real-time.
"""
try:
# The decode_responses=True makes the returned strings human-readable
r = redis.StrictRedis(host=host, port=port, db=db, decode_responses=True)
# Check connection
r.ping()
print(f"Successfully connected to Redis at {host}:{port}, DB {db}")
print("Monitoring for key events... (Press Ctrl+C to stop)")
print("-" * 40)
# Create a Pub/Sub object
# We subscribe to two channels:
# 1. All generic commands (set, del, etc.) on all keys in DB 0
# 2. All expiration events in DB 0
p = r.pubsub()
# The pattern '*' matches all keys
p.psubscribe(f"__keyspace@{db}__:*")
p.psubscribe(f"__keyevent@{db}__:expired")
# The listen() method is a blocking loop that yields messages
for message in p.listen():
if message['type'] == 'pmessage':
# pmessage is for pattern subscriptions
channel = message['channel']
pattern = message['pattern']
data = message['data']
# __keyspace@<db>__:<key> messages contain the command
if channel.startswith('__keyspace@'):
key_name = channel.split(':')[-1]
print(f"[KEYSPACE] Key '{key_name}' was affected by command: {data.upper()}")
# __keyevent@<db>__:expired messages contain the key name
elif channel.endswith(':expired'):
print(f"[KEYEVENT] Key '{data}' has EXPIRED.")
except redis.ConnectionError as e:
print(f"Could not connect to Redis: {e}")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\nMonitoring stopped by user.")
finally:
if 'p' in locals():
p.close()
print("Connection closed.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
monitor_redis_events()
How to Run It:
-
Start Redis:
redis-server
-
Run the Python script in one terminal:
python monitor_redis.py
-
Interact with Redis in another terminal using the
redis-cli:# In another terminal redis-cli # Set a key SET mykey1 "hello world" # Set another key with an expiration SET mykey2 "temporary" EX 5 # Delete a key DEL mykey1 # Wait for mykey2 to expire (it will print a message in your Python script)
Expected Output in the Python script:
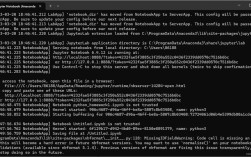
Successfully connected to Redis at localhost:6379, DB 0
Monitoring for key events... (Press Ctrl+C to stop)
----------------------------------------
[KEYSPACE] Key 'mykey1' was affected by command: SET
[KEYSPACE] Key 'mykey2' was affected by command: SET
[KEYSPACE] Key 'mykey1' was affected by command: DEL
[KEYEVENT] Key 'mykey2' has EXPIRED.Method 2: Polling for Statistics with the INFO Command
This method is less about real-time events and more about periodically collecting and reporting on the overall health and performance of your Redis instance. The INFO command is your best friend here.
Example: Polling Redis Stats and Printing a Summary
This script will connect to Redis, fetch the INFO stats, and print a summary of important metrics every 5 seconds.
Python Code (poll_redis_stats.py):
import redis
import time
import pprint
def get_redis_stats(host='localhost', port=6379, db=0):
"""
Connects to Redis and fetches server statistics.
"""
try:
r = redis.StrictRedis(host=host, port=port, db=db, decode_responses=True)
r.ping()
# Get the 'stats' section of the INFO command
info = r.info(section='stats')
return info
except redis.ConnectionError as e:
print(f"Could not connect to Redis: {e}")
return None
def print_stats_summary(stats):
"""
Prints a formatted summary of important Redis stats.
"""
if not stats:
return
print("\n--- Redis Stats Summary ---")
print(f"Total Connections: {stats.get('connected_clients', 'N/A')}")
print(f"Commands Processed (total): {stats.get('total_commands_processed', 'N/A')}")
print(f"Keyspace Hits: {stats.get('keyspace_hits', 'N/A')}")
print(f"Keyspace Misses: {stats.get('keyspace_misses', 'N/A')}")
# Calculate hit rate
hits = int(stats.get('keyspace_hits', 0))
misses = int(stats.get('keyspace_misses', 0))
if hits + misses > 0:
hit_rate = (hits / (hits + misses)) * 100
print(f"Cache Hit Rate: {hit_rate:.2f}%")
print(f"Evicted Keys: {stats.get('evicted_keys', 'N/A')}")
print(f"Expired Keys: {stats.get('expired_keys', 'N/A')}")
print("-" * 30)
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("Starting Redis stats poller. Press Ctrl+C to stop.")
while True:
stats = get_redis_stats()
print_stats_summary(stats)
time.sleep(5) # Poll every 5 seconds
How to Run It:
- Start Redis.
- Run the Python script:
python poll_redis_stats.py
- Interact with Redis in another terminal to see the numbers change.
Expected Output:
Starting Redis stats poller. Press Ctrl+C to stop.
--- Redis Stats Summary ---
Total Connections: 1
Commands Processed (total): 15
Keyspace Hits: 0
Keyspace Misses: 0
Cache Hit Rate: 0.00%
Evicted Keys: 0
Expired Keys: 0
------------------------------
--- Redis