Of course! Converting a String to a char in Java is a common task, but it's important to understand the distinction between converting a single-character string and getting a character from a specific position within a multi-character string.
Here’s a complete guide covering all the scenarios.
Quick Answer: The Most Common Case
If you have a String that contains only one character and you want to get it as a char:
String myString = "A"; // A string with a single character // The most direct way char myChar = myString.charAt(0); System.out.println(myChar); // Output: A
Detailed Explanation with Examples
Let's break down the different methods and their use cases.
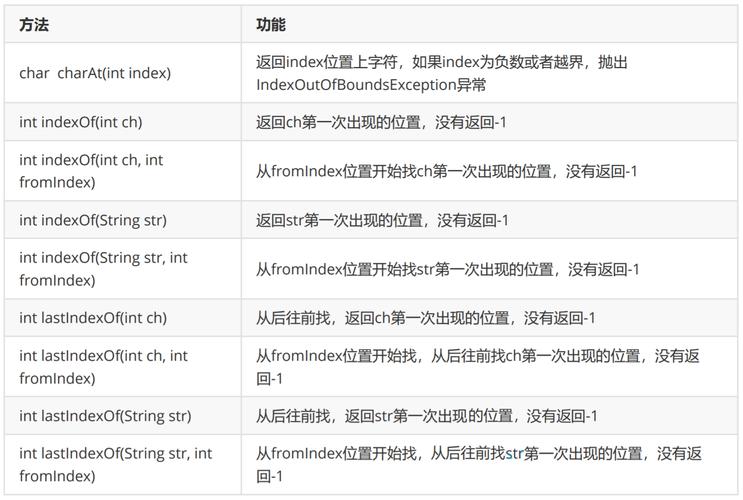
Method 1: charAt(int index) - The Standard Way
This is the most common and direct method. It retrieves the char value at a specific index (position) in the String.

Key Points:
- Indexing starts at 0. The first character is at index 0, the second at index 1, and so on.
- It works for strings of any length, not just single-character strings.
- It will throw an
StringIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionif you try to access an index that doesn't exist (e.g.,charAt(5)on a 5-character string, since the last valid index is 4).
Example: Getting a Character from a Position
String text = "Hello, World!";
// Get the first character 'H'
char firstChar = text.charAt(0);
System.out.println("First character: " + firstChar); // Output: First character: H
// Get the 7th character 'W' (index 6)
char seventhChar = text.charAt(6);
System.out.println("Seventh character: " + seventhChar); // Output: Seventh character: W
// Get the last character '!'
int lastIndex = text.length() - 1;
char lastChar = text.charAt(lastIndex);
System.out.println("Last character: " + lastChar); // Output: Last character: !
Example: Handling Errors
If you try to access an invalid index, your program will crash.
String shortText = "Hi";
try {
// This will cause an error because index 2 is out of bounds
char badChar = shortText.charAt(2);
} catch (StringIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("Error: Index is out of bounds!");
}
// Output: Error: Index is out of bounds!
Method 2: toCharArray() - When You Need All Characters
If you need to convert the entire String into an array of chars, this is the best method.
Key Points:
- It returns a
char[](a character array). - It's very useful for iterating over every character in a string.
Example: Converting the Whole String to a Char Array
String text = "Java";
char[] charArray = text.toCharArray();
// Now you can access any character using the array index
System.out.println(charArray[0]); // Output: J
System.out.println(charArray[1]); // Output: a
// You can also iterate over the array easily
for (char c : charArray) {
System.out.println(c);
}
/* Output:
J
a
v
a
*/
Method 3: String.valueOf(char c) - The Reverse Conversion
This method is for converting a char back into a String. It's the opposite of what you asked, but it's good to know.
char myChar = 'Z'; String myString = String.valueOf(myChar); System.out.println(myString); // Output: Z System.out.println(myString.getClass().getSimpleName()); // Output: String
Handling Edge Cases and Best Practices
What if the String is Empty?
If you try to call charAt(0) on an empty string (), you will get a StringIndexOutOfBoundsException.
String emptyString = "";
try {
char c = emptyString.charAt(0);
} catch (StringIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("Cannot get char from an empty string!");
}
// Output: Cannot get char from an empty string!
Best Practice: Always check if the string is empty or null before trying to access a character.
String myString = "A"; // or myString = ""; or myString = null;
if (myString != null && !myString.isEmpty()) {
char myChar = myString.charAt(0);
System.out.println("The character is: " + myChar);
} else {
System.out.println("The string is null or empty.");
}
What if the String Has More Than One Character?
charAt(index) will simply return the character at that specific position. It will not throw an error for a multi-character string.
String longString = "Java"; char firstChar = longString.charAt(0); // 'J' System.out.println(firstChar);
Summary Table
| Method | What It Does | Return Type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
charAt(int index) |
Gets the char at a specific position. |
char |
str.charAt(0) |
toCharArray() |
Converts the entire String into an array of chars. |
char[] |
str.toCharArray() |
String.valueOf(char c) |
Converts a char into a String. |
String |
String.valueOf('c') |
For your specific request of "string to char," the correct answer is charAt(0) for a single-character string, or using charAt(index) to get a character from any position in a longer string.