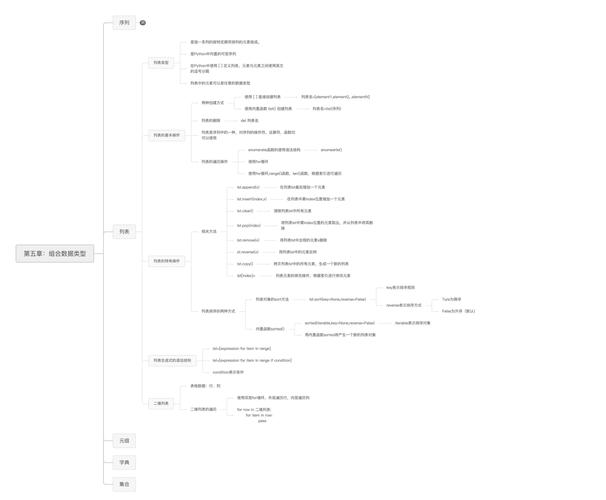
Of course! In Python, "intersection" most commonly refers to finding the common elements between two or more sets or lists. The most efficient and "Pythonic" way to do this is using Python's built-in set data type.
Here’s a complete guide covering the different methods, from the most common to more specialized ones.
The Best Way: Using set.intersection()
Sets are unordered collections of unique elements. Because of this property, set operations like intersection are extremely fast (average time complexity of O(min(len(s), len(t)))).
The & Operator (Recommended for Sets)
This is the most concise and readable way to find the intersection of two sets.
# Define two sets
set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
set2 = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
# Find the intersection using the & operator
intersection_set = set1 & set2
print(intersection_set)
# Output: {4, 5}
The .intersection() Method
This method does the same thing as the & operator but is more flexible, as it can accept any iterable (like a list or tuple) as an argument, not just another set.
# Define a set and a list
set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
list2 = [4, 5, 5, 6, 7, 8] # Note the duplicate 5
# The .intersection() method automatically converts the list to a set
intersection_set = set1.intersection(list2)
print(intersection_set)
# Output: {4, 5} (Duplicates in the original list are ignored)
You can also find the intersection of more than two sets at once.
set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4}
set2 = {2, 3, 5}
set3 = {2, 4, 6}
# Find common elements across all three sets
common_elements = set1.intersection(set2, set3)
print(common_elements)
# Output: {2}
Intersection for Lists (Common Pitfall)
If you have lists and want to find their common elements, the most straightforward way is to convert them to sets first.
Method 1: Convert to Sets (Most Efficient)
This is the recommended approach for performance, especially with large lists.
list1 = [1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5] list2 = [4, 5, 5, 6, 7, 8] # Convert lists to sets and find intersection intersection_list = list(set(list1) & set(list2)) print(intersection_list) # Output: [4, 5] (Order is not guaranteed)
Important Note: The result is a list, but the order of elements is not preserved because sets are unordered. If you need to preserve the original order of one of the lists, see the next method.
Method 2: Using a List Comprehension (Preserves Order)
If you need to maintain the order of elements as they appear in the first list, a list comprehension is a great solution.
list1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] list2 = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1] # Create a set from the second list for fast lookups (O(1) average time) set2 = set(list2) # Use a list comprehension to keep order from list1 intersection_ordered = [item for item in list1 if item in set2] print(intersection_ordered) # Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] (Order from list1 is preserved)
Intersection of Other Data Structures
For Dictionaries
You typically want to find the intersection of keys.
dict1 = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}
dict2 = {'b': 4, 'c': 5, 'd': 6}
# Intersection of keys
common_keys = dict1.keys() & dict2.keys()
print(common_keys)
# Output: {'b', 'c'}
# To get a new dictionary with the common key-value pairs from dict1
common_dict = {k: dict1[k] for k in common_keys}
print(common_dict)
# Output: {'b': 2, 'c': 3}
For Pandas DataFrames
In data analysis with the Pandas library, finding intersections is common. The .merge() method is the standard tool.
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'ID': [1, 2, 3], 'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie']})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'ID': [2, 3, 4], 'Score': [85, 90, 78]})
# Find intersection based on the 'ID' column
# 'inner' is the default merge type, which is an intersection
intersection_df = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='ID', how='inner')
print(intersection_df)
# Output:
# ID Name Score
# 0 2 Bob 85
# 1 3 Charlie 90
Summary Table
| Data Structure | Method | Example | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sets | & operator |
s1 & s2 |
Most concise, fast. |
| Sets | .intersection() |
s1.intersection(s2) |
Flexible, accepts any iterable. |
| Lists | Convert to Sets | list(set(l1) & set(l2)) |
Fastest method, order is not preserved. |
| Lists | List Comprehension | [x for x in l1 if x in set(l2)] |
Preserves order from the first list. |
| Dictionaries | Keys intersection | d1.keys() & d2.keys() |
Finds common keys. |
| Pandas DFs | .merge() |
pd.merge(df1, df2, on='col', how='inner') |
Standard for data analysis. |
Which One Should I Use?
- For sets: Use the
&operator for its simplicity. - For lists:
- If order doesn't matter, convert to sets. It's the most efficient.
- If order matters, use the list comprehension method.
- For data analysis: Use Pandas
.merge().