Of course. A "pip exception" is an error that occurs when the Python Package Installer (pip) is unable to complete a command, such as install, uninstall, or list. These exceptions are raised by the pip library itself and are distinct from Python syntax or runtime errors.

Understanding these exceptions is key to diagnosing and fixing package installation issues. Here’s a comprehensive guide covering common exceptions, their causes, and how to solve them.
The Most Common Exception: pip.exceptions.InstallationError
This is the base class for most installation-related errors. You'll rarely see this specific error message, but you'll see its subclasses. It means that during the execution of a command (like pip install), something went wrong that prevented the package from being installed or uninstalled.
Common Subclasses of InstallationError:
a) pip.exceptions.ConnectionError
-
What it means:
pipfailed to connect to the package repository (usually PyPI) or another server it needed to access. -
Typical Error Message:
 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删)Could not install packages due to an OSError: HTTPSConnectionPool(host='pypi.org', port=443): Max retries exceeded with url: /some/package/ (Caused by NewConnectionError('<urllib3.connection.HTTPSConnection object at 0x...>: Failed to establish a new connection: [Errno 11001] getaddrinfo failed')) -
Common Causes:
- No internet connection.
- DNS server issues (can't resolve
pypi.org). - Firewall blocking the connection.
- Proxy server misconfiguration.
- The PyPI server is temporarily down.
-
How to Fix:
-
Check your connection: Open a browser and go to
https://pypi.org. If it doesn't load, you have a network problem. -
Check your DNS: Try pinging
pypi.org. If it fails, you may need to use a public DNS like8.8.8(Google) or1.1.1(Cloudflare).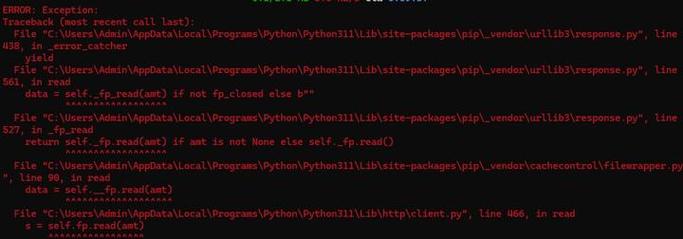 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删) -
Check your firewall/antivirus: Temporarily disable them and try the install again.
-
Configure a proxy: If you're behind a corporate or institutional proxy, you need to tell
pipabout it.# Set proxy for a single command pip install --proxy http://user:password@proxyserver:port requests # Or set environment variables (persistent for the terminal session) export HTTP_PROXY="http://user:password@proxyserver:port" export HTTPS_PROXY="http://user:password@proxyserver:port" pip install requests
-
Use the default index: Ensure you are not using a custom, broken index.
pipdefaults to PyPI, which is usually reliable.
-
b) pip.exceptions.CommandError
- What it means: There was a problem with the
pipcommand itself, not the network or the package. - Typical Error Message:
ERROR: Cannot install 'requests' and 'urllib3' together.or
ERROR: You must give at least one requirement to install (see "pip help install") - Common Causes:
- You provided no package name to install.
- Conflicting packages are specified.
- Invalid command-line arguments.
- How to Fix:
- Check your command: Make sure you've typed the command correctly. For example,
pip installrequires a package name. - Resolve conflicts: The error message is usually explicit. If it says two packages can't be installed together, you may need to choose one or find a compatible version of one of them.
- Check your command: Make sure you've typed the command correctly. For example,
c) pip.exceptions.InstallationError: ERROR: Cannot uninstall ...
- What it means:
piptried to uninstall a package but failed, often because it's in use or protected. - Typical Error Message:
ERROR: Cannot uninstall 'Pillow'. It is a distutils installed project.or
ERROR: Cannot uninstall 'numpy'. It is a distutils installed project. And the error is related to a permissions issue. - Common Causes:
- The package was not installed with
pip(e.g., it was installed by your operating system's package manager likeaptoryum). - The package is a "distutils" package, which has its own uninstall logic that
pipcan't manage. - Permission issues (you're trying to uninstall from a system directory without
sudo).
- The package was not installed with
- How to Fix:
- For system-installed packages: Use the system's package manager to remove it.
- On Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get remove python-numpy - On Fedora/CentOS:
sudo dnf remove python3-numpy
- On Debian/Ubuntu:
- For distutils packages: You might need to manually remove the files, but this is risky. A better approach is to use
pipwith the--ignore-installedflag if you know what you're doing, or better yet, use a virtual environment to avoid conflicts. - For permission issues: Use
sudocarefully, or better, use a virtual environment to avoid needingsudoaltogether.
- For system-installed packages: Use the system's package manager to remove it.
Other Common Exceptions and Errors
These are not always raised as formal pip.exceptions classes but are frequent error messages.
a) ERROR: Could not find a version that satisfies the requirement ...
- What it means: The package name you provided doesn't exist on the configured index (usually PyPI), or there are no versions compatible with your Python version.
- Typical Error Message:
ERROR: Could not find a version that satisfies the requirement fake-package-name (from versions: none) ERROR: No matching distribution found for fake-package-name - Common Causes:
- You misspelled the package name.
- The package has been removed from PyPI.
- The package doesn't support your Python version (e.g., you're using Python 3.12, but the package only supports up to 3.10).
- How to Fix:
- Check the spelling: Go to
https://pypi.organd search for the package name. If it's not there, it doesn't exist or has been removed. - Check Python version compatibility: Look at the package's page on PyPI for its "Supported Python Versions" or "Requires" section.
- Check the spelling: Go to
b) ERROR: Cannot open ...: [Errno 13] Permission denied
-
What it means:
pipis trying to write to a directory where your user doesn't have write permissions. -
Common Causes:
- You are installing packages globally without
sudo. - You are using a virtual environment but activated it incorrectly.
- You are installing packages globally without
-
How to Fix (The Best Way):
-
Use a Virtual Environment. This is the standard, recommended practice. It isolates your project's dependencies and avoids permission issues.
# Create a virtual environment python -m venv my-project-env # Activate it # On macOS/Linux: source my-project-env/bin/activate # On Windows: .\my-project-env\Scripts\activate # Now install packages. No sudo needed! pip install requests
-
The "Bad" Way (not recommended): Use
sudoto grant permissions.sudo pip install requests
Warning: This can lead to conflicts between system-wide packages and user-installed packages, making your system's Python environment unstable.
-
c) ERROR: The script ... is installed in ... which is not on PATH
- What it means: The package you installed includes a command-line script (like
django-adminorflake8), but the directory containing this script is not in your system'sPATHenvironment variable. - Common Causes:
- You installed the package into a virtual environment that you haven't activated.
- You installed it for the current user (
--user), and the user's localbindirectory isn't in yourPATH.
- How to Fix:
- Activate your virtual environment: This is the most common solution. The
PATHis automatically updated when you activate a venv. - Add the
--userdirectory to your PATH: If you installed withpip install --user <package>, find the directory and add it to yourPATH.- On macOS/Linux, this directory is typically
~/.local/bin. - On Windows, it's
%APPDATA%\Python\PythonXX\Scripts. - Add this path to your shell's configuration file (
.bashrc,.zshrc, etc.) or your system's environment variables.
- On macOS/Linux, this directory is typically
- Activate your virtual environment: This is the most common solution. The