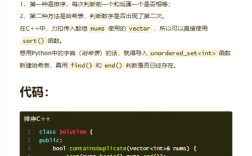
- 前端(客户端):如何构建一个包含图片的 HTML 表单。
- 后端(服务器):如何使用 Java(如 Servlet 或 Spring Boot)接收并处理这个图片。
我会分步讲解,并提供完整的代码示例。

核心概念:multipart/form-data
当表单中包含文件(如图片)时,不能使用普通的 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 编码方式,必须使用 multipart/form-data 编码类型。
enctype="multipart/form-data": 这个属性告诉浏览器,表单数据需要被分割成多个部分(multipart)进行编码,每个部分对应一个表单字段(包括文本字段和文件字段)。<input type="file">: 这个 HTML 标签用于创建一个文件选择框,让用户可以从本地选择文件。
第一步:前端表单代码 (HTML)
创建一个简单的 HTML 页面,用于选择图片并提交,关键点在于表单的 method 和 enctype 属性。
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">图片上传示例</title>
<style>
body { font-family: sans-serif; margin: 2em; }
form { border: 1px solid #ccc; padding: 20px; border-radius: 5px; }
input[type="file"] { margin-bottom: 10px; }
input[type="submit"] { background-color: #4CAF50; color: white; padding: 10px 15px; border: none; border-radius: 4px; cursor: pointer; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>提交图片表单</h2>
<!--
action: 指定表单提交到的服务器地址 (URL)
method: 必须是 POST,因为文件数据量很大,不能放在 URL 中
enctype: 必须是 multipart/form-data,用于上传文件
-->
<form action="/upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<!--
name 属性非常重要,后端将根据这个名称来获取文件
可以添加 accept 属性来限制可选的文件类型
-->
<label for="imageFile">选择图片:</label>
<input type="file" id="imageFile" name="imageFile" accept="image/*" required>
<br><br>
<!-- 可以同时提交其他文本字段 -->
<label for="description">图片描述:</label>
<input type="text" id="description" name="description">
<br><br>
<input type="submit" value="上传图片">
</form>
</body>
</html>
第二步:后端处理 (Java)
后端处理 multipart/form-data 数据比处理普通表单要复杂,因为它需要解析被分割成多块的数据流,幸运的是,有很多优秀的库可以帮助我们简化这个过程。

我们将介绍两种主流的后端技术:传统的 Servlet 和更现代的 Spring Boot。
使用传统 Servlet (需要额外依赖)
Servlet API 本身不提供解析 multipart 数据的工具,所以我们需要引入第三方库,最常用的是 Apache Commons FileUpload。
添加依赖 (Maven)
在你的 pom.xml 文件中添加以下依赖:
<dependencies>
<!-- Servlet API -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Apache Commons FileUpload -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Commons IO 是 FileUpload 的可选依赖,但强烈推荐 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.11.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
创建上传目录
在你的项目 webapp 目录下(src/main/webapp/uploads/)创建一个用于存放上传文件的目录,确保你的应用服务器(如 Tomcat)对该目录有读写权限。
编写 Servlet 代码
创建一个 Servlet 来处理 /upload 路径的请求。
ImageUploadServlet.java
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileItem;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.disk.DiskFileItemFactory;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.servlet.ServletFileUpload;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.List;
@WebServlet("/upload") // 映射和 HTML 中 action 属性相同的 URL
public class ImageUploadServlet extends HttpServlet {
// 上传文件存储目录
private static final String UPLOAD_DIRECTORY = "uploads";
// 设置上传文件的最大大小 (5MB)
private static final int MAX_MEMORY_SIZE = 1024 * 1024 * 5;
private static final int MAX_REQUEST_SIZE = 1024 * 1024 * 50; // 50MB
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 检查是否为 multipart/form-data 请求
if (!ServletFileUpload.isMultipartContent(req)) {
// 如果不是,则停止并返回错误信息
PrintWriter writer = resp.getWriter();
writer.println("Error: 表单必须包含 enctype=multipart/form-data");
writer.flush();
return;
}
// 配置上传参数
DiskFileItemFactory factory = new DiskFileItemFactory();
// 设置内存临界值 - 超过后将产生临时文件存储于临时目录
factory.setSizeThreshold(MAX_MEMORY_SIZE);
// 设置临时存储目录
factory.setRepository(new File(System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir")));
ServletFileUpload upload = new ServletFileUpload(factory);
// 设置最大文件上传值
upload.setSizeMax(MAX_REQUEST_SIZE);
// 构造上传后的文件保存目录
String uploadPath = getServletContext().getRealPath("") + File.separator + UPLOAD_DIRECTORY;
File uploadDir = new File(uploadPath);
if (!uploadDir.exists()) {
uploadDir.mkdir();
}
try {
// 解析请求的内容, 提取文件项
List<FileItem> formItems = upload.parseRequest(req);
if (formItems != null && formItems.size() > 0) {
for (FileItem item : formItems) {
// 处理不在表单中的字段
if (item.isFormField()) {
String name = item.getFieldName();
String value = item.getString("UTF-8"); // 指定编码,防止中文乱码
System.out.println("表单字段: " + name + ", 值: " + value);
}
// 处理上传的文件
else {
String fileName = new File(item.getName()).getName();
String filePath = uploadPath + File.separator + fileName;
File storeFile = new File(filePath);
// 在控制台输出上传文件的路径
System.out.println("文件上传到: " + filePath);
// 保存文件到硬盘
item.write(storeFile);
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
resp.getWriter().println("<h1>文件 '" + fileName + "' 上传成功!</h1>");
}
}
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
resp.getWriter().println("文件上传失败: " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
使用 Spring Boot (更简单、推荐)
Spring Boot 内置了对文件上传的完美支持,我们几乎不需要写任何解析代码,非常方便。
创建 Spring Boot 项目
你可以使用 Spring Initializr 快速创建一个项目,选择以下依赖:
- Spring Web: 用于构建 Web 应用。
- Spring Boot DevTools: (可选) 用于热部署。
配置上传参数
在 src/main/resources/application.properties 或 application.yml 文件中配置文件上传的相关设置。
application.properties
# 设置单个文件的最大大小 (5MB) spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=5MB # 设置总请求的最大大小 (50MB) spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=50MB # (可选) 设置临时文件存放目录 # spring.servlet.multipart.location=/tmp
编写 Controller 代码
创建一个 Controller 来处理文件上传。
FileUploadController.java
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.UUID;
@Controller
public class FileUploadController {
// 定义一个上传文件的目录,可以在项目根目录下创建一个 "uploads" 文件夹
private static final String UPLOADED_FOLDER = "uploads/";
@PostMapping("/upload") // 映射和 HTML 中 action 属性相同的 URL
@ResponseBody // 直接返回字符串作为响应体
public String handleFileUpload(@RequestParam("imageFile") MultipartFile file,
@RequestParam("description") String description) {
if (file.isEmpty()) {
return "请选择一个文件上传";
}
try {
// 创建上传目录(如果不存在)
Path uploadPath = Paths.get(UPLOADED_FOLDER);
if (!Files.exists(uploadPath)) {
Files.createDirectories(uploadPath);
}
// 为了防止文件名冲突,生成一个唯一的文件名
String originalFilename = file.getOriginalFilename();
String fileExtension = originalFilename.substring(originalFilename.lastIndexOf("."));
String newFilename = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + fileExtension;
// 构建目标文件路径
Path destination = uploadPath.resolve(newFilename);
// 将文件保存到目标路径
Files.copy(file.getInputStream(), destination);
System.out.println("接收到描述: " + description);
System.out.println("文件 '" + newFilename + "' 上传成功!");
return "文件上传成功! 文件名: " + newFilename;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return "文件上传失败: " + e.getMessage();
}
}
}
总结与对比
| 特性 | 传统 Servlet (Apache Commons FileUpload) | Spring Boot |
|---|---|---|
| 依赖 | 需要手动添加 commons-fileupload 等依赖 |
内置支持,只需 spring-boot-starter-web |
| 配置 | 需要编写大量 Java 代码来解析 FileItem |
通过 application.properties 简单配置 |
| 代码量 | 多,逻辑复杂(创建工厂、解析请求、写入文件) | 少,非常简洁(@RequestParam 直接获取 MultipartFile) |
| 灵活性 | 非常灵活,可以精细控制上传的每一个环节 | 框架封装了很多细节,灵活性稍低,但通常足够用 |
| 推荐度 | 适用于旧项目或不想引入 Spring 框架的场景 | 强烈推荐,是现代 Java Web 开发的标准选择 |
对于新的项目,毫无疑问应该选择 Spring Boot,它能让你从繁琐的底层解析工作中解放出来,更专注于业务逻辑,而对于学习或者维护老系统,了解 Servlet + Commons FileUpload 的方式也很有必要。