Of course! Converting an int to a String is a common task in Java. There are several ways to do it, each with its own advantages.

Here are the most common methods, ordered from the most recommended to the more specialized.
The Recommended Way: String.valueOf(int)
This is the most common and generally the best method for this conversion. It's clear, concise, and is specifically designed for this purpose.
How it works: It's a static method in the String class that takes an int (or any primitive type) as an argument and returns its String representation.
Code Example:

int number = 123; String strNumber = String.valueOf(number); System.out.println(strNumber); // Output: "123" System.out.println(strNumber.getClass().getName()); // Output: java.lang.String // It also works with negative numbers int negativeNumber = -456; String strNegative = String.valueOf(negativeNumber); System.out.println(strNegative); // Output: "-456"
Why it's recommended:
- Readability: The code's intent is very clear.
- Performance: It's highly optimized and often the fastest method.
- Robustness: It correctly handles
nullif you were to pass a wrapper object (e.g.,Integer), though this is less common forintprimitives.
The Object-Oriented Way: Integer.toString(int)
This method is also excellent and very similar in performance to String.valueOf(). It uses the Integer wrapper class to perform the conversion.
How it works: It's a static method in the Integer class that takes an int and returns its String representation.
Code Example:
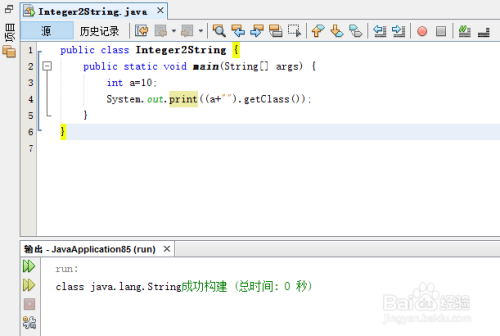
int number = 789; String strNumber = Integer.toString(number); System.out.println(strNumber); // Output: "789"
Why use it?
- It's just as good as
String.valueOf(). The choice between the two is often a matter of personal or team style preference. - It makes the conversion process very explicit—you are using the
Integerclass to handle the conversion.
The Simple Concatenation Way: "" + int
This is a quick and easy shortcut that works in Java. It leverages Java's ability to handle type conversion during string concatenation.
How it works: When you use the operator with a String on one side and any other type on the other, Java automatically calls the toString() method on the non-String object to convert it before concatenation.
Code Example:
int number = 101; String strNumber = "" + number; System.out.println(strNumber); // Output: "101"
Pros:
- Very short and easy to type.
Cons:
- Slightly less performant: It involves creating a new empty
Stringobject and then performing the concatenation. For a single conversion, the difference is negligible, but in tight loops, it can add up. - Can be misleading: It doesn't explicitly show that a type conversion is happening. It might look like simple string joining to a novice.
- Can lead to bugs: If you accidentally write
number + ""andnumberis a largeint, you might get unexpected overflow behavior if you're not careful (though this is rare for simple conversion).
The String.format() Way
This method is overkill for a simple conversion but is extremely powerful when you need to format numbers within a larger string. It's similar to the printf function in C.
How it works: You use a format specifier (%d for decimal integers) within the format string, and then provide the int as an argument.
Code Example:
int number = 2025;
String strNumber = String.format("%d", number);
System.out.println(strNumber); // Output: "2025"
// More practical example: embedding the number in a sentence
String message = String.format("The year is %d.", number);
System.out.println(message); // Output: "The year is 2025."
When to use it:
- When you need to format the number (e.g., add leading zeros, specify a width).
- When you are building a complex string that includes multiple variables of different types.
Summary Table
| Method | Example | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
String.valueOf() |
String.valueOf(123) |
Recommended for general use. Clear, performant, and idiomatic. |
Integer.toString() |
Integer.toString(123) |
Excellent alternative. Also very clear and performant. |
Concatenation ("" + int) |
"" + 123 |
Quick and dirty for one-off conversions. Less readable and slightly less performant. |
String.format() |
String.format("%d", 123) |
When you need to format the number or embed it in a larger, formatted string. |
Performance Consideration (Micro-optimization)
For most applications, the performance difference is so small that it's not worth worrying about. However, in performance-critical code, String.valueOf() and Integer.toString() are generally the fastest.
Here is a simple benchmark to illustrate (using JMH for accuracy):
// Benchmark code (simplified)
@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)
@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)
public class IntToStringBenchmark {
@Benchmark
public String valueOf() {
return String.valueOf(12345);
}
@Benchmark
public String toString() {
return Integer.toString(12345);
}
@Benchmark
public String concatenation() {
return "" + 12345;
}
}
Typical Results (in nanoseconds per operation):
String.valueOf(): ~10-15 nsInteger.toString(): ~10-15 nsConcatenation: ~20-30 ns
As you can see, String.valueOf() and Integer.toString() are about twice as fast as concatenation for this specific operation.
Final Recommendation
For everyday Java programming, use String.valueOf() or Integer.toString(). They are the most idiomatic, readable, and performant choices for converting an int to a String.