Of course! Let's break down everything you need to know about using pip to install and manage Selenium in Python. This is a fundamental skill for anyone getting into web automation, testing, or scraping.

What is pip and Selenium?
pip: The standard package installer for Python. It's a command-line tool that allows you to install and manage software packages (like libraries) from the Python Package Index (PyPI).Selenium: A powerful framework used for automating web browsers. You can write scripts in Python (and other languages) to make a web browser perform actions like clicking buttons, filling out forms, navigating to URLs, and extracting data, just like a human user would.
The Core Components of Selenium
When you install selenium with pip, you're primarily getting the Selenium WebDriver library for Python. This library acts as a bridge between your Python script and the actual web browser.
To make this work, you also need a WebDriver, which is a separate executable program that each browser provides. The WebDriver controls the browser based on commands from your Python script.
The Workflow:
- Your Python script uses the
seleniumlibrary to send a command (e.g., "open google.com"). - The
seleniumlibrary passes this command to the appropriate WebDriver (e.g.,chromedriver.exefor Chrome). - The WebDriver launches or controls the browser and executes the command.
- The browser performs the action.
- The WebDriver sends the results back to your script.
Step-by-Step Installation and Setup
Step 1: Install Selenium using pip
Open your terminal or command prompt and run the following command:
pip install selenium
- If you have multiple Python versions, you might need to be specific:
pip3 install selenium # For Python 3 py -m pip install selenium # For the Python associated with the 'py' launcher (Windows)
Step 2: Install the WebDriver for Your Browser
This is the most crucial and often overlooked step. You must download the WebDriver executable for the browser you intend to automate.
A. For Google Chrome (Recommended Method)
The easiest way is to use a library that automatically manages the driver for you.
- Install the
webdriver-managerlibrary:pip install webdriver-manager
- Use it in your script. This library will automatically download and manage the correct
chromedriverversion for you. You don't need to download anything manually! (See the example script below).
B. For Mozilla Firefox
- Download
geckodriver:- Go to the Mozilla Geckodriver Releases page.
- Download the version that matches your operating system (e.g.,
geckodriver-v0.34.0-win64.zip).
- Add
geckodriverto your PATH:- Recommended: Unzip the file and place the
geckodriver.exe(orgeckodriveron macOS/Linux) in a folder that is already in your system's PATH environment variable (likeC:\Windowsor/usr/local/bin). - Alternative: Keep it somewhere memorable (e.g.,
C:\selenium_drivers) and remember that path for your script.
- Recommended: Unzip the file and place the
C. For Microsoft Edge
- Download
msedgedriver:- Go to the Microsoft Edge Driver Downloads page.
- Download the version that matches your Edge browser version and OS.
- Add
msedgedriverto your PATH, just likegeckodriver.
Your First Selenium Script
This example automates Google Chrome using the webdriver-manager library, which is the simplest setup.
File: first_script.py
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service
from webdriver_manager.chrome import ChromeDriverManager
import time
# 1. Setup the WebDriver using webdriver-manager
# This will automatically download and manage the driver
service = Service(ChromeDriverManager().install())
driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=service)
# 2. Open a website
print("Opening Google...")
driver.get("https://www.google.com")
# 3. Find the search box element
# The 'name' attribute of the search box is 'q'
search_box = driver.find_element(By.NAME, "q")
# 4. Type a search query and press Enter
print("Searching for 'Selenium Python'...")
search_box.send_keys("Selenium Python")
search_box.send_keys(Keys.RETURN)
# 5. Wait for the results to load and print the page title
# time.sleep(5) # A simple way to wait, but not recommended for production
print(f"Page title is: {driver.title}")
# 6. Find and print the first result link
# We use a CSS selector to find the link
first_result = driver.find_element(By.CSS_SELECTOR, "div.g a")
print(f"First result link: {first_result.get_attribute('href')}")
# 7. Close the browser
print("Closing the browser.")
driver.quit()
How to Run It:
- Save the code as
first_script.py. - Make sure you have
seleniumandwebdriver-managerinstalled (pip install selenium webdriver-manager). - Run the script from your terminal:
python first_script.py
You should see a Chrome window open, perform the search, and then close automatically.
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| `selenium.common.exceptions.SessionNotCreatedException: Message: session not created: This version of ChromeDriver only supports Chrome version X` | Your chromedriver.exe version does not match your installed Google Chrome version. Best Fix: Use webdriver-manager as shown in the example. It handles this automatically. Manual Fix: Check your Chrome version ( Settings > About Chrome), download the matching chromedriver from the Chrome for Testing dashboard, and replace your old one. |
WebDriverException: Message: 'chromedriver' executable needs to be in PATH |
The chromedriver.exe file is not in a directory that your system's PATH environment variable can find. Best Fix: Use webdriver-manager. Manual Fix: Download the driver, unzip it, and move the .exe file to a folder that is in your PATH (like C:\Windows or C:\selenium_drivers). Then, add that folder to your PATH if it's not already there. |
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'selenium' |
You haven't installed the selenium library. Run pip install selenium. You might be running the script in a different Python environment than the one where you installed the package. |
ElementNotInteractableException |
The element you are trying to interact with (click, type) is not visible or is hidden by another element. Make sure the element is on the screen and ready before interacting with it. You might need to scroll to it first. |
Best Practices
-
Use Explicit Waits: Instead of
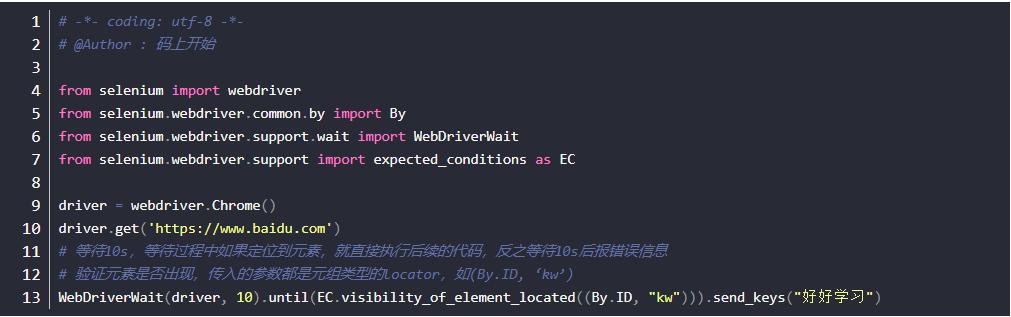
time.sleep(), use explicit waits. This tells Selenium to wait only as long as necessary for a specific condition to be met (e.g., for an element to be visible). This makes your scripts much faster and more reliable.from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC # Wait up to 10 seconds for the element with id 'myDynamicElement' to be visible element = WebDriverWait(driver, 10).until( EC.visibility_of_element_located((By.ID, "myDynamicElement")) ) -
Use Page Object Models (POM): For larger projects, organize your code by creating classes for each web page. Each class will contain the locators (e.g.,
By.NAME, "q") and interaction methods for that page. This makes your code cleaner, more reusable, and easier to maintain. -
Clean Up: Always use a
try...finallyblock to ensuredriver.quit()is called, even if your script encounters an error. This closes the browser and releases resources.driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=service) try: # Your automation code here driver.get("https://example.com") # ... finally: # This will always run driver.quit()