Of course! Building a RESTful web service in Java is a fundamental skill for any backend developer. Here’s a comprehensive guide covering the core concepts, modern best practices, and a complete, step-by-step example.
We'll focus on the most popular and modern approach: Spring Boot with Spring Web.
What is a REST Web Service?
REST (REpresentational State Transfer) is an architectural style for designing networked applications. It's not a standard but a set of constraints.
Key principles of REST:
- Client-Server Architecture: The client (e.g., a web browser, mobile app) and the server are separate. They communicate over a network.
- Stateless: Each request from the client must contain all the information needed to understand and process it. The server does not store any client session state.
- Cacheable: Responses should be explicitly labeled as cacheable or non-cacheable to prevent clients from re-requesting data they already have.
- Uniform Interface: This is the most important constraint. It includes:
- Resource Identification: Resources are identified by a URI (e.g.,
/users/123). - Manipulation of Resources through Representations: The client can manipulate a resource by sending a representation of it (usually JSON or XML).
- Self-Descriptive Messages: Each message should contain enough information to describe how it should be processed.
- Hypermedia as the Engine of Application State (HATEOAS): (Advanced) Responses should contain links to related resources. This allows the server to guide the client through a series of actions.
- Resource Identification: Resources are identified by a URI (e.g.,
The Modern Java Way: Spring Boot
For years, building web services in Java involved complex XML configurations and setting up a web server manually. Spring Boot changed this by providing an "opinionated" framework that simplifies this process dramatically.
- Convention over Configuration: It provides sensible defaults, so you only need to configure what's unique to your application.
- Embedded Server: It bundles a web server (like Tomcat) directly into your application, so you don't need to deploy a WAR file to an external server.
- Starter Dependencies: It provides pre-configured dependency sets (e.g.,
spring-boot-starter-web) that pull in all the necessary libraries (like Jackson for JSON parsing).
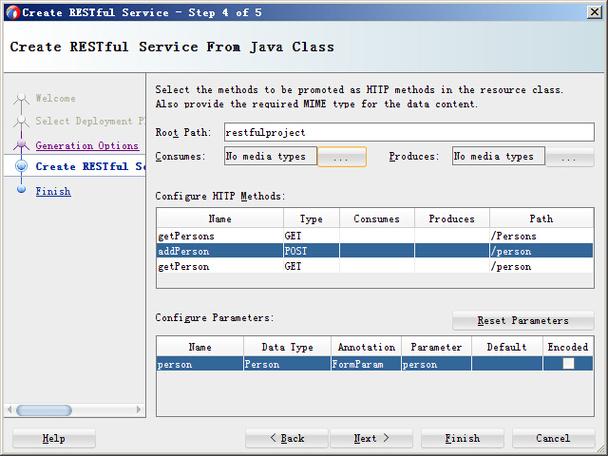
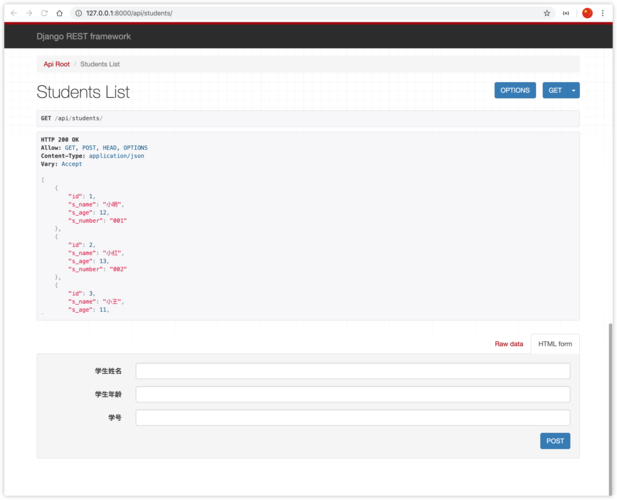
Step-by-Step Guide: Building a REST API with Spring Boot
Let's build a simple API to manage a list of "Books".
Step 1: Set up the Project
The easiest way to start is with the Spring Initializr.
- Go to start.spring.io.
- Project: Maven Project (or Gradle)
- Language: Java
- Spring Boot: Choose a stable version (e.g., 3.x.x).
- Project Metadata:
- Group:
com.example - Artifact:
book-api - Name:
book-api - Packaging: Jar
- Java: 17 or higher
- Group:
- Dependencies: Add
Spring Web. - Click "GENERATE". This will download a
.zipfile. Unzip it and open the project in your favorite IDE (like IntelliJ IDEA or VS Code).
Step 2: Create the Data Model (Entity)
This class represents a "Book" and will be automatically converted to JSON.
src/main/java/com/example/bookapi/model/Book.java
package com.example.bookapi.model;
// This annotation tells Jackson (the JSON library) to ignore this field
// during serialization/deserialization.
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties;
@JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true)
public class Book {
private long id;
private String title;
private String author;
// No-args constructor
public Book() {
}
// All-args constructor
public Book(long id, String title, String author) {
this.id = id;
this.title = title;
this.author = author;
}
// Getters and Setters
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"id=" + id +
", title='" + title + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
Step 3: Create the Repository (Data Access Layer)
For this simple example, we'll use an in-memory map as our "database". In a real application, this would be replaced with JPA to connect to a database like PostgreSQL or MySQL.
src/main/java/com/example/bookapi/repository/BookRepository.java
package com.example.bookapi.repository;
import com.example.bookapi.model.Book;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
@Repository // Marks this class as a Spring-managed bean that handles data access.
public class BookRepository {
// A simple in-memory store using a ConcurrentHashMap
private final ConcurrentHashMap<Long, Book> books = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final AtomicLong idCounter = new AtomicLong();
// Create a new book
public Book save(Book book) {
if (book.getId() == 0) {
book.setId(idCounter.incrementAndGet());
}
books.put(book.getId(), book);
return book;
}
// Find all books
public List<Book> findAll() {
return new ArrayList<>(books.values());
}
// Find a book by its ID
public Optional<Book> findById(Long id) {
return Optional.ofNullable(books.get(id));
}
// Delete a book by its ID
public void deleteById(Long id) {
books.remove(id);
}
}
Step 4: Create the Service Layer (Business Logic)
The service layer orchestrates the operations between the controller and the repository.
src/main/java/com/example/bookapi/service/BookService.java
package com.example.bookapi.service;
import com.example.bookapi.model.Book;
import com.example.bookapi.repository.BookRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
@Service // Marks this class as a Spring-managed bean that contains business logic.
public class BookService {
@Autowired // Injects the BookRepository bean.
private BookRepository bookRepository;
public List<Book> getAllBooks() {
return bookRepository.findAll();
}
public Optional<Book> getBookById(Long id) {
return bookRepository.findById(id);
}
public Book createBook(Book book) {
return bookRepository.save(book);
}
public Optional<Book> updateBook(Long id, Book bookDetails) {
// First, find the existing book
return bookRepository.findById(id).map(existingBook -> {
existingBook.setTitle(bookDetails.getTitle());
existingBook.setAuthor(bookDetails.getAuthor());
// Save the updated book
return bookRepository.save(existingBook);
});
}
public boolean deleteBook(Long id) {
if (bookRepository.existsById(id)) { // Good practice to check existence first
bookRepository.deleteById(id);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
Step 5: Create the REST Controller (API Endpoint)
This is where you define the HTTP endpoints (URLs) that clients will call.
src/main/java/com/example/bookapi/controller/BookController.java
package com.example.bookapi.controller;
import com.example.bookapi.model.Book;
import com.example.bookapi.service.BookService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
// Marks this class as a REST controller. @RestController combines @Controller and @ResponseBody.
@RestController
// Defines a base path for all endpoints in this controller.
@RequestMapping("/api/books")
public class BookController {
@Autowired // Injects the BookService bean.
private BookService bookService;
// GET /api/books - Get all books
@GetMapping
public List<Book> getAllBooks() {
return bookService.getAllBooks();
}
// GET /api/books/{id} - Get a book by its ID
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Book> getBookById(@PathVariable Long id) {
// Use Optional to handle cases where the book might not be found
Optional<Book> book = bookService.getBookById(id);
return book.map(value -> new ResponseEntity<>(value, HttpStatus.OK))
.orElseGet(() -> new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND));
}
// POST /api/books - Create a new book
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<Book> createBook(@RequestBody Book book) {
// The @RequestBody annotation maps the JSON request body to a Book object.
Book createdBook = bookService.createBook(book);
return new ResponseEntity<>(createdBook, HttpStatus.CREATED);
}
//