核心概念
在开始之前,我们先明确几个基本概念:
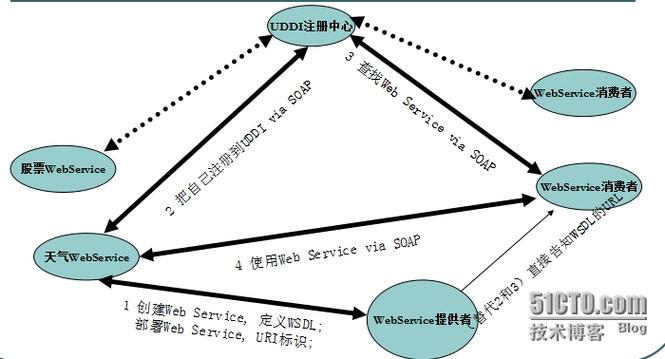
- Web Service (WS):一种跨编程语言、跨操作系统、跨网络的远程调用技术,通常基于 SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) 协议,使用 XML 格式进行数据交换。
- WSDL (Web Services Description Language):一个 XML 文件,用于描述 Web Service 的功能、接口、方法、参数、返回值以及如何访问它,它是客户端调用的“说明书”或“地图”。
- SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol):一种协议,用于在 Web 上交换结构化的和类型化的信息,SOAP 消息是 XML 格式的。
使用 JAX-WS (Java API for XML Web Services) - 最主流、推荐
JAX-WS 是 Java 官方推出的用于创建和调用 Web Service 的 API,它已经内置于 Java 标准库中(从 JDK 5 开始),这是目前 Java 开发中最常用、最标准的方法。
生成客户端代码
JAX-WS 提供了一个命令行工具 wsimport,它会根据 WSDL 文件自动生成一系列 Java 类(客户端存根/Stub),这些类封装了网络通信的细节,让你可以像调用本地方法一样调用远程的 Web Service。
如何使用 wsimport?
打开你的命令行(CMD 或 PowerShell),执行以下命令:
# 基本语法 wsimport -keep -p com.example.client -d . http://example.com/service?wsdl # 参数解释: # -keep: 生成源代码并保留,方便查看和调试。 # -p <package>: 指定生成类的包名,com.example.client。 # -d <dir>: 指定生成 .class 文件的输出目录,这里用 "." 表示当前目录。 # <wsdl-url>: Web Service 的 WSDL 文件地址。
执行成功后,你会得到一堆 .java 和 .class 文件,其中最重要的通常是一个名为 XXXService 的服务类和一个名为 XXX 的接口(HelloService 和 Hello)。
调用 Web Service
生成的代码中,XXXService 类有一个 getXXXPort() 方法,它会返回一个实现了 XXX 接口的代理对象,你只需要调用这个代理对象的方法即可。
示例代码:
假设我们根据一个天气预报的 WSDL 生成了 WeatherService 和 Weather 接口。
import com.example.client.Weather; // 生成的接口
import com.example.client.WeatherService; // 生成的服务类
public class JaxwsClientExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 创建服务 Service 实例
WeatherService service = new WeatherService();
// 2. 获取服务端点接口,这是一个代理对象
// getWeatherPort() 是根据 WSDL 生成的
Weather port = service.getWeatherPort();
try {
// 3. 像调用本地方法一样调用远程方法
String cityName = "北京";
String weatherInfo = port.getWeather(cityName); // 假设 getWeather 是 WSDL 中定义的方法
// 4. 处理返回结果
System.out.println("查询城市: " + cityName);
System.out.println("天气信息: " + weatherInfo);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
使用 Apache CXF - 功能强大、灵活
Apache CXF 是一个开源的 Services 框架,它支持多种 Web Service 标准,包括 SOAP、RESTful HTTP Services、WS-* 等,它比 JAX-WS 更灵活,支持更多高级特性,并且可以轻松集成到 Spring 框架中。
添加依赖
在你的 Maven pom.xml 文件中添加 CXF 的依赖:
<dependencies>
<!-- CXF 核心依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.cxf</groupId>
<artifactId>cxf-rt-frontend-jaxws</artifactId>
<version>3.4.5</version> <!-- 使用最新稳定版 -->
</dependency>
<!-- CXF 的 Jetty 服务器依赖 (如果需要作为服务器端运行) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.cxf</groupId>
<artifactId>cxf-rt-transports-http-jetty</artifactId>
<version>3.4.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
调用 Web Service
CXF 同样可以使用 wsimport(或其自己的 cxf-wsdl2java)来生成客户端代码,调用方式与 JAX-WS 几乎一样。
更重要的是,CXF 提供了更简洁的 无客户端代码 的调用方式,通过动态代理实现。
示例代码 (动态代理):
import org.apache.cxf.jaxws.JaxWsProxyFactoryBean;
import com.example.client.Weather; // 假设你已经有这个接口,或者从 WSDL 手动定义
public class CxfClientExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 创建 JaxWsProxyFactoryBean 实例
JaxWsProxyFactoryBean factory = new JaxWsProxyFactoryBean();
// 2. 设置服务接口
factory.setServiceClass(Weather.class);
// 3. 设置 Web Service 的地址
factory.setAddress("http://localhost:8080/weather?wsdl");
// 4. 创建客户端代理对象
Weather weatherService = factory.create(Weather.class);
// 5. 调用方法
try {
String result = weatherService.getWeather("上海");
System.out.println("上海天气: " + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
优点:
- 无需生成代码:直接通过接口和地址创建代理,非常方便。
- 集成度高:与 Spring 框架无缝集成,可以轻松将 Web Service 声明为 Bean。
- 功能丰富:支持 WS-Security, WS-Addressing 等企业级特性。
使用 Spring Boot + WebServiceTemplate - 现代化、Spring 生态首选
如果你正在使用 Spring Boot,WebServiceTemplate 是最佳选择,它由 Spring Framework 提供,为调用 Web Service 提供了模板化的操作,类似于 RestTemplate 对于 RESTful API。
添加依赖
在 Spring Boot 项目的 pom.xml 中添加:
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring WebService -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web-services</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- CXF 支持可选,但推荐 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.cxf</groupId>
<artifactId>cxf-spring-boot-starter-jaxws</artifactId>
<version>3.4.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
配置和调用
示例代码:
import org.springframework.oxm.jaxb.Jaxb2Marshaller;
import org.springframework.ws.client.core.WebServiceTemplate;
import org.springframework.ws.soap.client.core.SoapActionCallback;
// 你的请求和响应对象 (JAXB 注解的 POJO)
// import com.example.weatherschema.GetWeatherRequest;
// import com.example.weatherschema.GetWeatherResponse;
@Service
public class WeatherClient {
private final WebServiceTemplate webServiceTemplate;
// 通过构造器注入,推荐
public WeatherClient() {
Jaxb2Marshaller marshaller = new Jaxb2Marshaller();
// 设置要生成的包名,这个包名需要和 WSDL 中定义的 targetNamespace 一致
marshaller.setPackagesToScan("com.example.weatherschema");
this.webServiceTemplate = new WebServiceTemplate(marshaller);
}
public String getWeather(String city) {
// 1. 创建请求对象
// GetWeatherRequest request = new GetWeatherRequest();
// request.setCityName(city);
// 2. 定义消息的 URI (通常对应 WSDL 中的 portType 和 operation)
String uri = "http://example.com/weather/GetWeather";
// 3. 设置 SOAP Action (非常重要!通常在 WSDL 中定义)
String soapActionUri = "http://example.com/weather/GetWeatherRequest";
// 4. 发送请求并获取响应
// GetWeatherResponse response = (GetWeatherResponse) webServiceTemplate
// .marshalSendAndReceive(uri, request, new SoapActionCallback(soapActionUri));
// return response.getWeatherInfo();
// 为了简化,这里展示一个更通用的调用方式
// 实际项目中,你需要根据 WSDL