Of course! Here is a comprehensive guide to the Eclipse IDE for Java, covering what it is, how to get started, its key features, pros and cons, and best practices.

What is the Eclipse IDE for Java?
Eclipse is a free, open-source, and highly extensible Integrated Development Environment (IDE). While it can be used for many programming languages (C++, PHP, Python, etc.), its most famous and powerful incarnation is for Java development.
The "Eclipse IDE for Java Developers" is a specific package that comes pre-configured with the essential tools needed for Java programming, including:
- The Eclipse Platform
- The Java Development Tools (JDT)
- The Eclipse Debugger
- Maven Integration
- Git Integration
It's the go-to choice for many large enterprises, academic institutions, and individual developers for building everything from small applications to large, complex enterprise systems.
How to Get Started (A Quick Guide)
-
Download:
 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删)- Go to the official Eclipse download page: https://www.eclipse.org/downloads/
- Scroll down to the "Eclipse IDE for Java Developers" card and click the download link for your operating system (Windows, macOS, or Linux).
-
Install:
- Windows: Unzip the downloaded
.zipfile into a directory of your choice (e.g.,C:\). To launch Eclipse, navigate into theeclipsefolder and double-clickeclipse.exe. - macOS: Drag the
Eclipse.appinto yourApplicationsfolder. - Linux: Unzip the file, make the
eclipseexecutable (chmod +x eclipse), and run it from the terminal.
- Windows: Unzip the downloaded
-
Set Your Workspace:
The first time you launch Eclipse, it will ask you to choose a "workspace." This is the main folder where all your Java projects will be stored. You can accept the default or create a new one.
-
Create Your First Java Project:
 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删)- Go to
File > New > Java Project. - Give your project a name (e.g.,
HelloWorld). - Leave the default settings (like JRE version) and click
Finish.
- Go to
-
Write and Run Code:
- In the "Project Explorer" view on the left, right-click on your new project.
- Go to
New > Class. - Enter a package name (e.g.,
com.example) and a class name (e.g.,Main). - Check the box that says
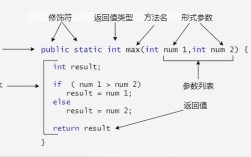
public static void main(String[] args)to create the main method. - Click
Finish. - Inside the
public static void mainmethod, type:System.out.println("Hello, Eclipse!"); - Right-click anywhere in the editor and select
Run As > Java Application. You should see "Hello, Eclipse!" printed in the "Console" view at the bottom.
Key Features for Java Development
Eclipse's power comes from its rich set of integrated tools.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Smart Editor (Code Completion) | As you type, Eclipse suggests methods, variables, and classes. Press Ctrl + Space to manually trigger it. This is incredibly fast and reduces typos. |
| Refactoring | Easily change your code structure without breaking it. Common refactorings include: • Rename: Renaming a variable or class and having it update everywhere. • Extract Method: Pulling a block of code into its own new method. • Change Method Signature: Updating parameters and return types across the project. |
| Integrated Debugger | A powerful tool for finding bugs. You can: • Set breakpoints (click in the margin) to pause execution. • Step through your code line by line. • Inspect variables to see their current values. • Watch expressions to monitor specific values. |
| Build Tools Integration | Seamlessly integrates with Maven and Gradle. It can automatically download dependencies, manage your project's build lifecycle, and generate project structure. |
| Version Control Integration | Excellent built-in support for Git. You can commit, push, pull, create branches, and resolve merge conflicts directly from the IDE without needing a separate client. |
| Plug-in System | This is Eclipse's superpower. If you need a feature, there's likely a plug-in for it. • Spring Tools Suite (STS): The best plug-in for Spring Boot development. • WindowBuilder: A powerful drag-and-drop GUI designer. • Checkstyle, PMD, FindBugs: Tools for static code analysis and enforcing coding standards. |
| Code Templates (Code Snippets) | Type a few letters (like sysout or main) and press Ctrl + Space to expand it into a full block of code (e.g., System.out.println() or the main method). |
Pros and Cons
Pros
✅ Free and Open Source: No cost to use or develop with. ✅ Highly Customizable and Extensible: The plug-in system allows you to tailor the IDE to your exact needs. ✅ Excellent for Large Projects: Its robust architecture handles complex, multi-million-line codebases very well. ✅ Powerful Refactoring Tools: Widely considered the best-in-class for code restructuring. ✅ Strong Community and Corporate Backing: Backed by the Eclipse Foundation, with a massive community and lots of documentation/tutorials. ✅ Great Integration: Works seamlessly with Maven, Git, and other essential Java tools.
Cons
❌ Can Be Slow: Especially on older hardware or with very large projects, it can sometimes feel sluggish compared to modern alternatives. ❌ Steep Learning Curve: The sheer number of windows, views, and options can be overwhelming for a complete beginner. ❌ Bundled with Unnecessary Features: The "Java Developers" package includes many tools you might not need initially, which can clutter the interface. ❌ Clunky UI: The user interface, while functional, is not as modern or polished as some competitors like IntelliJ IDEA.
Best Practices for Using Eclipse
-
Use Keyboard Shortcuts: This is the single biggest productivity booster. Learn the basics:
Ctrl + S: SaveCtrl + Shift + S: Save AllCtrl + Shift + R: Open a resource (file) by name.Ctrl + Shift + T: Open a type (class) by name.F11: Debug the last launched application.Ctrl + F11: Run the last launched application.
-
Organize Your Perspective: The "Java" perspective is optimized for coding. You can switch to other perspectives like "Debug" or "Git" and then switch back. You can also customize perspectives by dragging and dropping views to where you want them.
-
Configure Your Code Style: Go to
Window > Preferences > Java > Code Style > Formatter. Here you can import or create a code formatting profile to ensure your entire team's code looks consistent. You can even set it to format your code automatically on save. -
Use Code Templates: Go to
Window > Preferences > Java > Editor > Templates. Here you can create your own snippets for frequently used code blocks. -
Keep Your IDE Updated: Eclipse releases periodic updates that include bug fixes, performance improvements, and new features. It's a good idea to stay current.
Eclipse vs. IntelliJ IDEA vs. VS Code
This is a common point of comparison.
| Feature | Eclipse IDE for Java | IntelliJ IDEA (Community) | VS Code (with Java Extension Pack) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free | Free (Community) | Free |
| Best For | Enterprise projects, legacy code, Maven/Gradle purists | Modern Spring/Java development, deep tooling | Web development, microservices, light-weight setup |
| Learning Curve | Steep | Moderate | Moderate (once extensions are configured) |
| Refactoring | Excellent | The Best | Very Good |
| GUI Builder | Available via plugins | Built-in (for Swing/JavaFX) | Not available |
| Performance | Can be slow | Generally fast and responsive | Very fast, but Java-specific tasks can be slower |
| Extensibility | Plug-in based | Plugin based | Extension based |
Conclusion: You can't go wrong with any of them. Eclipse is a powerhouse that's been a standard for decades. IntelliJ IDEA is often favored for its superior out-of-the-box experience for modern Java development. VS Code is the new favorite for its speed and versatility, especially when working across web and Java.
For a beginner starting today, IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition is often recommended for its smoother experience, but Eclipse remains a vital and powerful tool that is still widely used in the industry.