Of course. Converting a long to an int in Java is a common task, but it's not as simple as a direct cast because you might lose data. Here’s a complete guide covering the different scenarios, from safe conversions to handling overflow.
The Short Answer: The Cast Operator (int)
The most direct way to convert a long to an int is to use the cast operator (int).
long longValue = 12345L; int intValue = (int) longValue; System.out.println(intValue); // Output: 12345
The Crucial Detail: Handling Overflow
The most important thing to understand is that an int has a limited range:
intrange: -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 (-2³¹ to 2³¹-1)longrange: -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 (-2⁶³ to 2⁶³-1)
A long can store numbers much larger (or smaller) than an int. When you use the cast (int) on a long whose value is outside the int range, something called integer overflow occurs.
What happens during overflow?
The long value is truncated to fit into the 32 bits of an int. The result is not an exception or an error; it's simply a "wrap-around" to the other end of the int range.
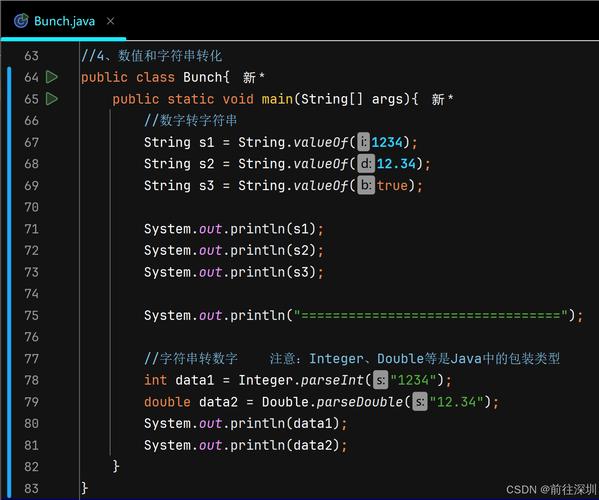
Example of Overflow
// A long value that is too large for an int
long longValueTooBig = 2147483650L; // This is > Integer.MAX_VALUE (2147483647)
// Using the cast operator
int intValue = (int) longValueTooBig;
// The value "wraps around"
System.out.println("Original long: " + longValueTooBig);
System.out.println("Casted int: " + intValue); // Output: -2147483638 (not 2147483650!)
As you can see, 2147483650 became -2147483638. This is often a bug and can lead to serious logic errors in your program.
Methods for Safe Conversion
Because of the risk of overflow, you should choose your conversion method carefully based on your requirements.
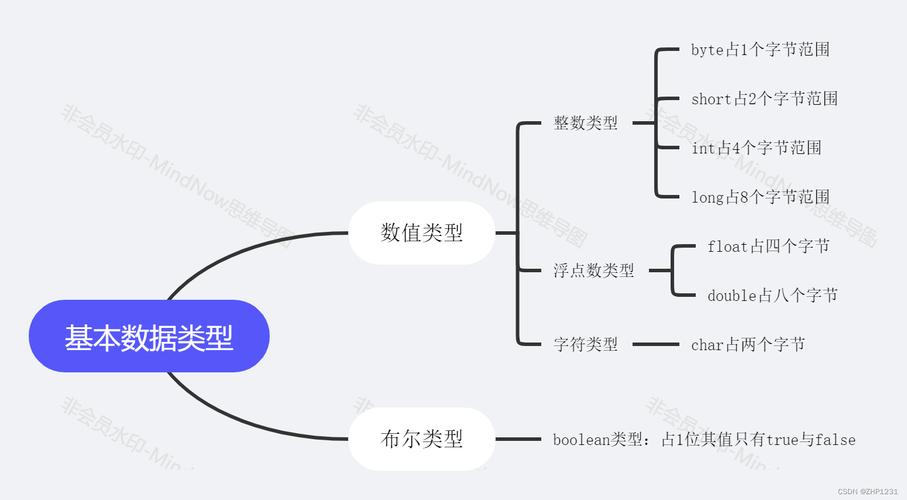
Using Math.toIntExact() (Java 8+)
This is the best method for a safe conversion where you expect the long to be within the int range. If the long value is outside the int range, it throws an ArithmeticException.
import java.lang.Math;
long safeLongValue = 100L;
int safeInt = Math.toIntExact(safeLongValue);
System.out.println(safeInt); // Output: 100
long overflowLongValue = 2147483648L; // Integer.MAX_VALUE + 1
try {
int overflowInt = Math.toIntExact(overflowLongValue);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("Caught expected exception: " + e.getMessage());
// Output: Caught expected exception: integer overflow
}
Use this when: You are certain the long will fit, and you want your program to fail explicitly with an exception if it doesn't.
Using Long.intValue()
This method is functionally identical to the cast operator (int). It performs a silent truncation and does not check for overflow.
Long longObject = 2147483650L; int intValue = longObject.intValue(); System.out.println(intValue); // Output: -2147483638 (same wrap-around as the cast)
Use this when: You are working with a Long object instead of a primitive long and you are intentionally handling the potential wrap-around yourself.
Manual Overflow Check
If you need to handle the overflow case yourself without throwing an exception, you can add a manual check before casting.
long longValue = 2147483650L;
int intValue;
if (longValue < Integer.MIN_VALUE || longValue > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
// Handle the overflow case
System.out.println("Error: Value is too large to fit in an int.");
intValue = 0; // or some other default/error value
} else {
// Safe to cast
intValue = (int) longValue;
System.out.println("Converted value: " + intValue);
}
Use this when: You need to provide custom logic or a fallback value when an overflow occurs.
Summary Table
| Method | Behavior | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
(int) myLong |
Silent Truncation/Wrap-around. If myLong is outside int range, it wraps around. |
When you are certain the value is in range, or when you explicitly want and understand the wrap-around behavior (e.g., in low-level bit manipulation). |
Math.toIntExact(myLong) |
Throws ArithmeticException if myLong is outside int range. |
Recommended for most cases. When you expect the value to be in range and want the program to fail fast and clearly if it's not. |
myLongObject.intValue() |
Silent Truncation/Wrap-around. Identical to the cast (int). |
When you have a Long object and want the same behavior as the primitive cast. |
| Manual Check | Custom Logic. You can decide what to do on overflow (e.g., return an error code, clamp the value). | When you need to handle overflow gracefully without crashing the application. |
Complete Example
Here is a full program demonstrating all the methods.
public class LongToIntConversion {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// A value that fits safely
long safeLong = 150000L;
// A value that overflows Integer.MAX_VALUE
long overflowLong = 2147483650L;
// A value that underflows Integer.MIN_VALUE
long underflowLong = -2147483650L;
System.out.println("--- Safe Value (150000L) ---");
System.out.println("Using (int): " + (int) safeLong);
System.out.println("Using Math.toIntExact: " + Math.toIntExact(safeLong));
System.out.println("Using Long.intValue(): " + new Long(safeLong).intValue());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("--- Overflow Value (2147483650L) ---");
// Using cast (silent truncation)
System.out.println("Using (int): " + (int) overflowLong);
// Using Math.toIntExact (throws exception)
try {
System.out.println("Using Math.toIntExact: " + Math.toIntExact(overflowLong));
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("Using Math.toIntExact: " + e.getMessage());
}
// Using manual check
System.out.print("Using manual check: ");
if (overflowLong < Integer.MIN_VALUE || overflowLong > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
System.out.println("Overflow detected! Value: " + overflowLong);
} else {
System.out.println("Converted value: " + (int) overflowLong);
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("--- Underflow Value (-2147483650L) ---");
// Using cast (silent truncation)
System.out.println("Using (int): " + (int) underflowLong);
// Using Math.toIntExact (throws exception)
try {
System.out.println("Using Math.toIntExact: " + Math.toIntExact(underflowLong));
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("Using Math.toIntExact: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Output of the program:
--- Safe Value (150000L) ---
Using (int): 150000
Using Math.toIntExact: 150000
Using Long.intValue(): 150000
--- Overflow Value (2147483650L) ---
Using (int): -2147483638
Using Math.toIntExact: integer overflow
Using manual check: Overflow detected! Value: 2147483650
--- Underflow Value (-2147483650L) ---
Using (int): 2147483646
Using Math.toIntExact: integer overflow