核心概念
-
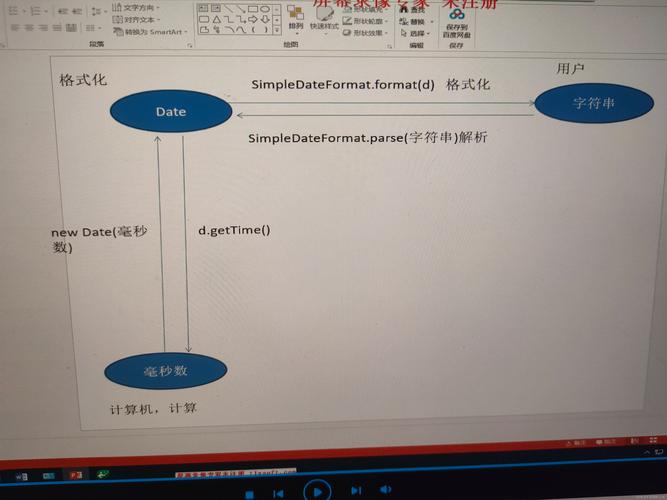
long时间戳 (Timestamp): (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删)- 通常指的是 自 1970 年 1 月 1 日 00:00:00 UTC (Unix 纪元) 以来的毫秒数。
- 它是一个长整型数字,代表了 UTC 时间。
- 在 Java 中,
System.currentTimeMillis()返回的就是这种格式的时间戳。
-
java.util.Date:- 一个表示特定瞬间的日期和时间类。
- 它内部也存储了一个
long值,表示从 Unix 纪元开始的毫秒数。Date对象本质上是时间戳的一个包装。
-
java.time包 (Java 8 及以上推荐):- Java 8 引入了全新的日期和时间 API (
java.time包),旨在替代旧的java.util.Date和java.util.Calendar。 Instant: 代表时间线上的一个瞬时点,类似于Date,但它基于纳秒精度,并且是 UTC 时间。ZonedDateTime/LocalDateTime: 分别表示带时区的日期时间和不带时区的日期时间,更贴近人类的日常使用。
- Java 8 引入了全新的日期和时间 API (
转换方法
我们将分为两种主要方式来讲解:旧版 API (java.util.Date) 和 新版 API (java.time)。
使用旧版 API (java.util.Date)
这种方法在旧代码或需要兼容 Java 7 及以下版本时使用。

long 时间戳 → Date 对象
这是最直接的转换。Date 类的构造函数可以直接接收一个 long 值(毫秒数)。
import java.util.Date;
public class LongToDateOld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取当前时间的毫秒数时间戳
long timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("当前时间戳: " + timestamp);
// 将 long 时间戳转换为 Date 对象
// Date 的构造函数参数就是毫秒数
Date date = new Date(timestamp);
System.out.println("转换后的 Date 对象: " + date);
// 输出示例: 转换后的 Date 对象: Wed Oct 26 10:30:55 CST 2025
}
}
Date 对象 → long 时间戳
这个转换更简单,直接调用 Date 对象的 getTime() 方法即可。
import java.util.Date;
public class DateToLongOld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个 Date 对象
Date date = new Date();
// 将 Date 对象转换为 long 时间戳
long timestamp = date.getTime();
System.out.println("Date 对象: " + date);
System.out.println("转换后的时间戳: " + timestamp);
}
}
使用新版 API (java.time - 强烈推荐)
这是现代 Java 开发的首选方式,API 更清晰、更安全、更易用。
long 时间戳 → Instant → ZonedDateTime / LocalDateTime
这个过程通常是分两步:
- 将
long转换为java.time.Instant。 - 将
Instant转换为更具体的日期时间类型(如ZonedDateTime或LocalDateTime)。
示例:转换为 ZonedDateTime (带时区)
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
public class LongToDateTimeNew {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 假设这是一个 UTC 时间戳
long timestamp = 1698328255000L;
// 1. 将 long 转换为 Instant
Instant instant = Instant.ofEpochMilli(timestamp);
// 2. 将 Instant 转换为指定时区的 ZonedDateTime
// 转换为 Asia/Shanghai (北京时间) 时区
ZonedDateTime shanghaiTime = instant.atZone(ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
System.out.println("时间戳: " + timestamp);
System.out.println("Instant: " + instant); // 输出 UTC 时间
System.out.println("北京时间 (ZonedDateTime): " + shanghaiTime);
// 输出示例: 北京时间 (ZonedDateTime): 2025-10-26 18:30:55+08:00[Asia/Shanghai]
}
}
示例:转换为 LocalDateTime (不带时区)
如果你不关心时区,只想得到一个“本地”的日期时间视图。
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
public class LongToLocalDateTimeNew {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long timestamp = 1698328255000L;
// 1. 将 long 转换为 Instant
Instant instant = Instant.ofEpochMilli(timestamp);
// 2. 将 Instant 转换为指定时区的 LocalDateTime
// 注意:这里仍然需要一个时区来确定“本地”时间
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.ofInstant(instant, ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
System.out.println("时间戳: " + timestamp);
System.out.println("北京时间 (LocalDateTime): " + localDateTime);
// 输出示例: 北京时间 (LocalDateTime): 2025-10-26T18:30:55
}
}
ZonedDateTime / LocalDateTime → Instant → long
这个转换是上面过程的逆过程。
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
public class DateTimeToLongNew {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个 ZonedDateTime 对象 (北京时间)
ZonedDateTime shanghaiTime = ZonedDateTime.of(2025, 10, 26, 18, 30, 55, 0, ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
// 1. 将 ZonedDateTime 转换回 Instant
// Instant 总是基于 UTC 的,所以会自动进行时区转换
Instant instant = shanghaiTime.toInstant();
// 2. 将 Instant 转换为 long 时间戳
long timestamp = instant.toEpochMilli();
System.out.println("原始 ZonedDateTime: " + shanghaiTime);
System.out.println("转换后的 Instant (UTC): " + instant);
System.out.println("最终得到的时间戳: " + timestamp);
// 输出示例: 最终得到的时间戳: 1698328255000
}
}
格式化输出 (日期字符串)
转换后,我们通常需要将日期时间对象格式化为易读的字符串。
使用新版 API (java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter)
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
public class FormatDateTime {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long timestamp = 1698328255000L;
Instant instant = Instant.ofEpochMilli(timestamp);
ZonedDateTime shanghaiTime = instant.atZone(ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
// 定义一个格式化模式
// yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
// 格式化 ZonedDateTime
String formattedDateTime = shanghaiTime.format(formatter);
System.out.println("格式化后的日期时间字符串: " + formattedDateTime);
// 输出示例: 格式化后的日期时间字符串: 2025年10月26日 18:30:55
}
}
总结与最佳实践
| 任务 | 旧版 API (java.util.Date) |
新版 API (java.time) |
推荐度 |
|---|---|---|---|
long → Date |
new Date(longMillis) |
Instant.ofEpochMilli(longMillis) |
⭐⭐⭐ |
Date → long |
date.getTime() |
date.toInstant().toEpochMilli() |
⭐⭐⭐ |
long → ZonedDateTime |
new Date(long).toInstant().atZone(zoneId) |
Instant.ofEpochMilli(long).atZone(zoneId) |
⭐⭐⭐ |
ZonedDateTime → long |
zonedDateTime.toInstant().toEpochMilli() |
zonedDateTime.toInstant().toEpochMilli() |
⭐⭐⭐ |
| 格式化 | new SimpleDateFormat("...").format(date) |
DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("...").format(zonedDateTime) |
⭐⭐⭐ |
核心建议:
- 优先使用
java.timeAPI:如果你使用的是 Java 8 或更高版本,java.time是不二之选,它设计更优秀,能有效避免很多线程安全问题。 - 注意时区:在处理跨时区的应用时,始终要明确你使用的时区。
Instant是无时区的,而ZonedDateTime是有时区的,从Instant转换到LocalDateTime时,必须指定一个ZoneId。 - 明确时间戳单位:确保你的
long值单位是 毫秒,有些系统可能使用秒作为单位,如果是秒,需要乘以 1000 (timestamp * 1000L) 再进行转换。