Of course! Converting an Excel file to an HTML table in Java is a common task. There are several excellent libraries available to achieve this. I'll cover the two most popular and robust options:

- Apache POI: The industry standard for handling Microsoft Office files (
.xls,.xlsx). It's powerful but can be more verbose. - EasyExcel: A modern library from Alibaba, built on top of POI. It's significantly simpler and faster, especially for reading, and is the recommended choice for most new projects.
Method 1: Using Apache POI (The Classic Approach)
Apache POI is a comprehensive library that gives you fine-grained control over the Excel file.
Step 1: Add Dependencies
You need to add the Apache POI dependencies to your project. For a modern .xlsx file, you need the ooxml library.
Maven (pom.xml):
<dependencies>
<!-- For processing .xlsx files -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>5.2.5</version> <!-- Use the latest version -->
</dependency>
<!-- For processing .xls files (optional, if you need legacy support) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>5.2.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Gradle (build.gradle):
implementation 'org.apache.poi:poi-ooxml:5.2.5' // Use the latest version implementation 'org.apache.poi:poi:5.2.5' // Optional, for legacy .xls files
Step 2: Java Code
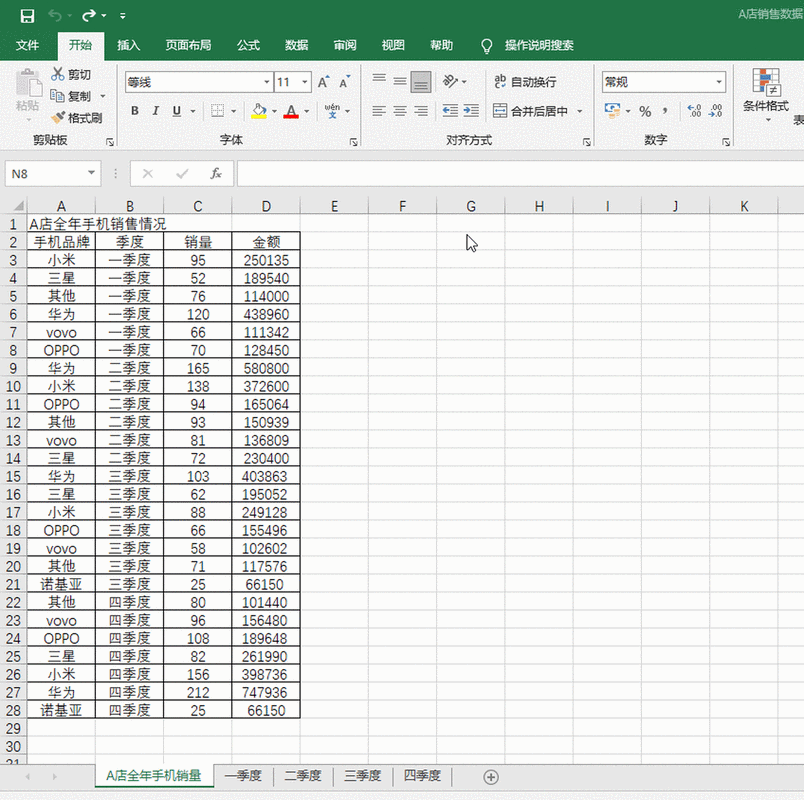
This code will read the first sheet of an Excel file and convert it into an HTML string.
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ExcelToHtmlWithPoi {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String excelFilePath = "path/to/your/input.xlsx";
String htmlOutput = convertExcelToHtml(excelFilePath);
System.out.println(htmlOutput);
// You can now write the htmlOutput string to a file
// Files.write(Paths.get("output.html"), htmlOutput.getBytes());
}
public static String convertExcelToHtml(String excelFilePath) {
StringBuilder html = new StringBuilder();
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(excelFilePath);
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fis)) {
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0); // Get the first sheet
// Start building the HTML table
html.append("<table border='1'>\n");
// Iterate over rows
for (Row row : sheet) {
html.append("<tr>\n");
// Iterate over cells in the current row
for (Cell cell : row) {
html.append("<td>");
// Get cell value and handle different types
switch (cell.getCellType()) {
case STRING:
html.append(cell.getStringCellValue());
break;
case NUMERIC:
if (DateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)) {
html.append(cell.getDateCellValue().toString());
} else {
html.append(cell.getNumericCellValue());
}
break;
case BOOLEAN:
html.append(cell.getBooleanCellValue());
break;
case FORMULA:
// Evaluating a formula can be complex. Here we just get the cached value.
html.append(cell.getCachedFormulaResultString());
break;
case BLANK:
html.append(" "); // Non-breaking space for empty cells
break;
default:
html.append("UNKNOWN");
}
html.append("</td>\n");
}
html.append("</tr>\n");
}
html.append("</table>");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return "<p>Error reading Excel file: " + e.getMessage() + "</p>";
}
return html.toString();
}
}
Pros:
- Extremely powerful and feature-rich.
- Supports both legacy
.xlsand modern.xlsxformats. - Gives you access to all cell-level formatting (though not used in the simple example above).
Cons:
- Can be verbose for simple tasks.
- Can be memory-intensive for very large files.
Method 2: Using EasyExcel (Recommended & Modern Approach)
EasyExcel is designed for high performance and ease of use. It uses a SAX (Event) model for reading, which makes it much more memory-efficient than POI's DOM model.
Step 1: Add Dependencies
You only need one main dependency from EasyExcel.
Maven (pom.xml):
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>easyexcel</artifactId>
<version>3.3.2</version> <!-- Use the latest version -->
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Gradle (build.gradle):
implementation 'com.alibaba:easyexcel:3.3.2' // Use the latest version
Step 2: Java Code
EasyExcel works by using a "listener" that gets called as it reads the file row by row. This approach is very clean and efficient.
import com.alibaba.excel.EasyExcel;
import com.alibaba.excel.context.AnalysisContext;
import com.alibaba.excel.event.AnalysisEventListener;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.metadata.ReadRowHolder;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ExcelToHtmlWithEasyExcel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String excelFilePath = "path/to/your/input.xlsx";
String htmlOutput = convertExcelToHtml(excelFilePath);
System.out.println(htmlOutput);
// You can now write the htmlOutput string to a file
// Files.write(Paths.get("output.html"), htmlOutput.getBytes());
}
public static String convertExcelToHtml(String excelFilePath) {
StringBuilder html = new StringBuilder();
html.append("<table border='1'>\n");
// Use a listener to process data as it's read
EasyExcel.read(excelFilePath)
.sheet() // Read the first sheet by default
.headRowNumber(0) // The first row is the header
.registerReadListener(new AnalysisEventListener<List<String>>() {
private boolean isHeaderProcessed = false;
@Override
public void invoke(List<String> data, AnalysisContext context) {
// The first invoke is the header row
if (!isHeaderProcessed) {
html.append("<tr>\n");
for (String header : data) {
html.append("<th>").append(header != null ? header : " ").append("</th>\n");
}
html.append("</tr>\n");
isHeaderProcessed = true;
} else {
// Subsequent invokes are data rows
html.append("<tr>\n");
for (String cellValue : data) {
html.append("<td>").append(cellValue != null ? cellValue : " ").append("</td>\n");
}
html.append("</tr>\n");
}
}
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext context) {
// This method is called after all data is read
System.out.println("Excel file parsing completed.");
}
})
.doRead(); // Start reading
html.append("</table>");
return html.toString();
}
}
Note: The EasyExcel.read() method with a file path is convenient. For more control, you can use EasyExcel.read(inputStream, ...).
Pros:
- Much simpler and more readable code.
- Extremely memory-efficient, ideal for large Excel files (e.g., millions of rows).
- High performance.
- Actively maintained by Alibaba.
Cons:
- Primarily focused on reading, not writing (though it has writing capabilities).
- The event-driven model can be slightly less intuitive for simple, one-off scripts than POI's direct object model.
Comparison and Recommendation
| Feature | Apache POI | EasyExcel |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Verbose, more complex | Simple, clean, and intuitive |
| Performance | Good, but can be slow for huge files (DOM model) | Excellent (SAX model), very fast and low-memory |
| Memory Usage | High (loads entire file into memory) | Very Low (processes row-by-row) |
| Features | Extremely comprehensive (formatting, charts, etc.) | Focused on high-performance reading/writing |
| Best For | Complex tasks requiring deep Excel manipulation | Most use cases, especially large files |
Recommendation:
For almost all new projects, start with EasyExcel. It's faster, uses less memory, and the code is much easier to write and maintain. Use Apache POI only if you have specific, advanced requirements that EasyExcel doesn't cover, such as manipulating embedded charts or complex cell styles.
Important Considerations
- File Paths: Replace
"path/to/your/input.xlsx"with the actual path to your Excel file. Using an absolute path is often easier for testing. - Styling: Both examples above produce a basic HTML table. Excel files contain rich formatting (fonts, colors, borders, merged cells). Replicating this perfectly in HTML is complex. Libraries like POI provide access to this styling data, but you would need to write additional logic to translate CSS styles.
- Merged Cells: Handling merged cells correctly requires extra logic. You need to track which cells are part of a merged region and ensure the
colspanorrowspanattributes are set correctly in the HTML<td>tag. This is a significant challenge with both libraries. A simpler approach is to just repeat the value of the merged cell into each of the constituent cells. - Encoding: When writing the HTML string to a file, ensure you use the correct character encoding (e.g.,
StandardCharsets.UTF_8) to prevent issues with special characters.