Of course! The shutil module in Python provides a number of high-level file operations, and copy is one of its most fundamental and useful functions.
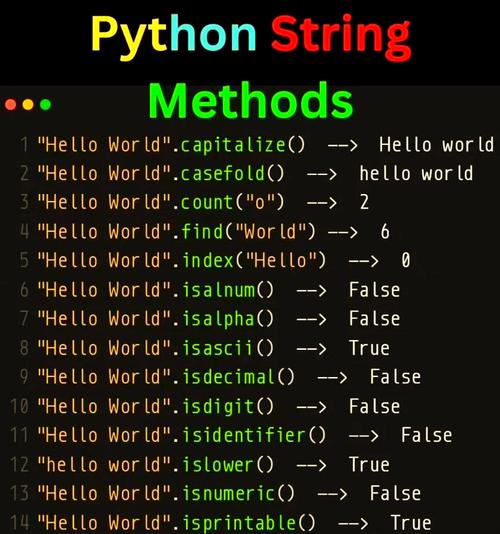
Let's break down shutil.copy in detail, including its usage, key considerations, and how it compares to other shutil functions.
What is shutil.copy?
The shutil.copy() function copies a source file to a destination. It's designed to be a simple, high-level way to duplicate files.
Syntax:
shutil.copy(src, dst, *, follow_symlinks=True)
Parameters:
src(string): The path to the source file you want to copy.dst(string): The path to the destination.- If
dstis a directory, the source file is copied into that directory with the same filename. - If
dstis a full file path (including a filename), the source file is copied to that new path.
- If
follow_symlinks(boolean, keyword-only): IfTrue(the default), the function will copy the file that the symbolic link points to. IfFalse, it will copy the symbolic link itself. (This is an advanced feature).
Return Value: It returns a string containing the path to the newly created file or directory.
Key Behavior: Metadata is NOT Preserved
This is the most important thing to remember about shutil.copy(). It copies the file contents and the permission bits (e.g., read/write/execute) but does not copy other metadata like:
- File creation/modification timestamps
- Owner and group information
- Extended file attributes
If you need to preserve all metadata, you should use shutil.copy2().
Examples
Let's set up a simple scenario. Imagine you have the following directory structure:
/my_project/
├── source_folder/
│ └── my_document.txt
└── destination_folder/The content of my_document.txt is:
Hello, this is the original file.Example 1: Copying to a Directory
This is the most common use case. You copy a file into a target folder, keeping the original filename.
import shutil
import os
# Define source and destination paths
source_file = 'source_folder/my_document.txt'
destination_dir = 'destination_folder'
# Perform the copy
# shutil.copy will create 'destination_folder/my_document.txt'
copied_file_path = shutil.copy(source_file, destination_dir)
print(f"Source: {source_file}")
print(f"Destination: {copied_file_path}")
# Verify the copy
print("\n--- Verifying Contents ---")
with open(source_file, 'r') as f:
print(f"Original content: {f.read()}")
with open(copied_file_path, 'r') as f:
print(f"Copied content: {f.read()}")
Output:
Source: source_folder/my_document.txt
Destination: destination_folder/my_document.txt
--- Verifying Contents ---
Original content: Hello, this is the original file.
Copied content: Hello, this is the original file.Example 2: Copying to a New File Path
Here, the destination includes a new filename. The file is copied to a new location with a new name.
import shutil
source_file = 'source_folder/my_document.txt'
new_file_path = 'destination_folder/renamed_document.txt'
# Perform the copy
# shutil.copy will create 'destination_folder/renamed_document.txt'
copied_file_path = shutil.copy(source_file, new_file_path)
print(f"Source: {source_file}")
print(f"Destination: {copied_file_path}")
Output:
Source: source_folder/my_document.txt
Destination: destination_folder/renamed_document.txtshutil.copy vs. Other shutil Functions
It's easy to confuse shutil.copy with its relatives. Here’s a quick guide to help you choose the right one.
| Function | Copies File Contents? | Copies Metadata? | Copies Directories? | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
shutil.copy(src, dst) |
Yes | No (only permissions) | No | Quick and simple file duplication. When metadata like timestamps isn't critical. |
shutil.copy2(src, dst) |
Yes | Yes (all metadata) | No | The "true" copy. Use when you need an exact replica of the file, including timestamps and ownership. This is often the best choice. |
shutil.copyfile(src, dst) |
Yes | No | No | Copies only the file contents. It doesn't handle permissions or directories. dst must be a file path, not a directory. More basic than copy(). |
shutil.copytree(src, dst) |
Yes (recursively) | Yes (recursively) | Yes | The equivalent of cp -r in Linux/macOS. Copies an entire directory and all its contents (subdirectories and files) to a new location. |
shutil.copymode(src, dst) |
No | Yes (only permissions) | No | Useful for just updating the permission bits of a file to match another, without changing its content. |
When to use shutil.copy vs. shutil.copy2?
- Use
shutil.copy2()by default. It's safer and more complete. If you're making a backup or need to preserve the state of a file,copy2is the right choice. - Use
shutil.copy()if you are intentionally ignoring metadata and just need the file contents and basic permissions. It's slightly faster, but the difference is usually negligible.
Error Handling
shutil.copy will raise common OS-related errors, so it's good practice to wrap it in a try...except block.
FileNotFoundError: If the source file does not exist.FileExistsError: If the destination file already exists and you are trying to copy over it on a system that doesn't allow overwriting (this is rare on modern OSes, which usually just overwrite).PermissionError: If you don't have the necessary read permissions for the source or write permissions for the destination.
import shutil
source_file = 'non_existent_file.txt'
destination_dir = 'destination_folder'
try:
shutil.copy(source_file, destination_dir)
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"Error: The source file '{source_file}' was not found.")
except PermissionError:
print(f"Error: Permission denied when accessing '{source_file}' or writing to '{destination_dir}'.")
except Exception as e:
print(f"An unexpected error occurred: {e}")
Summary
| Feature | shutil.copy |
|---|---|
| Purpose | High-level file copying. |
| Copies Content? | Yes |
| Copies Metadata? | No (only permissions) |
| Best For | Quick copies where preserving timestamps/ownership is not important. |
| Common Alternative | shutil.copy2() for full metadata preservation. |