Of course! This is a fundamental concept in programming, especially in Java. Let's break down the relationship between UTF-8 and ASCII, and how Java handles them.
The Core Difference: Character Set vs. Encoding
This is the most important distinction to understand:
- Character Set (e.g., ASCII, Unicode): This is a list of characters and numbers assigned to them. It defines what characters exist. For example, it says that the number 65 is the letter 'A'. It doesn't care how you store it.
- Encoding (e.g., UTF-8, ISO-8859-1): This is a set of rules for how to represent characters from a character set in binary (bytes). It's the translation from characters to bytes.
ASCII is both a character set and an encoding. Unicode is a massive character set. UTF-8 is the most popular encoding for Unicode.
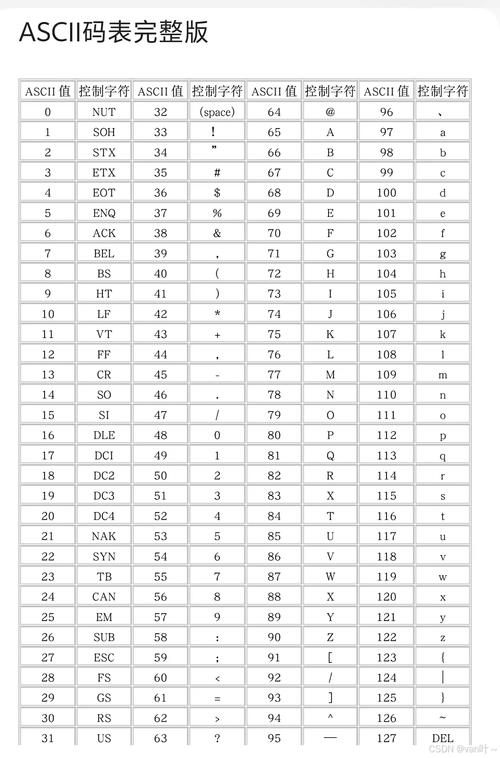
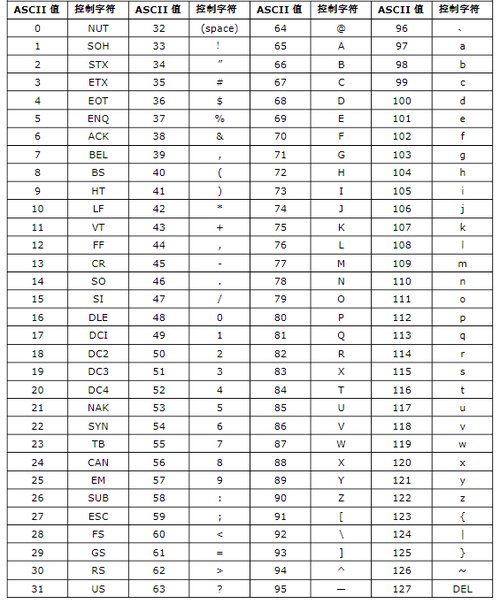
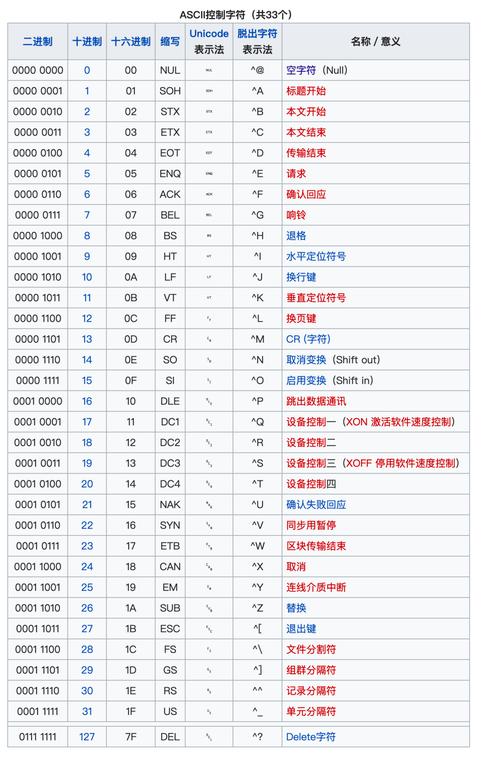
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange)
- What it is: A 7-bit character set.
- Size: It defines 128 characters.
- Content: It includes:
- English alphabet (A-Z, a-z)
- Numbers (0-9)
- Basic punctuation (., !, ?, etc.)
- Control characters (like newline
\n, carriage return\r, tab\t).
- Key Limitation: It cannot represent characters from other languages like , , ,
你好, or . - In Java: The
chartype in Java is based on the Unicode character set (specifically, the UTF-16 encoding). However, the first 128 characters of Unicode are identical to ASCII. This means ASCII characters are a perfect, 1-to-1 subset of Java'schartype.
UTF-8 (8-bit Unicode Transformation Format)
- What it is: A variable-width character encoding for Unicode.
- Size: It can represent every single character in the Unicode character set.
- How it works:
- ASCII Characters (0-127): Are encoded using 1 byte, and the byte value is identical to the ASCII value. This is why UTF-8 is "ASCII-compatible".
- Other Characters (e.g., ,
你, ): Are encoded using 2, 3, or 4 bytes.
- Advantages:
- Backwards Compatible: It can handle old ASCII text without any problems.
- Efficient: For text that is mostly English (like code), it's very compact. For text with many non-English characters, it can use more bytes per character.
- Dominant: It is the standard encoding for the web (HTML, XML, JSON) and is the default encoding on most modern Linux and macOS systems.
The Relationship: ASCII is a Subset of UTF-8
This is the key takeaway.
| Character | ASCII Code (Decimal) | UTF-8 Bytes (Hexadecimal) |
|---|---|---|
A |
65 | 41 |
z |
122 | 7A |
0 |
48 | 30 |
| 46 | 2E |
|
你 |
Not in ASCII | E4 BD A2 (3 bytes) |
| Not in ASCII | E2 82 AC (3 bytes) |
As you can see, for any character that exists in ASCII, its UTF-8 representation is just the single byte corresponding to its ASCII code. This makes converting between them trivial for the common ASCII characters.
Practical Java Examples
Java's internal representation of characters is UTF-16. This is crucial. When you read from or write to a stream (like a file or the network), you must specify the encoding to convert between UTF-16 and the external encoding (like UTF-8).
Example 1: Writing Strings to a File in UTF-8
If you don't specify the encoding, Java uses the platform's default encoding, which can be a source of bugs (it might be ISO-8859-1 on Windows, for example). Always be explicit!
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class Utf8Writer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// A string with ASCII and non-ASCII characters
String text = "Hello World! 你好! €";
Path path = Paths.get("output_utf8.txt");
// Use try-with-resources to ensure the writer is closed
try (BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(Files.newOutputStream(path), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))) {
writer.write(text);
System.out.println("File written successfully in UTF-8.");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Explanation:
Files.newOutputStream(path): Gets an output stream to the file. This stream handles bytes.new OutputStreamWriter(...): This is a bridge. It takes a byte-oriented stream (OutputStream) and wraps it in a character-oriented writer (Writer).StandardCharsets.UTF_8: This is the most important part. We tell theOutputStreamWriterhow to encode the JavaString(which is in UTF-16) into bytes for the file. We use theStandardCharsetsenum for safety.
Example 2: Reading a File in UTF-8
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class Utf8Reader {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Path path = Paths.get("output_utf8.txt");
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(Files.newInputStream(path), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))) {
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println("Read from file: " + line);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Explanation:
This is the reverse of the writer. InputStreamReader reads bytes from the stream and decodes them from UTF-8 into Java's internal UTF-16 String representation.
Example 3: The Pitfall of Using the Default Encoding
This code might work on your machine but fail on another.
// DANGEROUS: Relies on the platform's default encoding
try (BufferedWriter writer = Files.newBufferedWriter(Paths.get("output_bad.txt"))) {
writer.write("Café"); // The 'é' will be encoded incorrectly on some systems.
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
On a system where the default encoding is ISO-8859-1, the character (Unicode code point U+00E9) cannot be represented and will be replaced with a or cause an error. Always specify StandardCharsets.UTF_8.
Summary Table
| Feature | ASCII | UTF-8 |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Character Set & Encoding | Encoding (for Unicode) |
| Characters | 128 English characters, numbers, symbols. | Over 1 million characters from all languages. |
| Byte Size | Always 1 bit per character (7 bits used). | Variable: 1, 2, 3, or 4 bytes per character. |
| Relationship | A subset of Unicode. | ASCII characters are represented as 1 byte identical to the ASCII value. |
| Java Handling | The first 128 Unicode characters match ASCII. | Java's String is UTF-16. You must specify UTF-8 when reading/writing to streams. |
| Best Practice | Use for legacy systems or data that is strictly English. | The modern standard. Use for everything unless you have a specific legacy requirement. |